Material containing sheet-shaped wolfram carbide grain and preparation method thereof as well as method for using same to prepare alloy
A technology of tungsten carbide particles and tungsten carbide, which is applied in the field of cemented carbide, can solve problems such as decreased wear resistance, reduced fracture resistance, and impact on the performance of cemented carbide products, and achieves the effect of improving quality, good hardness and toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
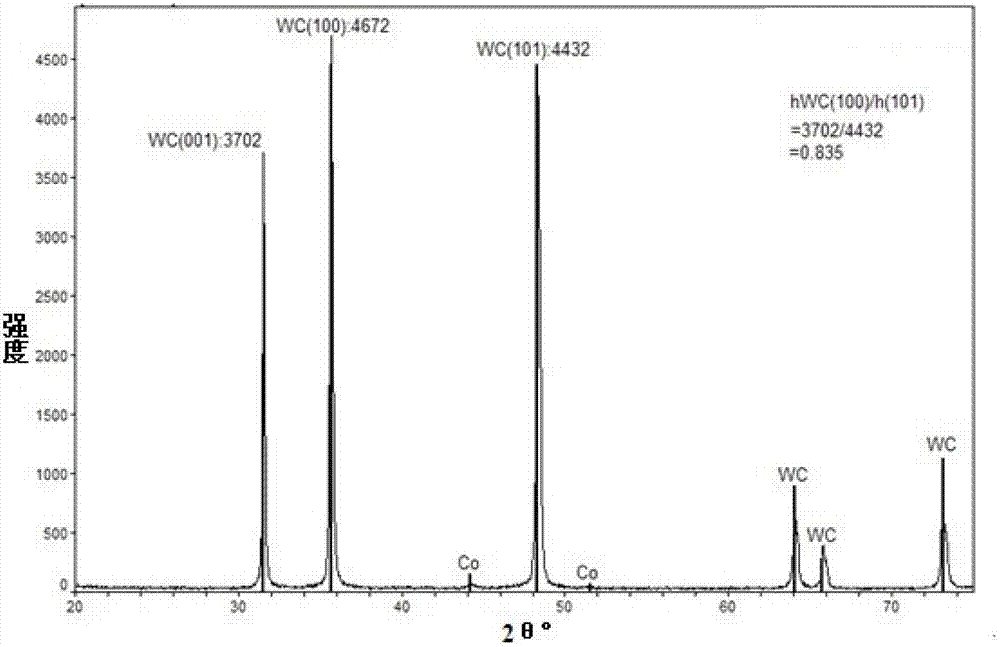
[0042] Firstly, 500g of tungsten powder with Fsss particle size of 3.0μm is selected and flattened. The method of flattening is as follows: 500g of tungsten powder and 1500g of cemented carbide rods are put together into a stainless steel cylinder, wherein the cemented carbide rods are used as grinding bodies. Then, add 1500ml of absolute alcohol to the cylinder as a grinding medium. After the cylinder is sealed, put it into a roller mill for 90 hours to get tungsten powder composed of flaky tungsten particles. Then, the tungsten powder after the flattening process and 34g of cobalt powder as the binder phase material and 33g of graphite as the carbon source material are carried out by rolling ball milling and uniformly mixed to obtain the weight of the tungsten powder: the weight of the binder phase material: the weight of the carbon source material Raw material powder with a weight equal to 88.2:6:5.8. Finally, the raw material powder was carbonized at a temperature of 115...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Firstly, 500g of tungsten powder with Fsss particle size of 3.0μm is selected and flattened. The flattening method is the same as that in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here. Then, the weight of the tungsten powder obtained by uniformly mixing the tungsten powder after the flattening process with 43g cobalt powder as the binder phase material and 33g graphite as the carbon source material: the weight of the binder phase material: the weight of the carbon source material is equal to 86.8: Raw material powder of 7.5:5.7. Finally, the raw material powder was carbonized at a temperature of 1150° C. under a hydrogen atmosphere to obtain a material 2 containing flaky tungsten carbide.
