Medical devices and methods including polymers having biologically active agents therein
A bioactive agent and medical device technology, applied in medical preparations containing active ingredients, organic active ingredients, medical preparations with non-active ingredients, etc., can solve the impact on the final performance of the device, the side effects of medical devices, and the side effects of bioactive agents And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0121] Example 1 - Preparation of spray-dried clonidine hydrochloride
[0122] Dissolve clonidine hydrochloride in methanol to form a 12% (w / w) solution. The solution was spray dried in a Buchi B-290 pocket spray dryer (Buchi Laboratorium AG, Switzerland) using a 120 kHz Sono-Tek ultrasonic nozzle (Sono-Tek Corp., Milton, NY). The processing parameters were set as follows: inlet temperature (70 °C), aspirator (80%), nitrogen inlet (50 mm), spray flow rate (80 mL / h), and ultrasonic generator (0.8 W). The spray-dried powder was collected and dried for an additional 24 hours at 70°C and 15 mmHg vacuum.
Embodiment 2
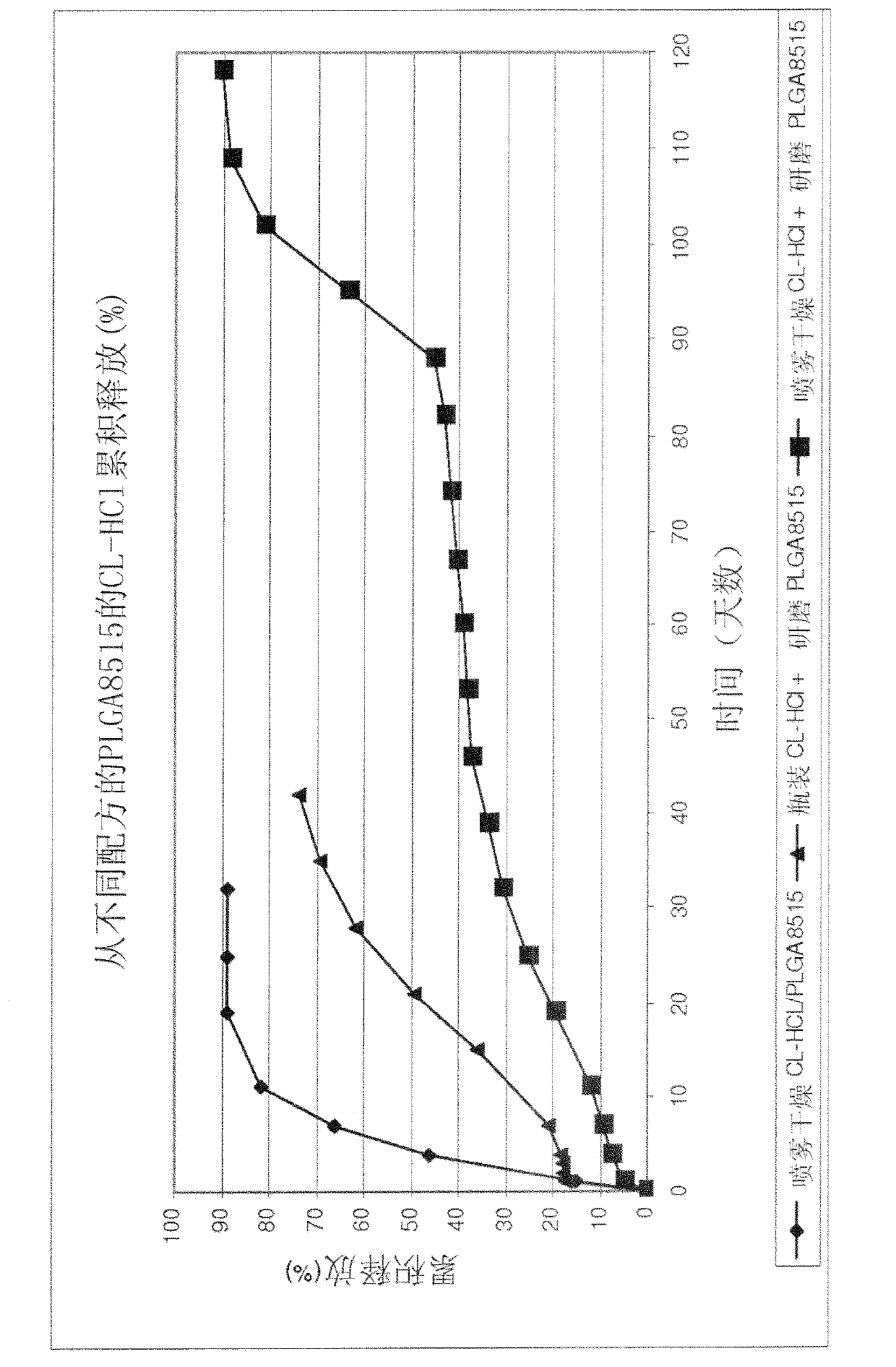
[0123] Example 2 -Preparation of spray-dried clonidine hydrochloride / PLGA8515
[0124] Clonidine hydrochloride and PLGA8515 were individually dissolved in acetone to form a 2% (w / w) solution. A mixed solution of 10% clonidine hydrochloride solution and 90% PLGA8515 solution was spray-dried in a Buchi spray dryer. The processing parameters were set as follows: inlet temperature (60 °C), aspirator (80%), nitrogen inlet (50 mm), spray flow rate (80 mL / h) and ultrasonic generator (0.8 W). The spray-dried powder was collected and dried for an additional 24 hours at 30°C and 15 mmHg vacuum.
