Glyphosate resistant EPSP synthetase GmEPSPS, and coding gene and application thereof
A glyphosate-resistant, coding technology that can be used in applications, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., and can solve problems such as low expression efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] Example 1. Modification and synthesis of GmEPSPS gene
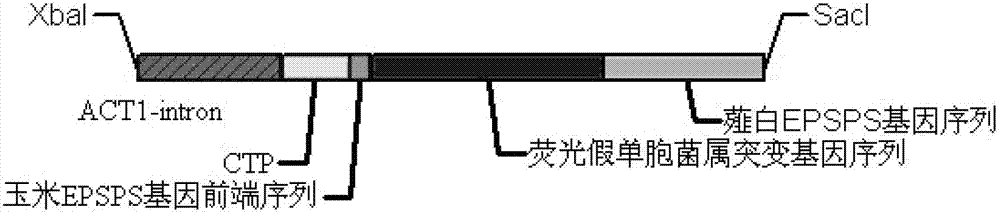
[0074] Based on the 5-enolpyrul-shikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) mutant gene derived from Pseudomonas fluorescens, the original ORF sequence of the gene was removed5 The two base sequences of 147bp at the'end and 531bp at the 3'end, leaving only a base sequence of 654bp in the middle core domain sequence, and a base sequence of 591bp from the scallion white EPSPS gene are spliced; When the composition of the amino acid sequence of the EPSP synthetase protein remains unchanged, base substitutions are made with plant-preferred codons to initially obtain a modified DNA sequence; exclude the presence of AT-rich sequences in the DNA sequence that cause plant transcription instability and Commonly used restriction sites (BamH I, EcoR I, Hind III, Nco I, Xho I, Xba I, etc.), then correct and eliminate them by replacing codons; and add rice ACT1-intron sequence at the 5'end (Positions 7-460 of sequence 2), petunia CTP4...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Example 2. Construction of plant expression vector for glyphosate-resistant fusion gene
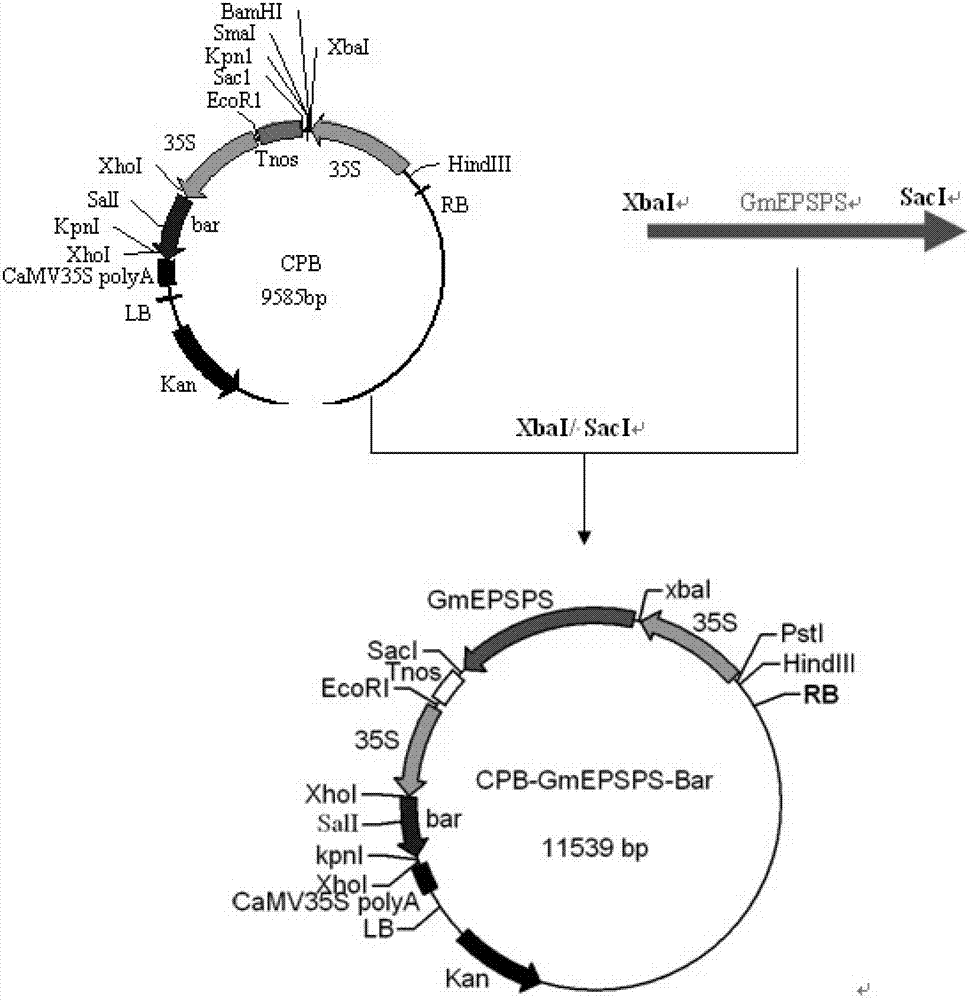
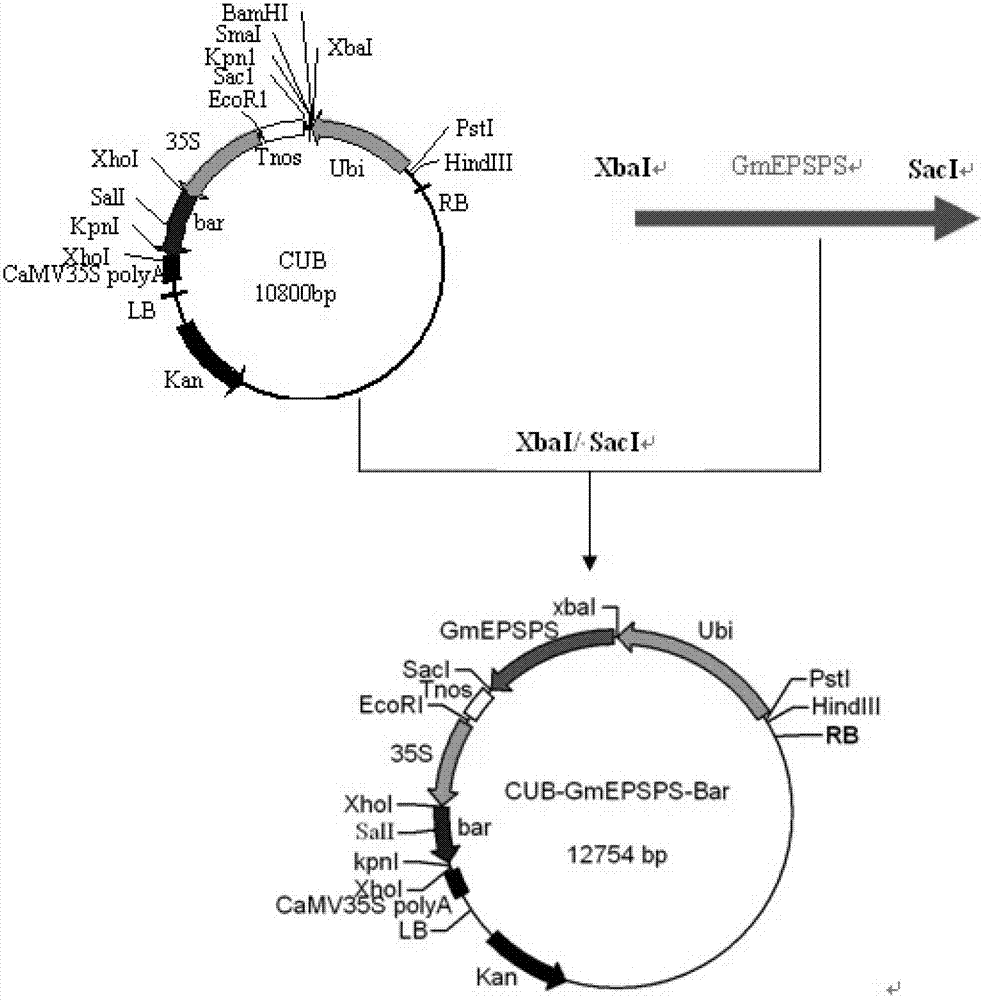
