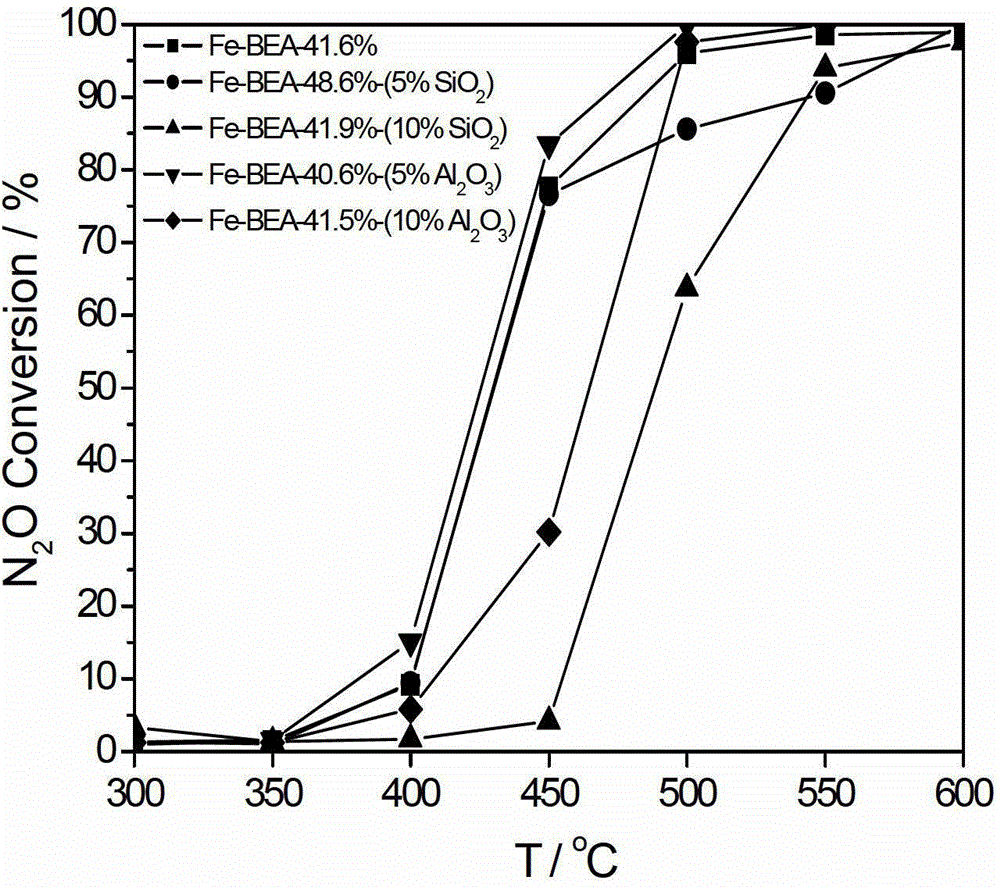
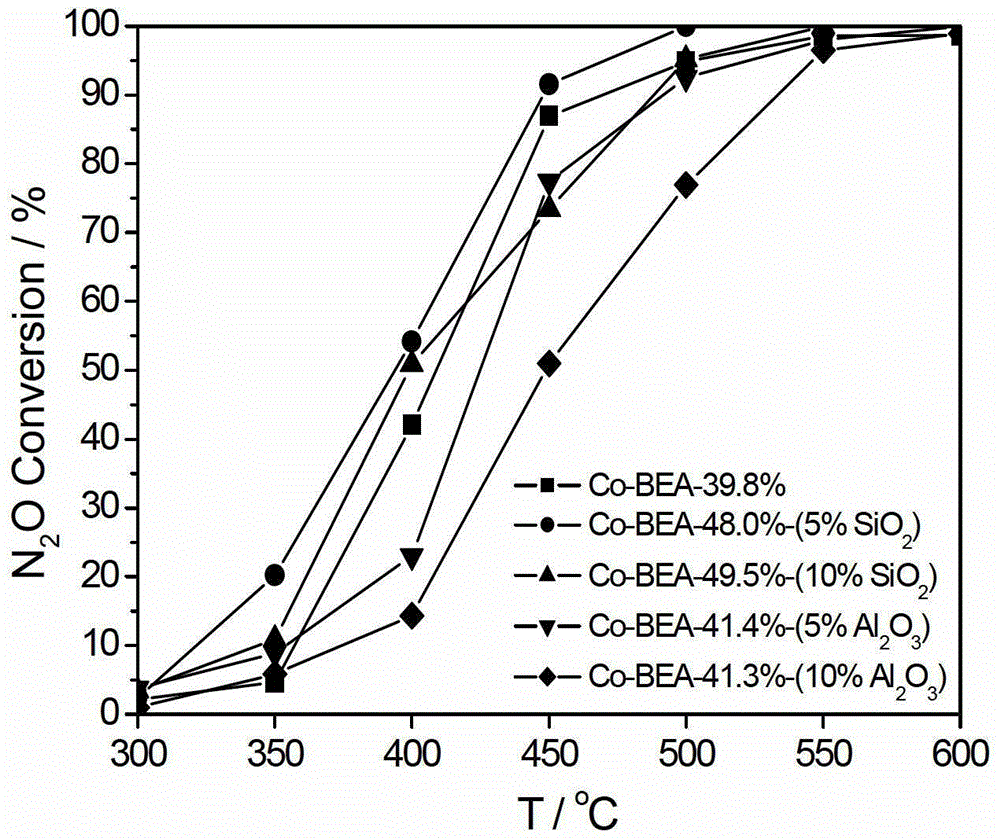
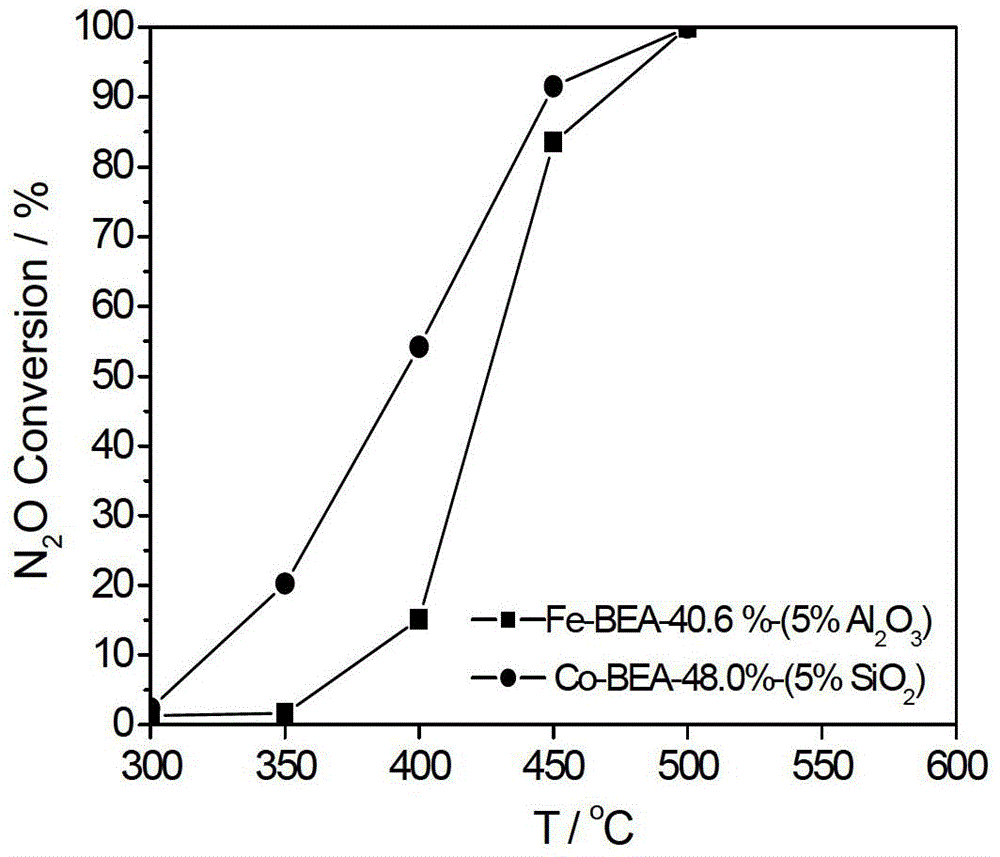
Preparation method of monolithic BEA molecular sieve catalyst for direct N2O catalysis decomposition
A catalytic decomposition and molecular sieve technology, which is applied in the fields of chemical and chemical technology and environmental protection, to achieve the effects of stable catalytic activity, high selectivity and low conversion temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Preparation of 5% aluminum sol Fe-BEA monolithic molecular sieve catalyst
[0039] Accurately weigh the H-BEA molecular sieve catalyst (SiO 2 / Al 2 o 3 =30) (commercial molecular sieve) 10.0g, Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O (analytical pure) 0.729g, deionized water 300mL, put it in a three-necked flask, and stir in a constant temperature water bath at 90°C for 6 hours. Then it was filtered and washed 3 times, dried in a drying oven at 100°C for 12 hours, then placed in a muffle furnace to program the temperature to 550°C, and roasted at a constant temperature for 5 hours to obtain a Fe ion-modified BEA molecular sieve powder sample, in which Fe The mass percentage of ions in the modified molecular sieve is 1%.
[0040] A large piece of cordierite (diameter 16.5mm, height 11mm, hole density 400cell / inch 2 ) into a small piece of cordierite with a hole number of 10×10, then grind it to a height of 5mm, and finally pick it into the required cylindrical shape with a p...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2: Preparation of 10% aluminum sol Fe-BEA monolithic molecular sieve catalyst
