High-activity blood pressure lowering peptide and preparation method thereof
A blood pressure lowering peptide and high activity technology, applied in the field of high activity blood pressure lowering peptide and its preparation, can solve the problem that natural blood pressure lowering peptide needs to be improved and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] First, dissolve defatted walnut powder and water at a ratio of 1:10, hydrolyze for 5 hours at pH 8.0, hydrolysis temperature 65°C, stop the hydrolysis reaction, centrifuge to take the supernatant, and carry out acid precipitation under the condition of isoelectric point 4.5 , centrifuged to take the precipitate, washed the precipitate to neutrality, and then it was quickly vacuum freeze-dried and stored, and its protein content was determined to be 86.32% by the Coomassie brilliant blue method.
[0052] Then, use protease to carry out hydrolysis respectively, hydrolysis conditions:
[0053] 1) Papain: The ratio of solid to liquid is 25g / L, the amount of enzyme added is 3% (m / v), the pH is 6, the temperature is 50°C, and the hydrolysis time is 4h.
[0054] 2) Pepsin: The ratio of solid to liquid is 25g / L, the amount of enzyme added is 4% (m / v), pH 2, the temperature is 55°C, and the hydrolysis time is 4h.
[0055] 3) Alkaline protease: The ratio of solid to liquid is 25...
Embodiment 2
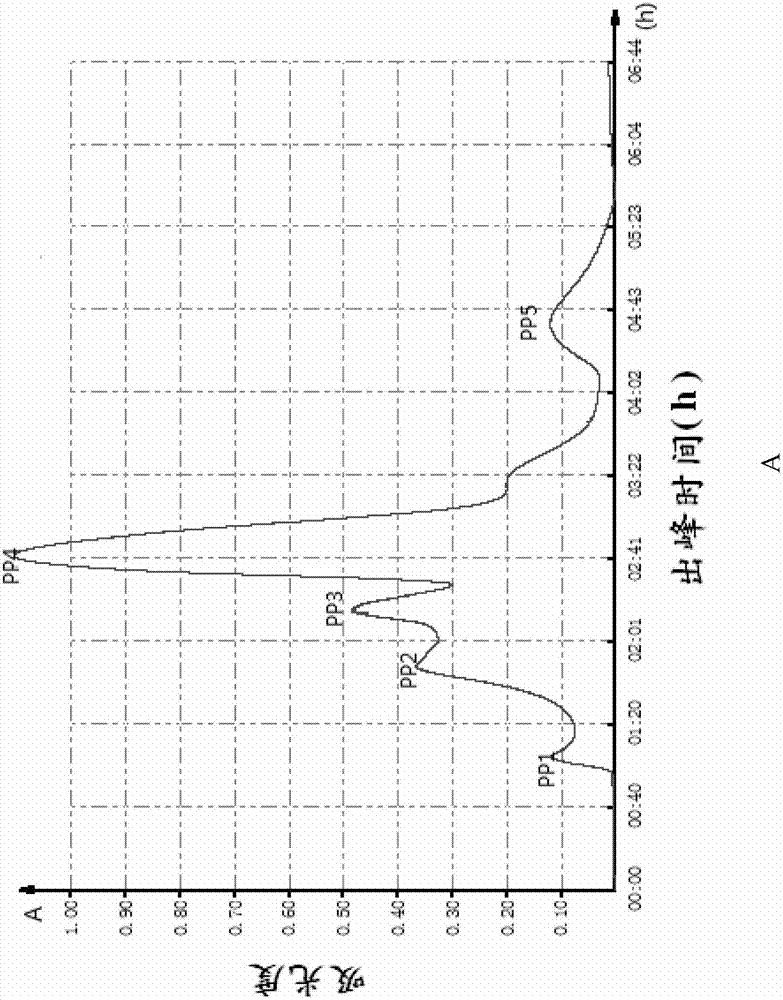
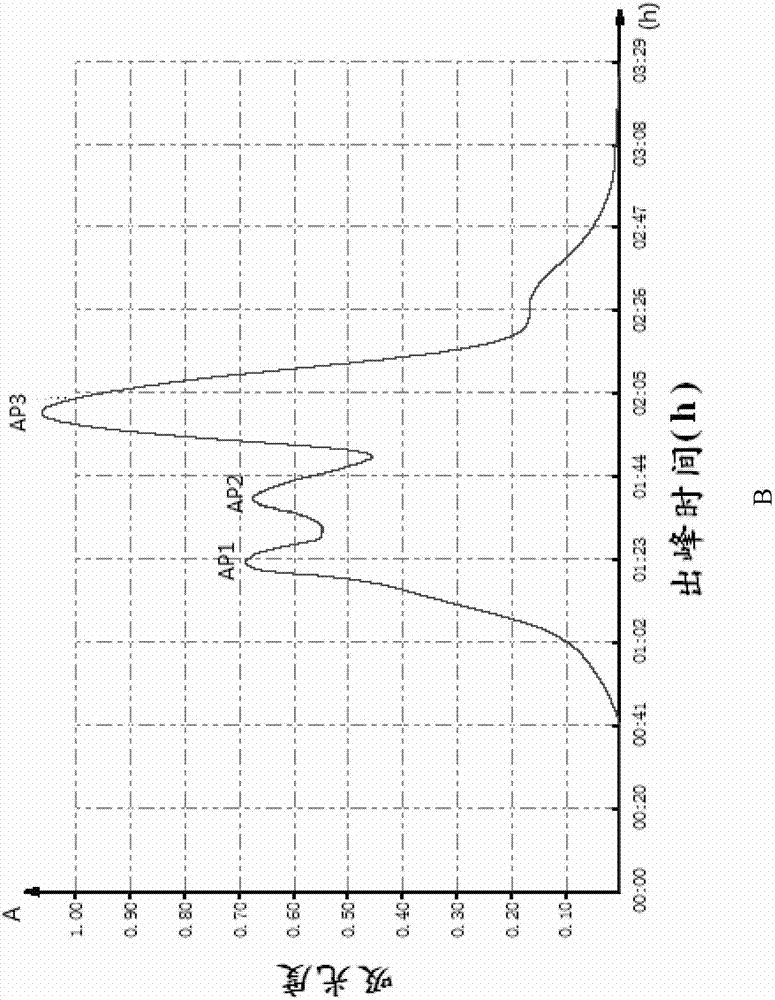
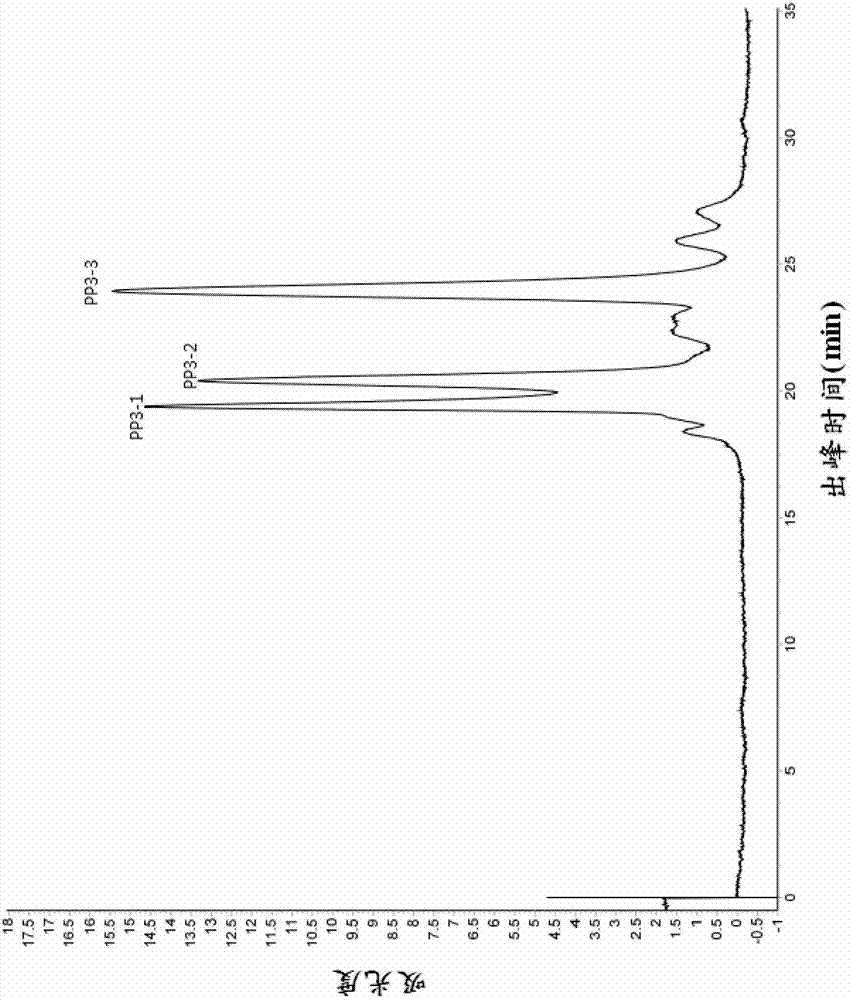
[0060] The lyophilized powder of pepsin and alkaline protease with high ACE inhibitory activity and molecular weight less than 5000 obtained in Example 1 was dissolved in 5ml of 10mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.0), and degassed and passed through the membrane , separated and purified by Sephadex G25 Medium column (i.e. the first gel chromatography treatment), the elution peak was detected at 280nm and collected to determine the ACE inhibitory activity of each component (the detection method of ACE inhibitory activity is as described in the general method), wherein Chromatogram see figure 1 , the activity test results are shown in Table 2 below, and the collected solution was quickly vacuum freeze-dried.
[0061] Table 2 The IC of the ACE inhibitory activity of the different components obtained from the first gel chromatography 50
[0062]
[0063] figure 1 Shows the chromatograms of the first gel chromatographic treatment during the preparation of highly active antihypertensive pepti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com