Thin-film solar cell composite back electrode utilizing polymers as substrate and preparation method
A technology for solar cells and back electrodes, which is applied in the manufacture of circuits, electrical components, and final products. It can solve the problems of high resistivity, large surface roughness, and inability to meet the requirements of thin-film solar cell metal back electrodes, etc., to reduce the surface area. Resistance, short sputtering time, saving material usage and energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The structural features and process of the present invention will be described in detail with a specific embodiment below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
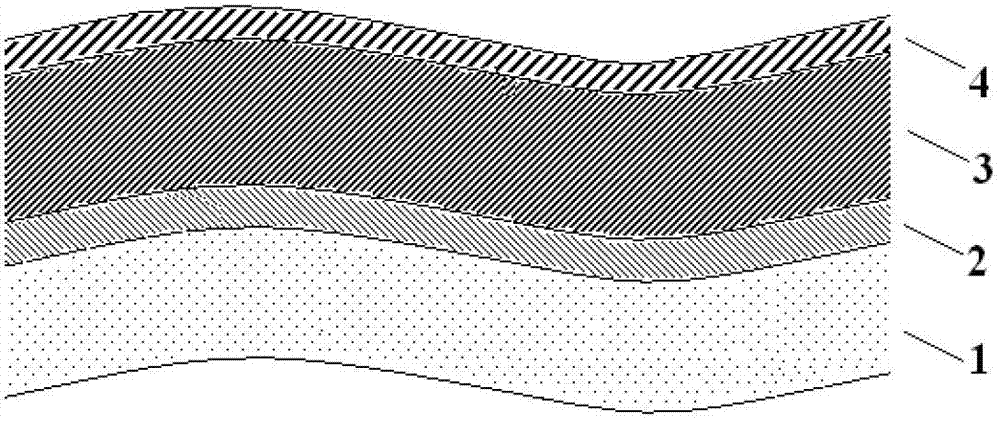
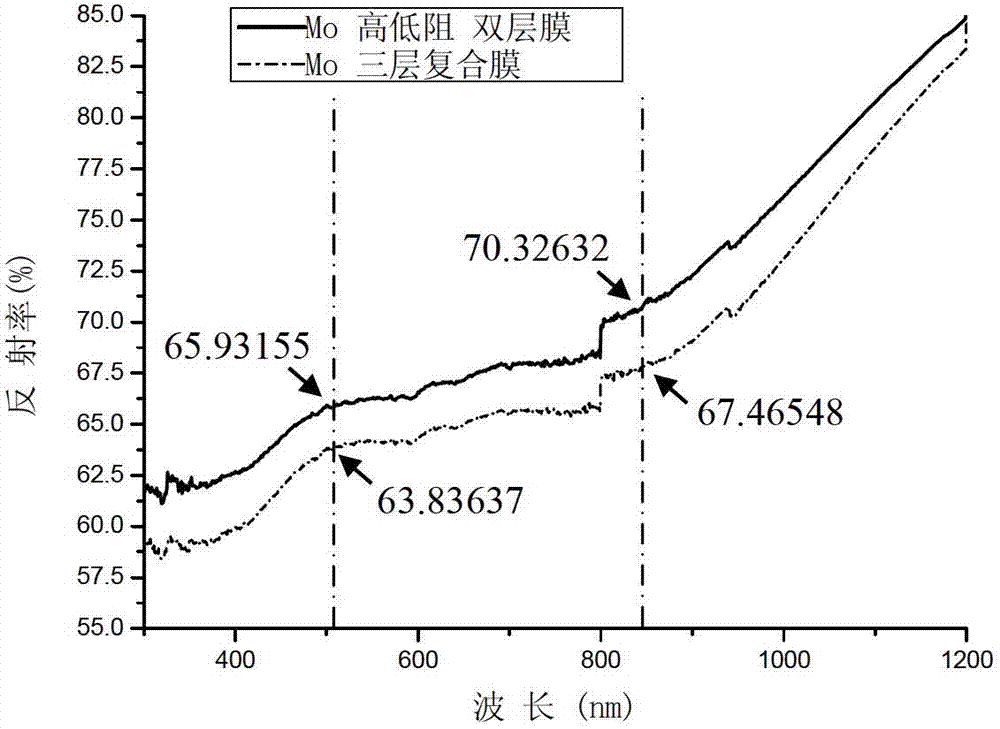
[0022] In this embodiment, a 100nm thick high-resistance residual tensile stress metal Mo film 2, a 500nm thick low resistance residual compressive stress metal Mo film 3, a 25nm thick low-resistance compressive stress metal Mo film 3, and a 25nm thick low-residual compressive stress metal Mo film are sequentially sputtered on a flexible polymer substrate 1 by magnetron sputtering. High-resistance reflective residual compressive stress metal Mo thin film 4.
[0023] The specifications of the magnetron sputtering target used: the target is a circular metal Mo target with a diameter of 3 inches, the purity is greater than 99.95%, and the distance between the surface of the sputtering target and the surface of the substrate is 100mm. The background vacuum of the sputtering vacuum chamber is about 10 -5 P...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com