[0044] The preparation of Fe-BEA powder molecular sieve is as described in Example 1. Select aluminum sol with a mass percentage of 20% as a binder, accurately weigh 4.000 g of Fe-BEA molecular sieve, 6.858 g of aluminum sol, and 2.824 g of deionized water. The rest of the preparation steps are as described in Example 1, and a Fe-BEA monolithic molecular sieve catalyst with 10% aluminum sol and a Fe-BEA loading capacity of 41.5% can be obtained. The activity evaluation means are the same as in Example 1, and the activity evaluation results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3: Preparation of 5% silica sol Co-BEA monolithic molecular sieve catalyst
[0046] Accurately weigh 10.0 g of H-BEA molecular sieve catalyst (commercial molecular sieve), Co(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O (analytical pure) 0.490g and deionized water 300mL, the rest of the preparation steps are the same as the preparation process of Fe-BEA modified molecular sieve in Example 1 to obtain Co-BEA powder molecular sieve, wherein Co accounts for the mass of modified molecular sieve (Co-BEA) The percentage is 1%.
[0047] The pretreatment of the original carrier of cordierite is the same as in Example 1.
[0048] Select silica sol with a mass percentage of 30% as a binder, accurately weigh 4.000 g of Co-BEA molecular sieve, 2.131 g of silica sol, and 6.528 g of deionized water. The remaining preparation steps are as described in Example 1, and 5% silica sol, 48.0% (mass percentage, based on the Co-BEA monolithic molecular sieve catalyst, the same below) Co-BEA monolithic molecu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com