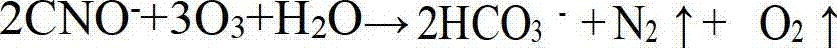Method for separating and recovering gold and copper from copper-bearing cyanide pregnant solution
A technology for recovering gold and precious liquid, which can be applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, and can solve the problems of large dosage of chemicals, high operating costs, and equipment corrosion protection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1: A certain oxidized ore dressing and smelting plant has a daily processing capacity of 2,000 tons, and adopts the technological process of "grinding → combined leaching with cyanide → three-stage countercurrent washing → gold extraction with activated carbon". High, the water volume is about 400m3 / hr, and the water quality is shown in Table 1.
[0030] Table 1 Analysis results of water quality of copper-containing cyanide precious liquid in an oxide ore dressing and smelting plant
[0031]
[0032] Get this copper-containing cyanide precious liquid of 15L and adopt the process of the present invention to process:
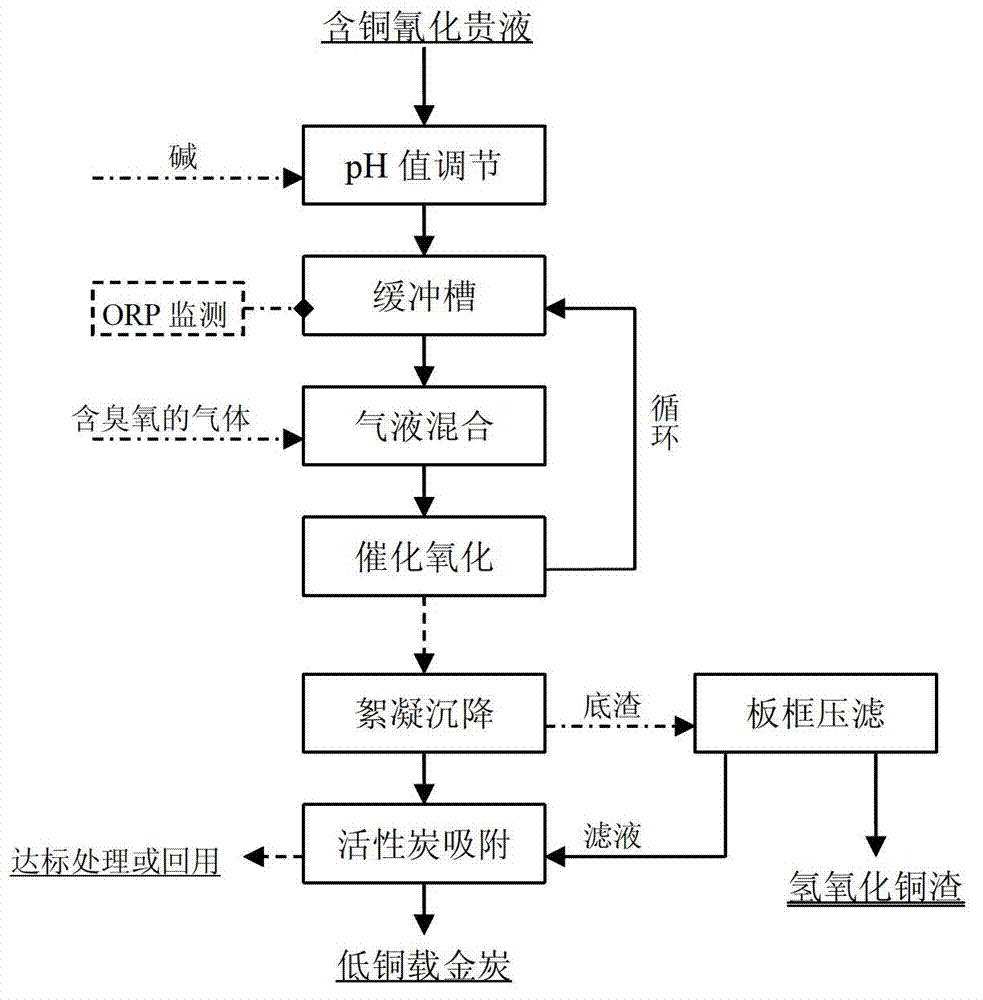
[0033] Step 1: pH adjustment process. Add lime 0.28g / L, mechanically stir for about 10 minutes, and the pH value is about 10.07; then, pump into the buffer tank for the next step of circular catalytic oxidation. The second step: cyclic catalytic oxidation process. Use a dissolved air pump to mix the ozone-containing gas with the copper-contain...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Repeat Example 1 according to the above-mentioned same steps, but the difference is that the water quality of the original copper-containing cyanide noble liquid is different (see Table 6). The first step adjusts the pH value of the water body to 11.2 and the alkali used is caustic soda. The gas-liquid ratio in the step is 25%, and the ultraviolet light intensity at λ=254nm is 400 μW-SEC / cm2; other technical parameters and steps are the same as in Example 1.
[0048] Table 6 Analysis results of water quality of copper-containing cyanide precious liquid in an oxide ore dressing and smelting plant
[0049]
[0050] Example 2 After being treated by the above method, the amount of caustic soda consumed in the first step is 0.1 g / L;
[0051] Table 7 Analysis results of water quality after oxidation of copper-containing cyanide precious liquid in an oxidation ore dressing and smelting plant
[0052]
[0053] The slag produced in the third step is 0.29g / L (dry weight), ...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Repeat Example 1 according to the same steps above, but the difference is that the water quality of the original copper-containing cyanide noble liquid is different (see Table 10). In the first step, the pH value of the water body is adjusted to 10.82. In the second step, the gas-liquid mixing device is a jet device, the gas-liquid ratio is 20%, and the ultraviolet light intensity of λ=254nm is 350μW-SEC / cm2; other technical parameters and steps are the same as in Example 1.
[0065] Table 10 Water quality analysis results of copper-containing cyanide precious liquid in an oxide ore dressing and smelting plant
[0066]
[0067] Example 2 After being treated by the above method, the amount of lime consumed in the first step is 0.29g / L;
[0068] Table 11 Analysis results of water quality after oxidation of copper-containing cyanide precious liquid in an oxidation ore dressing and smelting plant
[0069]
[0070] The slag produced in the third step is 0.35g / L (dry w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com