[0078] The GmEPSPS gene shown in sequence 2 in the sequence table was artificially synthesized, and the GmEPSPS gene was double-cut with Xba I and Sac I, and the plant expression vectors CPB and CUB were double-cut with Xba I and Sac I, and recovered by gel The purification kit was used to recover the digested GmEPSPS fragments, as well as the backbone fragments of CPB vector and CUB vector. The GmEPSPS fragment was ligated with the backbone fragments of the CPB vector and the CUB vector to obtain the target plasmid. Transform the target plasmid into Escherichia coli, select for resistance screening, pick the positive single clone, culture the positive clone in liquid, extract the positive clone plasmid for double enzyme digestion with Xba I and Sac I, and it will be preliminarily judged to be correct after digestion The recombinant plasmid samples were sent for sequencing.
[0079] S...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Embodiment 3, glyphosate herbicide tolerance experiment
[0082] The preparation of M9 medium:
[0083] (1) Prepare 1M MgSO first 4 :Weigh MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 2.46g add 10mL double distilled water to dissolve, autoclave sterilize for later use;
[0084] (2) Prepare 1M CaCl 2 : CaCl 2 ·6H 2 O 2.191g add 10mL double distilled water to dissolve, autoclave for later use;
[0085] (3) Prepare 5×M9 salt solution again:
[0086] Na 2 PO 4 ·7H 2 O 12.8g
[0087] KH 2 PO 4 3.0g
[0088] NaCl 0.5g
[0089] NH 4 Cl 1.0g
[0090] Add 200ml of double distilled water to dissolve, sterilize at 121℃ for 15 minutes,
[0091] Remarks: The above three samples are prepared separately, bottled separately, and can be sent to high pressure together.
[0092] (4) Prepare 20% glucose solution: 4g glucose is dissolved in 20ml double distilled water, filtered and sterilized by 0.22 micron filter;
[0093] (5) Aseptic operation to prepare M9 medium
[0094] 5×M9 salt solution 200ml
[0095] 1M of MgSO 4 2ml
[0096] 20%...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com