Preparation method of low-anticoagulant heparin with anti-tumor activity
A technology with anti-tumor activity and low anti-coagulation, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of lack of selectivity, insignificant anti-tumor activity, and low degree of sulfation, achieve great social and economic value, and broaden the scope of clinical applications. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
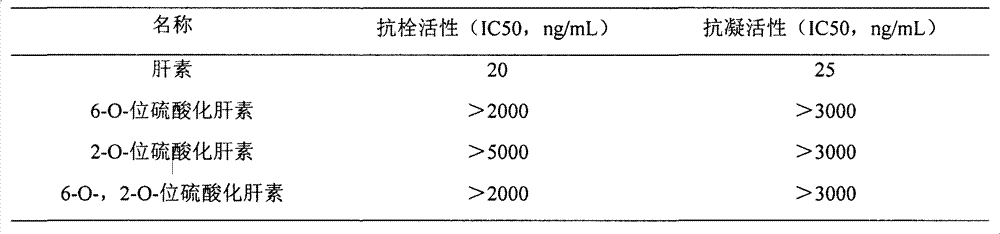
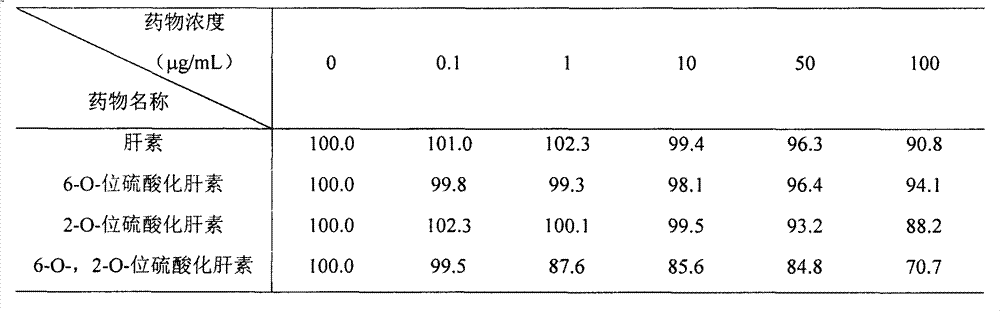
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0011] Example 1: Preparation of Completely Desulfated Heparin
[0012] Dissolve 1 g of heparin sodium in 20 mL of deionized water, pass through a hydrogen ion exchange column to obtain a heparin acid solution, adjust the pH of the solution to about 5.5 with tributylamine (TBA), and freeze-dry to obtain heparin tributylamine salt. The freeze-dried powder was dissolved in 25 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide solution containing 10% methanol, and reacted at 105° C. for 24 h. After the reaction was completed, the pH of the reaction liquid was adjusted to 9 after being diluted with an equal volume of water, and then alcohol precipitation with 4 times the volume of saturated sodium acetate ethanol solution, dialyzed, desalted, and freeze-dried to obtain completely desulfated heparin. The sulfur content is determined by elemental analysis to determine that the desulfurization rate is above 95%.
Embodiment 2
[0013] Example 2: Preparation of N-position sulfated heparin
[0014] Completely desulfated heparin was dissolved in water, and trimethylammonium sulfur trioxide copolymer (trimethylamine sulfurtrioxide complex, TMA·SO3) was gradually added at a mass ratio of 1:2, and reacted at 55°C and pH 9 for 6 hours. After the reaction, adjust the pH to neutral, dialyze and freeze-dry to obtain N-position sulfated heparin.
Embodiment 3
[0015] Example 3: Preparation of N-position, 6-O-position sulfated heparin
[0016] Usually, the enzymatic sulfation reaction condition is 1 mg of N-sulfated heparin in 20 ml of reaction liquid and shaken (300 rpm) at room temperature for 6 h. The reaction solution contains 50mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.2), 1% Triton X-100, 1% BSA, 1mM MgCl 2 , 1mM MnCl 2 , 1 mM PNPS, 40 μM PAP, 8 mg 6-OST-1 and 4 mg AST-IV. Heating the reaction solution at 100°C for ten minutes to stop the reaction, centrifuging to obtain the supernatant, mixing the supernatant with twice the volume of 2.0% NaCl aqueous solution, and loading the DEAE column; sequentially with 2.0% NaCl aqueous solution and 3.0 % NaCl aqueous solution was used for gradient elution, and the eluate obtained from the second elution was collected. The obtained solution was dialyzed with deionized water for 24 hours, and freeze-dried to obtain freeze-dried powder of N-position, 6-O-position sulfated heparin.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com