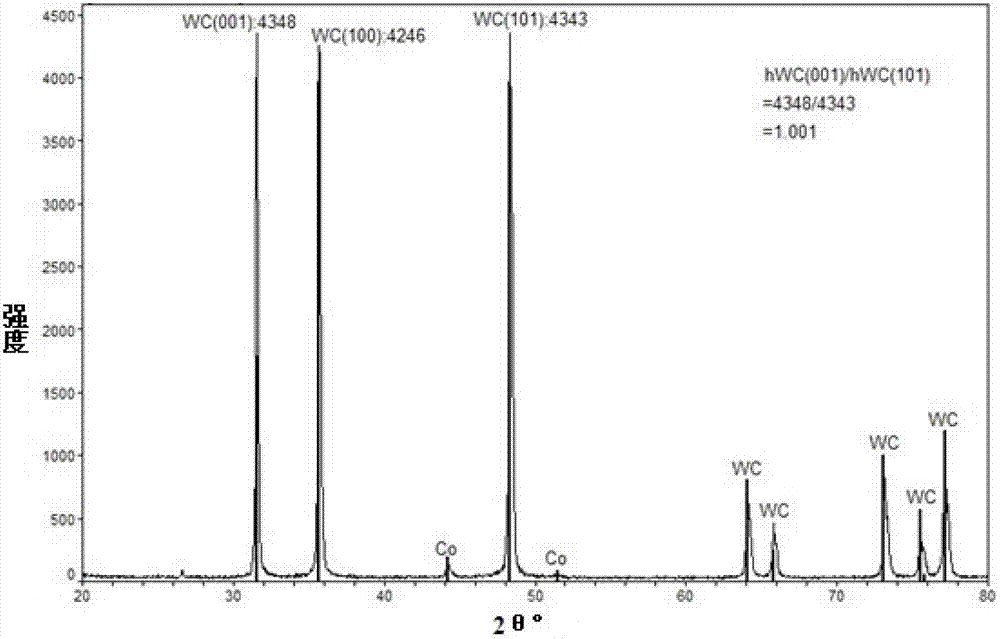
[0048] Carry out XRD analysis to material 2, such as figure 2 Shown, where tungsten exists only in the form of tungsten carbide. According to the method of Example 1, the weight content of cobalt in material 2 is 7.5%, and the weight content of tungsten carbide is 92.5%. In additi...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Firstly, 500g of tungsten powder with Fsss particle size of 3.0μm is selected and flattened. The flattening method is the same as that in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here. Then, the weight of the tungsten powder obtained by uniformly mixing the tungsten powder after the flattening process with 59g cobalt powder as the binder phase material and 33g graphite as the carbon source material: the weight of the binder phase material: the weight of the carbon source material is equal to 84.5: 10:5.5 raw material powder. Finally, the raw material powder is carbonized at a temperature of 1150° C. under a hydrogen atmosphere to obtain a material 3 containing flaky tungsten carbide.
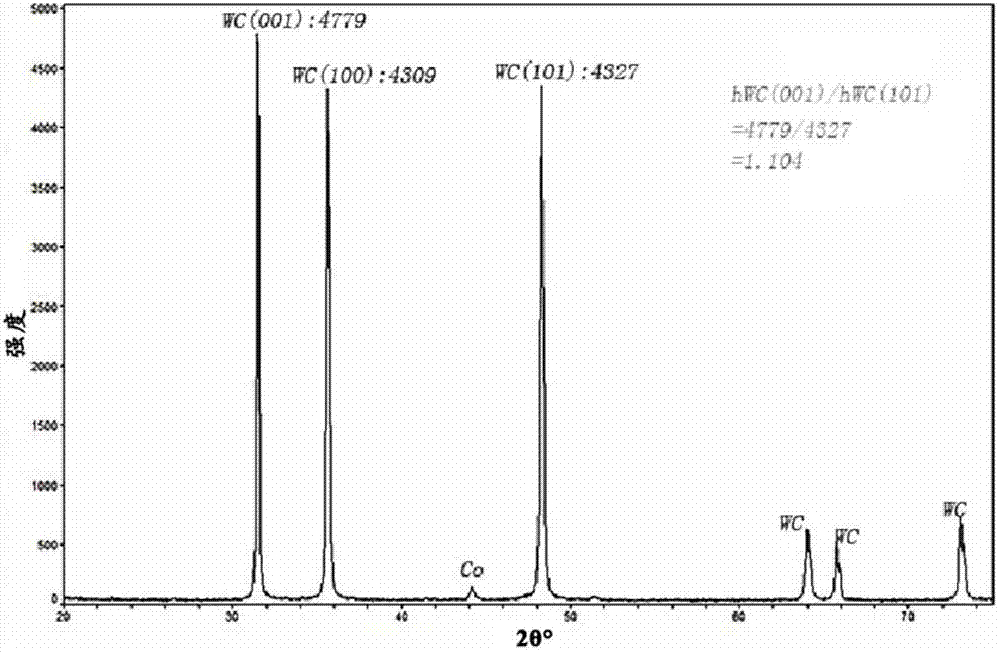
[0053] Carry out XRD analysis to material 3, such as image 3 Shown, where tungsten exists only in the form of tungsten carbide. According to the method of Example 1, the weight content of cobalt in material 3 is 10%, and the weight content of tungsten carbide is 89.8%. Also analyzed ac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| crystal size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com