Low temperature phase change cool storage agent and preparation method thereof
A low-temperature phase transition and cooling agent technology, applied in the field of energy storage, can solve the problems of inability to achieve low temperature, high phase transition temperature, and inability to popularize, and achieve the effects of easy production, low phase transition temperature, and no latent heat value decay.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
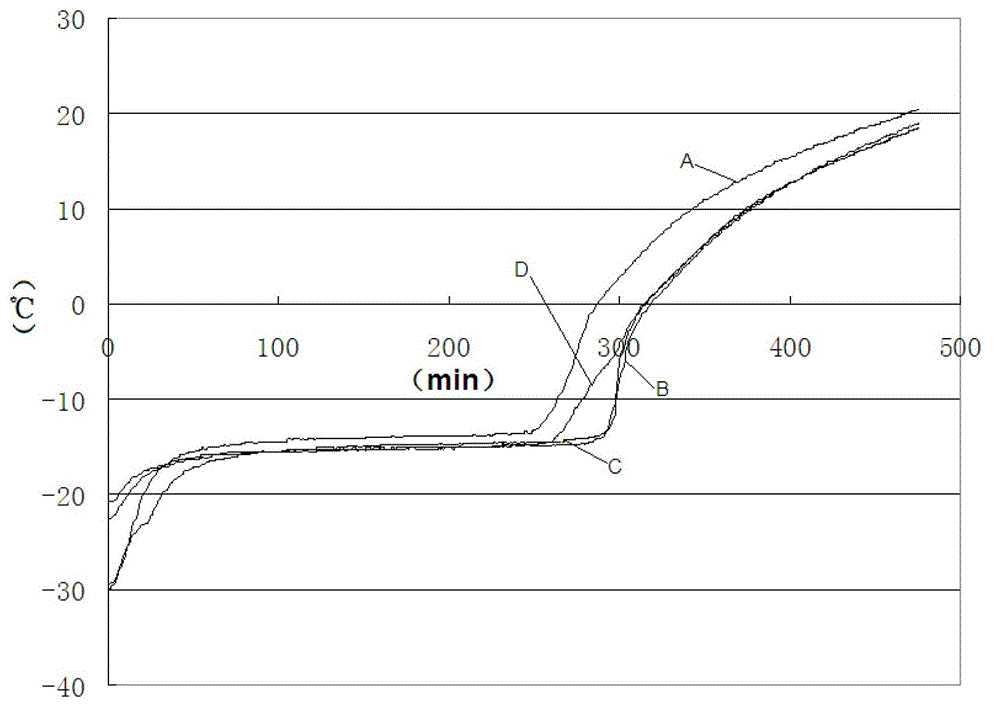
[0025] Add 19kg of ammonium chloride, 400g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, and 100g of nano-titanium dioxide (with a particle size of 20nm) into 80kg of deionized water, heat it to 70°C in a stainless steel heating furnace, and stir it evenly after melting. Slowly add 500 g of sodium hydroxyethyl cellulose with a viscosity of 40,000 s under stirring, and stir while adding until the sodium hydroxyethyl cellulose is uniformly dispersed, stir for 4 hours, and cool to 25°C to obtain the product. Take 200g of low-temperature phase-change cool storage agent and pretreat it at -30°C for 12 hours, and compare the temperature rise curve at room temperature of 27°C as shown in figure 1 shown by figure 1 It can be seen that the phase transition temperature of the cold storage agent prepared in this way is -15.2°C, and the latent heat value is 300KJ / Kg.
Embodiment 2
[0027] Add 13kg of ammonium chloride, 1kg of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, and 75g of nano-titanium dioxide (with a particle size of 30nm) into 85.1kg of deionized water, heat it to 75°C in a stainless steel heating furnace, and stir it evenly after melting. Slowly add 750g of sodium hydroxyethyl cellulose with a viscosity of 30,000s under high-speed stirring, and stir while adding until the sodium hydroxyethyl cellulose is uniformly dispersed, stir for 3 hours, and cool to 25°C to obtain the product. Take 200g of low-temperature phase-change cool storage agent and pretreat it at -30°C for 12 hours, and compare the temperature rise curve at room temperature of 27°C as shown in figure 1 shown by figure 1 It can be seen that the phase transition temperature of the cold storage agent prepared in this way is -15.5°C, and its latent heat value is 321KJ / Kg.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Add 19.5kg of ammonium chloride, 2kg of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, and 80g of nano-titanium dioxide (with a particle size of 50nm) into 77.42kg of deionized water, heat it to 70°C in a stainless steel heating furnace, and stir it evenly after melting. Slowly add 1 kg of sodium hydroxyethyl cellulose with a viscosity of 20,000 s under high-speed stirring at 4000 rpm, and stir while adding until the sodium hydroxyethyl cellulose is uniformly dispersed, stir for 4 hours, and cool to 25°C to obtain the product. Take 200g of low-temperature phase-change cool storage agent and pretreat it at -30°C for 12 hours, and compare the temperature rise curve at room temperature of 27°C as shown in figure 1 shown by figure 1 It can be seen that the phase transition temperature of the cold storage agent prepared in this way is -15.5°C, and its latent heat value is 318KJ / Kg.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com