Embodiment 3
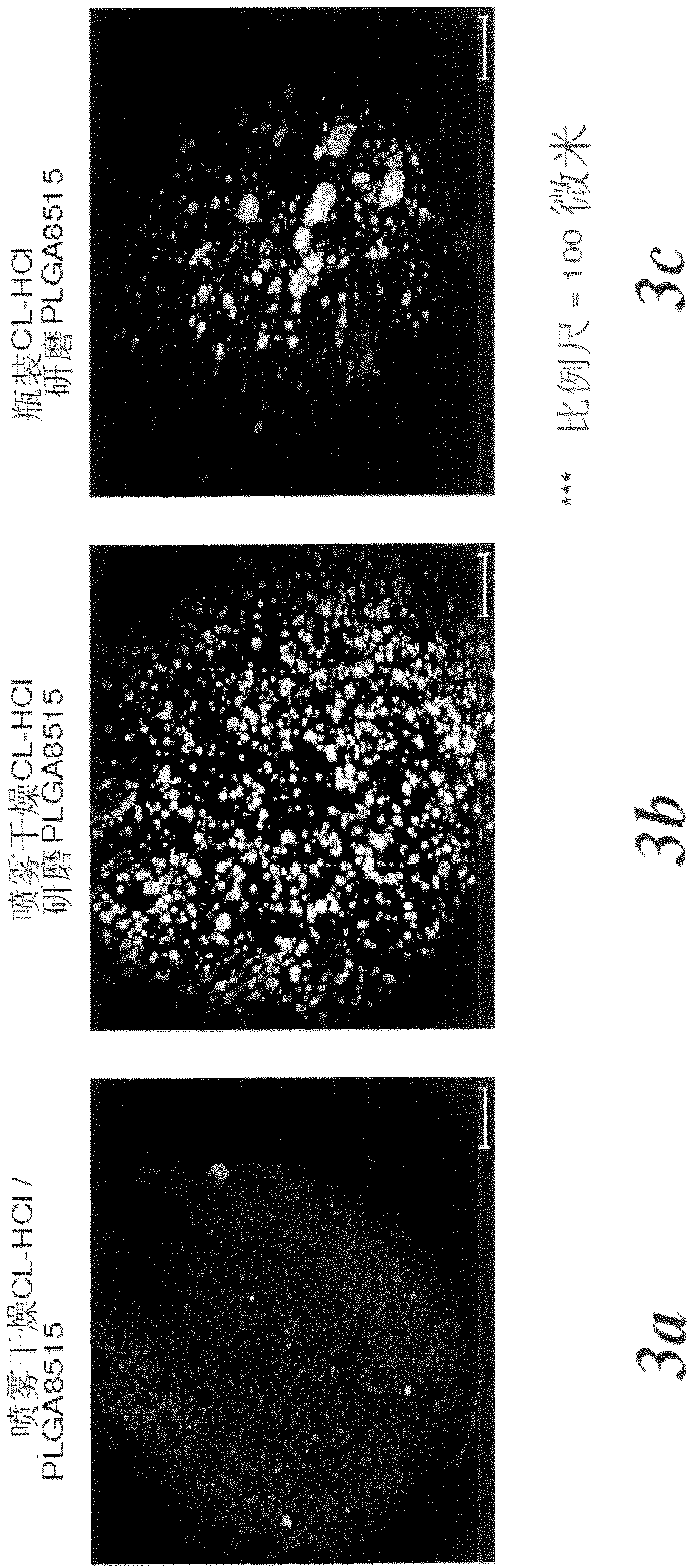
[0125] Example 3 - Preparation of melt extruded rods
[0126] Three formulations with different clonidine hydrochloride preparation methods were prepared for melt extrusion. The first formulation contained PLGA8515 ground to a powder using a Retsch (Retsch GmbH, Germany) rotor mill with an 80 micron mesh filter and clonidine hydrochloride directly from the manufacturer. The second formulation contained milled PLGA8515 and spray-dried clonidine hydrochloride from Example 1. The third formulation contained spray-dried clonidine hydrochloride / PLGA8515 from Example 2. Each formulation contained 10% (w / w) clonidine hydrochloride and 90% (w / w) PLGA8515. The formulations were dry mixed with spatulas before being fed into a twin-screw extruder (Thermo Fischer Scientific, Waltham, MA) set at 120°C and 30 RPM. The rods were extruded from a die with a diameter of 0.75 mm.
[0127] Microscopic analysis
[0128] TOF-SIMS data acquisition was performed on the rods of Example 3 usin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com