Direct-electroplating conductive liquid and preparation method thereof
A kind of conductive liquid, direct technology, applied in the field of conductive liquid, can solve the problems of weak conductivity, poor adsorption force, low electroplating efficiency, etc., to achieve the effect of small particle size, inhibition of agglomeration, and high electroplating efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
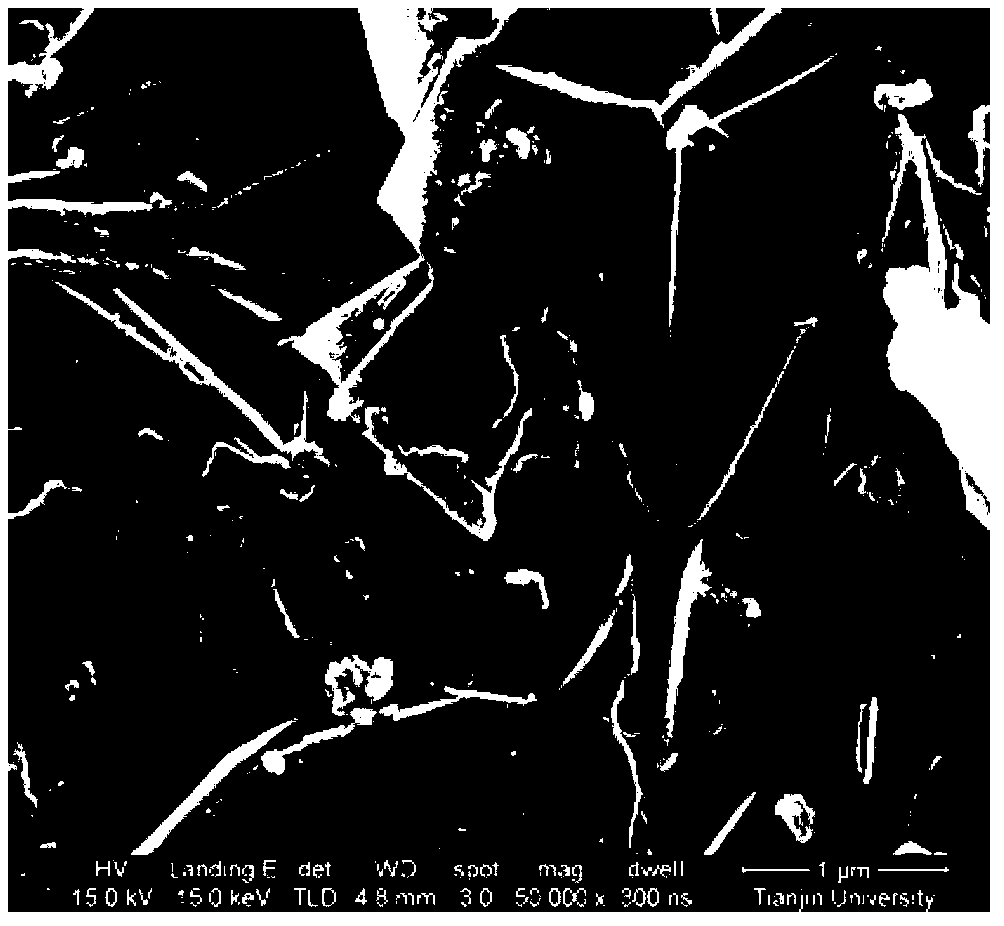
[0030] This embodiment is a direct electroplating conductive solution. The conductive liquid is composed of 0.5g / L graphene and 0.2g / L polyacrylic acid stabilizer, and is prepared by using ammonia water as a pH regulator and deionized water.
[0031] The thickness of the graphene ≤ 1.0nm, particle size ≤ 200nm
[0032] The process of preparing said direct electroplating conductive solution is:
[0033] Step 1, prepare graphene dispersion liquid. Heat 500 mL of deionized water to 60 °C. 0.5 g / L graphene was added into the deionized water, and dispersed by ultrasonic waves for 1 h to obtain a graphene dispersion.
