Preparation method of multifunctional surface enhanced raman scattering (SERS) substrate
A surface-enhanced Raman and multi-functional technology, applied in the field of analysis and detection, can solve the problems of complex preparation process, waste of energy and resources, and inability to reuse, etc., and achieve the effect of small sample volume, real-time on-site detection, and convenient sampling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
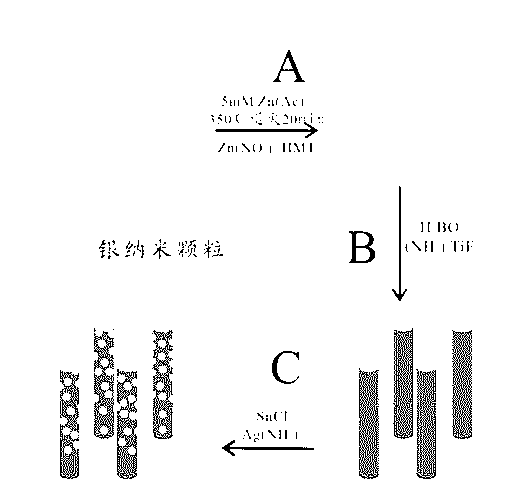
[0022] Such as figure 1 As shown, the multifunctional capillary surface-enhanced Raman substrate preparation method includes the following steps: A: A layer of ZnO seeds is generated on the inner wall of the capillary by thermal decomposition, and then the capillary is exposed to Zn(NO 3 ) 2 and HMT solutions to grow ZnO arrays; B: Transform ZnO arrays into TiO 2 array; C: on TiO 2 Nanotubes are decorated with silver particles.
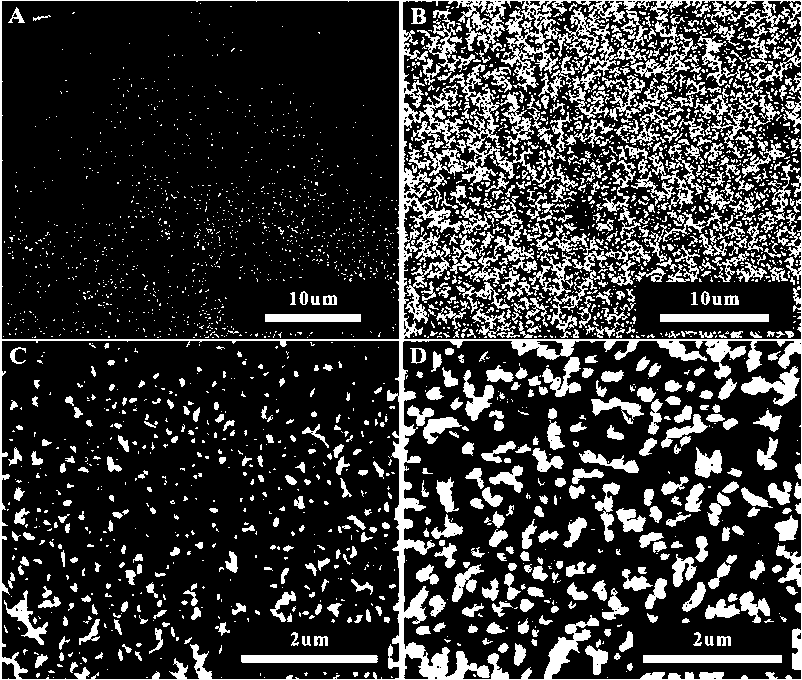
[0023] figure 2 Conversion of ZnO arrays to TiO 2 Scanning electron microscope image of the array. It consists of four parts: A, B, C, and D. Among them, A: SEM images of zinc oxide nanorod arrays grown in a large area; B: SEM images of titanium dioxide nanotube arrays in a large area; C: A partial view of Figure A In the enlarged picture, we can see the array of zinc oxide nanorods neatly arranged; D: the partial enlarged picture of Figure B, we can see that the array of titanium dioxide nanotubes grows neatly on the inner wall of the capilla...
Embodiment 1
[0027] Building TiO on the inner wall of the capillary 2 Nanotube array:
[0028] First, let the ethanol solution of zinc acetate enter the inside of the capillary, dry it in an oven at 60 degrees Celsius, and then anneal it at 350 degrees Celsius for 20 minutes, so that a layer of zinc oxide seeds can be produced on the inner wall. Then, place the capillary in Zn(NO 3 ) 2 React with HMT solution at 90 degrees for 90 minutes to grow a layer of ZnO array on the inner wall. ZnO array in (NH 4 ) 2 TiF 6 and H 3 BO 3 Reacting in medium for 90 minutes, the titanium oxide nanotube array can be obtained. figure 2 A and C are SEM photos of zinc oxide arrays under different magnifications, respectively, and zinc oxide arrays distributed in a wide range can be seen; figure 2 B and D are SEM pictures of replacing zinc oxide with titanium oxide.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Silver particles modified on TiO 2 surface:
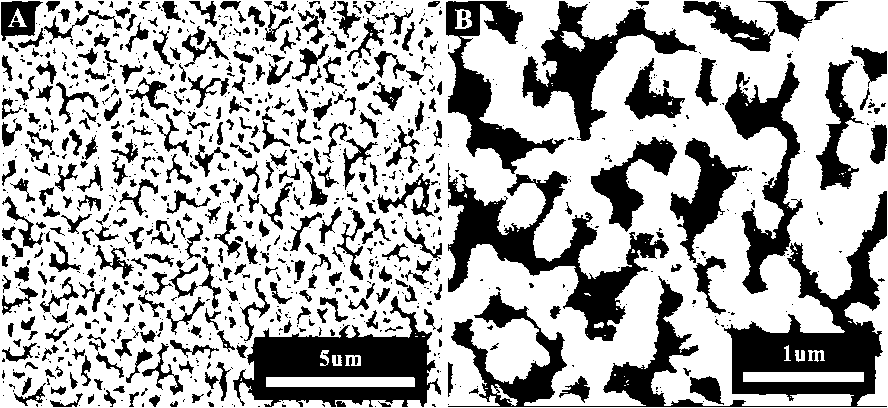
[0031] Immerse the capillary with the titanium oxide nanotube array in 0.05g / 20mL tin dichloride aqueous solution first, and rinse it with secondary water several times after one hour, so that a layer of divalent tin ions will be adsorbed on the surface of the titanium oxide. Then put it in the silver ammonia solution of 1mmol / L, take it out after 30 minutes and wash it, you can get the titanium oxide nanotube array modified by silver particles, as image 3 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com