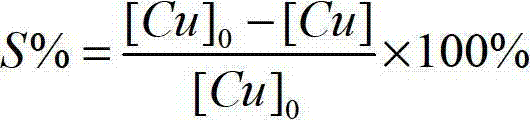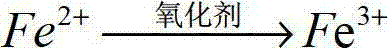Copper sulfate de-ironing process
A technology of copper sulfate and copper sulfate solution, which is applied in the iron removal process of copper sulfate and the deep iron removal field of industrial copper sulfate, which can solve the problems of high equipment investment cost, poor iron removal effect, and large copper loss rate, and achieve production The effect of low equipment requirements, low copper loss rate and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] (1) Make a nearly saturated solution of industrial copper sulfate and distilled water, and filter to remove insoluble impurities. The copper content of the obtained solution is 78g / L, and the iron content is 12mg / L, which is recorded as "solution 1";
[0045] (2) Add sodium hypochlorite (oxidant) to solution 1 in an amount of 1.5g / L, stir, and leave to oxidize for 6 hours to obtain solution 2;
[0046](3) Slowly drop the mixed solution of sodium hydroxide and sodium phosphate (precipitant) into solution 2, the concentration and dosage of which are 2% and 30ml / L respectively, adjust the pH value of the solution to 3.7, hydrolyze at 30°C for 12h, filter , to obtain solution 3;
[0047] (4) Evaporate and crystallize solution 3 to obtain high-purity copper sulfate.
[0048] The iron content of the filtrate obtained by this method is 0.8mg / L, the copper loss rate is 5%, and the purity of copper sulfate is more than or equal to 99%.
Embodiment 2
[0050] (1) Make a nearly saturated solution of industrial copper sulfate and distilled water, and filter to remove insoluble impurities. The copper content of the obtained solution is 80g / L, and the iron content is 14mg / L, which is recorded as "solution 1";
[0051] (2) Add sodium chlorate (oxidant) to solution 1 in an amount of 2.5g / L, stir, and leave to oxidize for 12 hours to obtain solution 2;
[0052] (3) Slowly drop a mixed solution of sodium phosphate and sodium stearate (precipitant) into solution 2, the concentration and dosage of which are 5% and 8ml / L respectively, adjust the pH value of the solution to 3.0, and hydrolyze at 25°C for 24 hours, Filter to obtain solution 3;
[0053] (4) Evaporate and crystallize solution 3 to obtain high-purity copper sulfate.
[0054] The iron content of the filtrate obtained by this method is 0.4mg / L, the copper loss rate is 9%, and the purity of copper sulfate is more than or equal to 99%.
Embodiment 3
[0056] (1) Make a nearly saturated solution of industrial copper sulfate and distilled water, and filter to remove insoluble impurities. The copper content of the obtained solution is 70g / L, and the iron content is 11mg / L, which is recorded as "solution 1";
[0057] (2) Add potassium persulfate (oxidant) to solution 1 in an amount of 0.025g / L, stir, and leave to oxidize for 8 hours to obtain solution 2;
[0058] (3) Slowly drop sodium phosphate solution (precipitant) into solution 2, the concentration and dosage of which are 1% and 80ml / L respectively, adjust the pH value of the solution to 4.0, hydrolyze at 50°C for 3 hours, and filter to obtain solution 3;
[0059] (4) Evaporate and crystallize solution 3 to obtain high-purity copper sulfate.
[0060] The iron content of the filtrate obtained by this method is 0.5mg / L, the copper loss rate is 8%, and the purity of copper sulfate is more than or equal to 99%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com