[0034] Step 2, preparing a stabilizer solution. Another 200 mL of deionized water was taken, and 0.2 g / L powdered polyacrylic acid stabilizer was added into the 200 mL of deionized water to dissolve to obtain a stabilizer solution.
[0035] Step 3, add the stabilizer solution. The obtained polyacrylic acid stabilizer solution was added to the graphene-added deio...
Embodiment 2
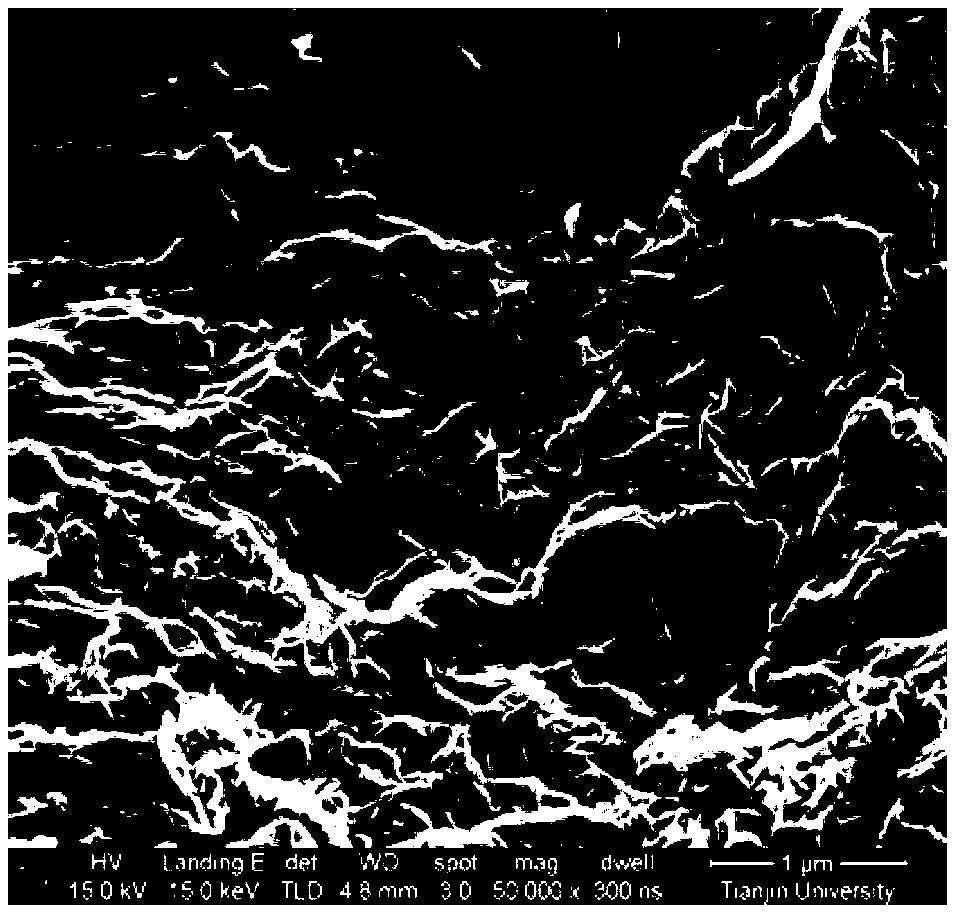
[0042] This embodiment is a direct electroplating conductive solution. The conductive liquid is composed of 1.0g / L graphene, 0.4g / L polyacrylic acid stabilizer, ammonia water as a pH regulator, and deionized water.
[0043] The thickness of the graphene ≤ 1.0nm, particle size ≤ 200nm
[0044] The process of preparing said direct electroplating conductive solution is:
[0045] Step 1, prepare graphene dispersion liquid. Heat 500 mL of deionized water to 70 °C. 1.0 g / L graphene was added into the deionized water, and dispersed by ultrasonic wave for 2 h to obtain a graphene dispersion.
[0046] Step 2, preparing a stabilizer solution. Another 200 mL of deionized water was taken, and 0.4 g / L powdered polyacrylic acid stabilizer was added into the 200 mL of deionized water to dissolve to obtain a stabilizer solution.
