Method for recycling tricalcium phosphate from expandable polystyrene industrial wastewater
An expandable polystyrene, tricalcium phosphate technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, natural water treatment, etc. The effect of reducing production costs, reducing consumption, and reducing wastewater treatment volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
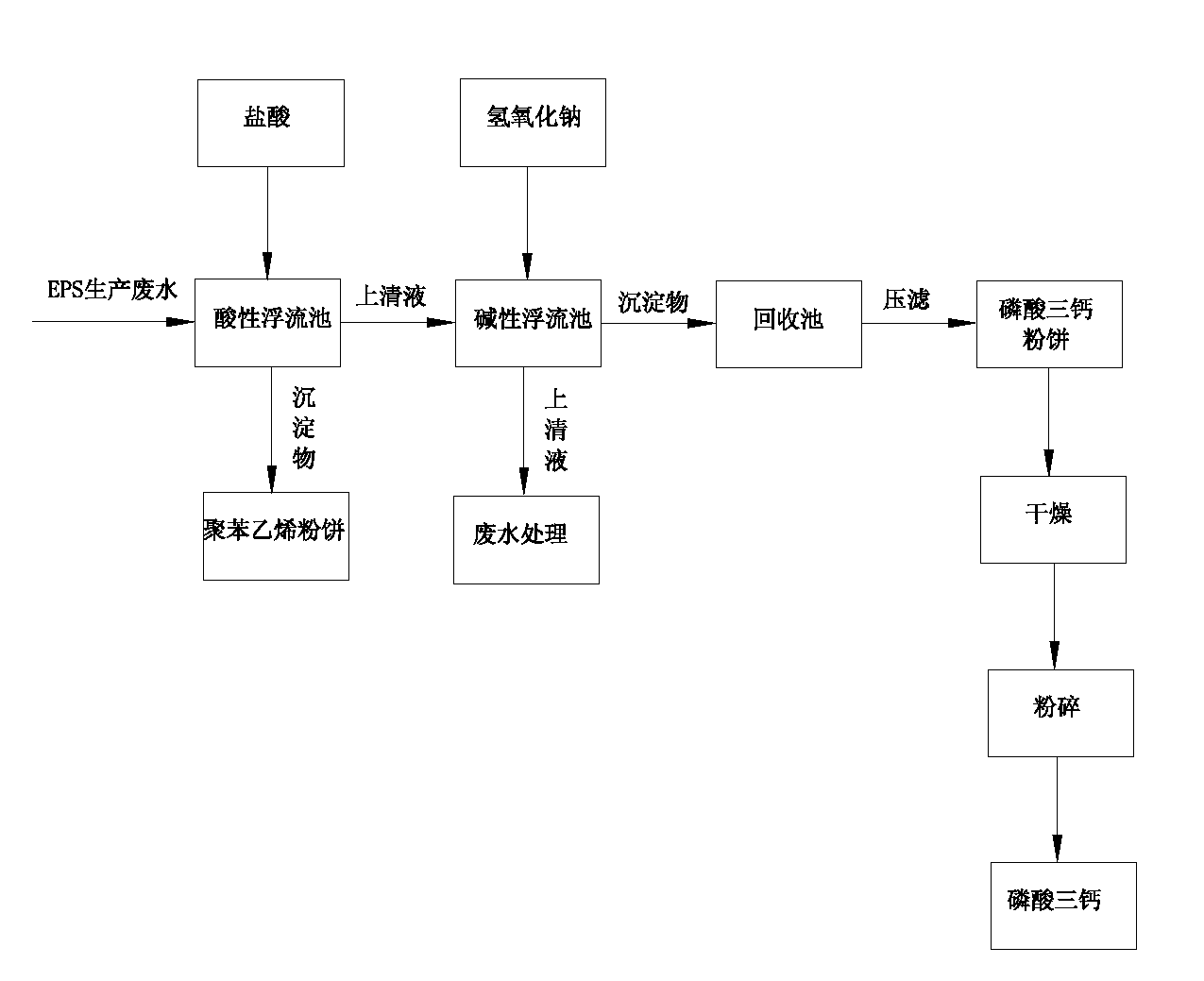
[0024] Such as figure 1 Shown, EPS production waste water is reclaimed and prepared tricalcium phosphate by the following steps:
[0025] Step 1: Build an acidic floating pond and an alkaline floating pond
[0026] Build an acidic floating flow pool and an alkaline floating flow pool with a water storage capacity of 50 tons with a stirring device respectively. The length*width*height is: 4.5M*4.5M*3.2M (such as figure 2 and image 3 shown);
[0027] Step 2: Acid pool dissolves tricalcium phosphate in wastewater
[0028] Pump 50 tons of EPS production wastewater into the acidic floating flow tank, then add 18.9L of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 30%, stir for 2 hours, adjust the pH value to 3.0-3.2, control the reaction temperature at 25-40°C, and after 36 hours of static sedimentation, Obtain polystyrene-containing precipitate and supernatant;
[0029] The chemical reaction that occurs in this step is: Ca 3 (PO4) 2 +2HCl=2H 3 PO 4 +3CaCl 2 ;
[0030] S...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The main technical scheme of this embodiment is the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0043] Step 1: Acid pool dissolves tricalcium phosphate in wastewater
[0044] Pump 50 tons of EPS production wastewater into an acid floating flow tank with a capacity of 50 tons, then add 23.6L of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 25%, stir for 2.5 hours, adjust the pH value to 3.0-3.2, control the reaction temperature at 30-40°C, and settle still After 36 hours, the precipitate and supernatant containing polystyrene were obtained;
[0045] Step 3: Remove the sediment
[0046] The supernatant is pumped into the alkaline floating flow tank, and the sediment is pumped into the filter press with a mud pump to obtain polystyrene powder and remove it;
[0047] Step 4: Alkaline pool precipitation
[0048] Add 72.5L of industrial liquid caustic soda (NaOH solution) with a concentration of 25% into the alkaline floating flow pool, stir for 3 hours, adjust the pH value to ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The main technical scheme of this embodiment is the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0053] Step 1: Acid pool dissolves tricalcium phosphate in wastewater
[0054]Pump 50 tons of EPS production wastewater into an acid floating flow tank with a capacity of 50 tons, then add 23.6L of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 30%, stir for 3 hours, adjust the pH value to 3.2-3.5, control the reaction temperature at 25-35°C, and settle still After 32 hours, a precipitate containing polystyrene and a supernatant were obtained;
[0055] Step 3: Remove the sediment
[0056] The supernatant is pumped into the alkaline floating flow tank, and the sediment is pumped into the filter press with a mud pump to obtain polystyrene powder and remove it;
[0057] Step 4: Alkaline pool precipitation
[0058] Add 72.5L of industrial liquid caustic soda (NaOH solution) with a concentration of 30% to the alkaline floating flow pool, stir for 2 hours, adjust the pH value to 7.5-7...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com