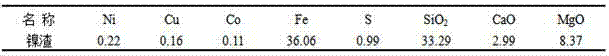Method for recovering valuable metals from nickel-copper molten slag through selective reduction
A valuable metal and molten slag technology, which is applied to the selective reduction and recovery of valuable metals in nickel-copper molten slag, comprehensive utilization of smelting molten slag, and step-by-step selective reduction of high-temperature nickel-copper smelting molten slag, which can solve the problem of crude iron. The problems of high copper content in products and difficult positioning of subsequent products have achieved the effect of realizing economy, saving costs, and broadening the application field of the market.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] The chemical composition of the raw material nickel molten slag that the inventive method adopts is as shown in table 1.
[0020] Table 1 Chemical composition of nickel molten slag (%)
[0021]
[0022] (1) Selective reduction: Add 500kg of nickel-copper smelting slag directly into the reduction furnace in a molten state at a high temperature of 1200°C, add 10kg of reducing agent lignite lump coal and 50kg of flux limestone respectively, and carry out nickel melting slag at 1400°C selective reduction smelting;
[0023] (2) Deep reduction: When 500kg of intermediate nickel molten slag is at 1500°C, 100kg of reducing agent lignite lump coal and 125kg of flux limestone are respectively added to carry out deep reduction smelting of intermediate nickel molten slag. The slag components after selective reduction smelting and deep reduction smelting of nickel molten slag are shown in Table 2 and Table 3, respectively. The composition of reduced crude iron is shown in Table...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The chemical composition of the melted raw material nickel used in the method of the present invention is shown in Table 5.
[0032] Table 5 Chemical composition of nickel molten slag (%)
[0033]
[0034] (1) Selective reduction: Put 500kg of nickel-copper smelting slag directly into the reduction furnace at a high temperature of 1350°C, add 20kg of reducing agent block anthracite, and 75kg of flux lime powder, and melt the molten slag at 1450°C for nickel melting Selective reduction smelting of slag;
[0035] (2) Deep reduction: When 500kg of intermediate nickel molten slag is at 1450°C, 125kg of reducing agent block anthracite and 175kg of flux lime powder are respectively added to carry out deep reduction smelting of intermediate nickel molten slag.
[0036] The slag components after selective reduction smelting and deep reduction smelting of nickel molten slag are shown in Table 6 and Table 7, respectively. The composition of reduced crude iron is shown in Tab...
Embodiment 3
[0044] The chemical composition of the melted raw material nickel used in the method of the present invention is shown in Table 9.
[0045] Table 9 Chemical composition of nickel molten slag (%)
[0046]
[0047] (1) Selective reduction: Put 500kg of nickel-copper smelting slag directly into the reduction furnace at a high temperature of 1300°C, add 30kg of reducing agent powdered bituminous coal, and 100kg of flux powdered limestone respectively, and carry out nickel slag melting at 1500°C selective reduction smelting;
[0048] (2) Deep reduction: When 500kg of intermediate nickel molten slag is at 1600°C, 150kg of reducing agent block bituminous coal and 200kg of flux limestone are respectively added to carry out deep reduction smelting of nickel molten slag.
[0049] The slag components after selective reduction smelting and deep reduction smelting of nickel molten slag are shown in Table 10 and Table 11, respectively. The composition of reduced crude iron is shown in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com