[0047] Step 3, add the stabilizer solution. The obtained polyacrylic acid stabilizer solution was added to the graphene-added deionized water in the dispersio...
Embodiment 3
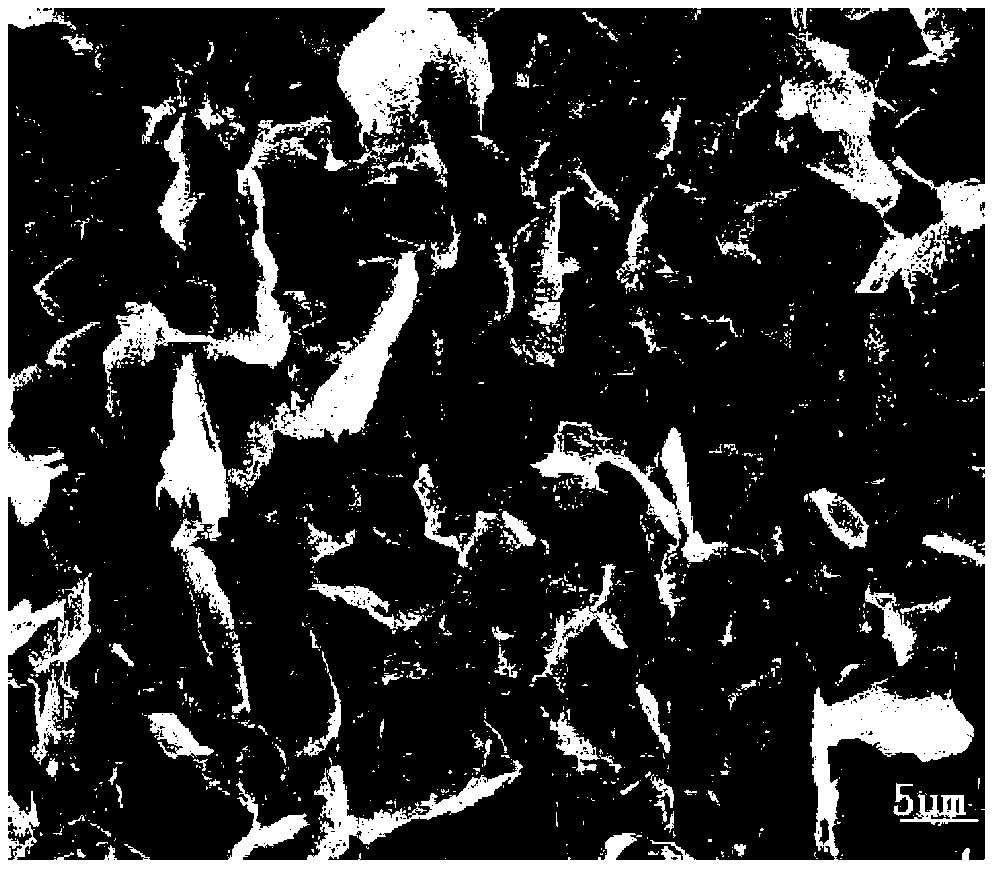
[0054] This embodiment is a direct electroplating conductive solution. The conductive liquid is composed of 2.0g / L graphene, 0.6g / L polyacrylic acid stabilizer, ammonia water as a pH regulator, and deionized water.
[0055] The thickness of the graphene ≤ 1.0nm, particle size ≤ 200nm
[0056] The process of preparing said direct electroplating conductive solution is:
[0057] Step 1, prepare graphene dispersion liquid. Heat 500 mL of deionized water to 80 °C. 2.0 g / L graphene was added into the deionized water, and dispersed by ultrasonic wave for 3 h to obtain a graphene dispersion.
[0058] Step 2, preparing a stabilizer solution. Another 200 mL of deionized water was taken, and 0.6 g / L powdered polyacrylic acid stabilizer was added into the 200 mL of deionized water to dissolve to obtain a stabilizer solution.
[0059] Step 3, add the stabilizer solution. The obtained polyacrylic acid stabilizer solution was added to the graphene-added deionized water in the dispersio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com