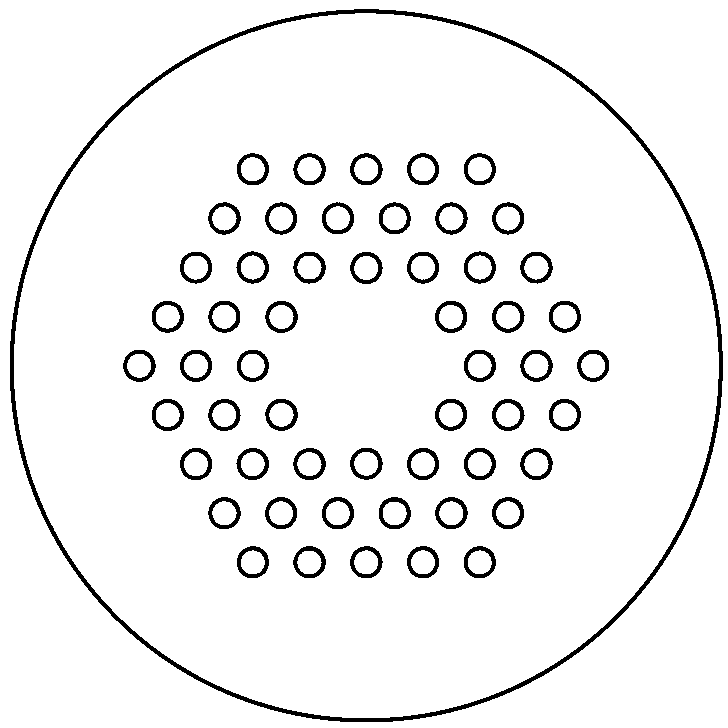
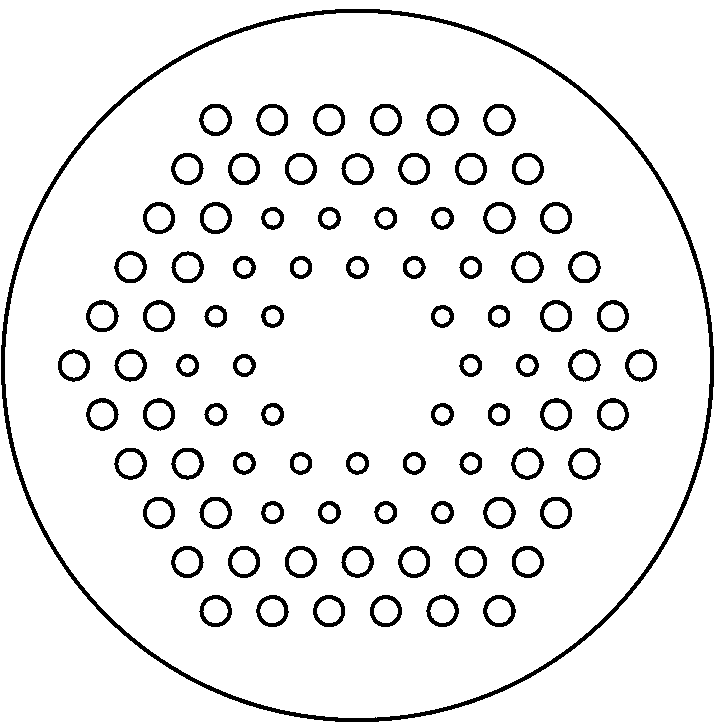
Method for preparing multihole infrared chalcogenide glass photonic crystal optical fiber preform
A photonic crystal fiber, chalcogenide glass technology, applied in glass manufacturing equipment, glass fiber products, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as interface defects, difficult to accurately arrange capillaries, and interface bubbles.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Embodiment 1: A method for preparing a porous infrared chalcogenide glass photonic crystal optical fiber preform, comprising the following steps:
[0015] 1) Accurately weigh chalcogenide glass raw materials with a purity level of 5N and put them into a quartz tube. The length of the quartz tube is 400 mm, and the diameter of the quartz tube is 20 mm. Vacuumize the quartz tube containing the chalcogenide glass raw materials processing, the vacuum degree reaches 3′10 -4 After pa, the quartz tube was sealed with a hydrogen-oxygen flame; the sealed quartz tube containing the chalcogenide glass raw material was put into a swing furnace at 900°C for 6 hours, and the temperature of the swing furnace dropped to After 650°C, the quartz tube was taken out from the swing furnace, and the temperature of the quartz tube was quenched with compressed air until the surface of the glass melt was separated from the inner wall of the quartz tube, and the quartz tube was immediately place...
Embodiment 2
[0019] Embodiment 2: A method for preparing a porous infrared chalcogenide glass photonic crystal optical fiber preform, which is characterized in that it includes the following steps:
[0020] 1) Accurately weigh chalcogenide glass raw materials with a purity level of 5N and put them into a quartz tube. The length of the quartz tube is 800mm, and the diameter of the quartz tube is 50mm. Vacuumize the quartz tube containing the chalcogenide glass raw materials processing, vacuum up to 6′10 -4 After pa, the quartz tube was sealed with a hydrogen-oxygen flame; the sealed quartz tube containing the chalcogenide glass raw material was put into a swing furnace at 950°C for 8 hours, and the temperature of the swing furnace dropped to After 700°C, the quartz tube was taken out of the swing furnace, and the temperature of the quartz tube was quenched with compressed air until the surface of the glass melt was separated from the inner wall of the quartz tube, and the quartz tube was i...
Embodiment 3
[0025] Embodiment 3: A method for preparing a porous infrared chalcogenide glass photonic crystal optical fiber preform, comprising the following steps:
[0026] 1) Accurately weigh chalcogenide glass raw materials with a purity level of 5N and put them into a quartz tube. The length of the quartz tube is 600mm, and the diameter of the quartz tube is 35mm. Vacuumize the quartz tube containing the chalcogenide glass raw materials processing, vacuum up to 5′10 -4 After pa, the quartz tube was sealed with a hydrogen-oxygen flame; the sealed quartz tube containing the chalcogenide glass raw material was put into a swing melting furnace at 925°C for 7 hours, and the temperature of the swing furnace dropped to After 680°C, take the quartz tube out of the swing furnace, and use compressed air to quench the temperature of the quartz tube until the surface of the glass melt separates from the inner wall of the quartz tube. Keep warm in the furnace for 5 hours, the temperature of the p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com