Mass acquisition method of different loci and flanking sequence thereof in genome DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids)
A technology of differential sites and flanking sequences, which is applied in the field of batch acquisition of differential sites and flanking sequences in genomic DNA, can solve the problems of inability to widely apply genome differential analysis, low analysis throughput, high cost, etc., and achieve low cost, Simple and convenient operation, wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
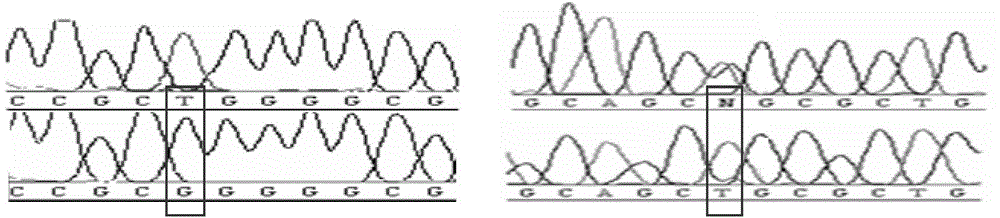
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1. Obtaining differential sites in genomic DNA in batches
[0034] 1. Obtaining genomic DNA
[0035] According to the method of phenol-chloroform extraction DNA in the literature (Lu Shengdong. Modern Molecular Biology Experimental Technology. Beijing: China Union Medical University Press, 1999), the coarse wool sheep (Altay sheep) and the fine wool sheep (Chinese Merino sheep) were extracted respectively. Genomic DNA from the ear tissue of Xinjiang Junken fine-wool sheep) with ddH 2 O The final concentration of genomic DNA was diluted to 200ng / μL.
[0036] 2. Hybridization of genomic DNA
[0037] Take the same amount of coarse and fine wool sheep genomic DNA obtained in step 1 (5 μL each, that is, 1 μg genomic DNA)) and mix them, and carry out molecular hybridization according to the following reaction system and conditions:
[0038] Hybridization reaction system: 1 μL 50×Denhardt’s (purchased from Invitrogen, catalog number 750018), 2.5 μL 20×SSC (solvent i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com