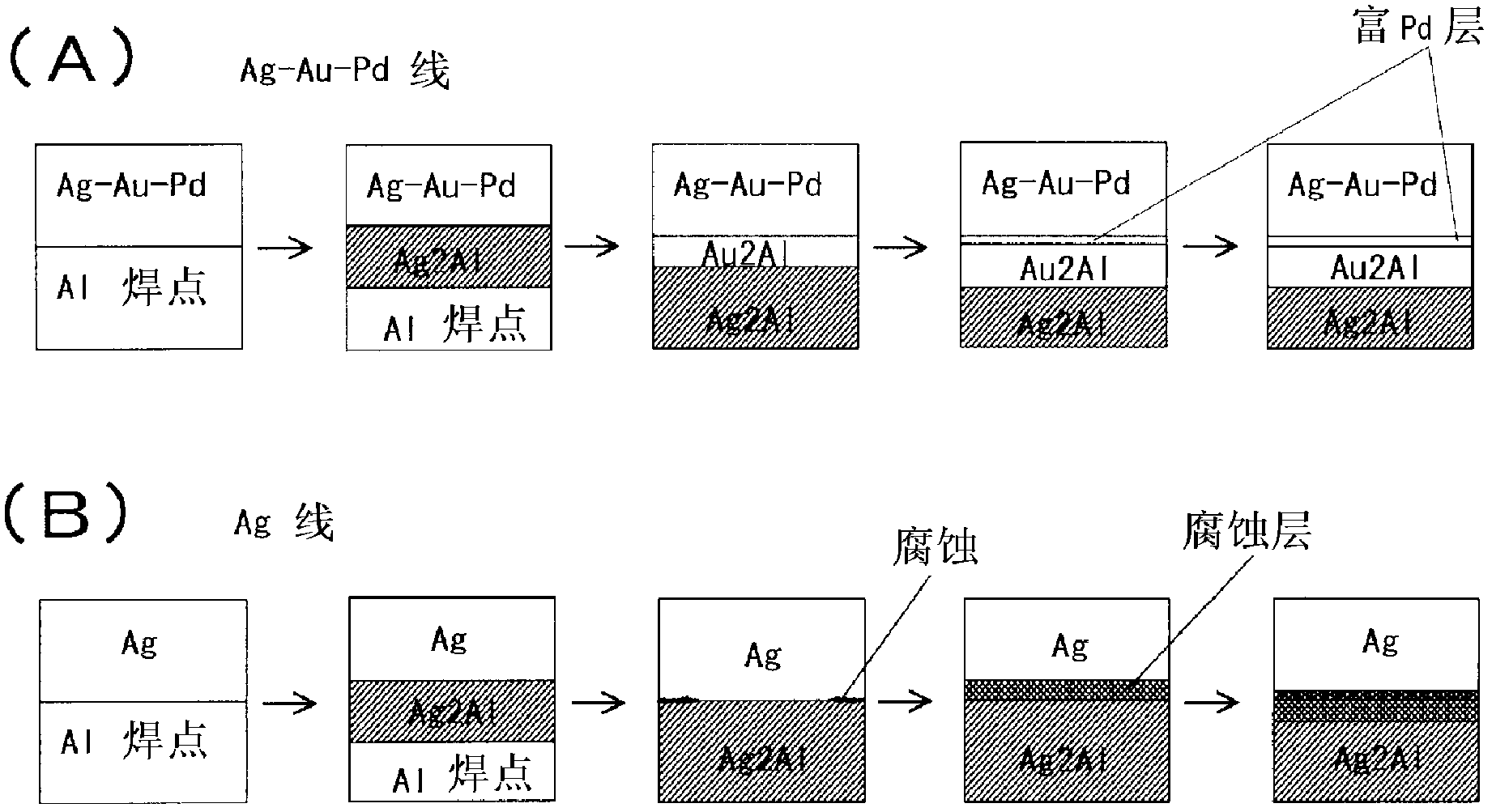
Ag-au-pd ternary alloy-based bonding wire
An ag-au-pd, ternary alloy technology, applied in the field of Ag-Au-Pd ternary alloy bonding wire, can solve the problem of unused Ag-Au-Pd ternary alloy bonding wire, unstable molten ball shape, Inability to maintain performance and other problems, to achieve the effect of reducing irregularity, high bonding reliability, and corrosion inhibition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] Invention embodiment
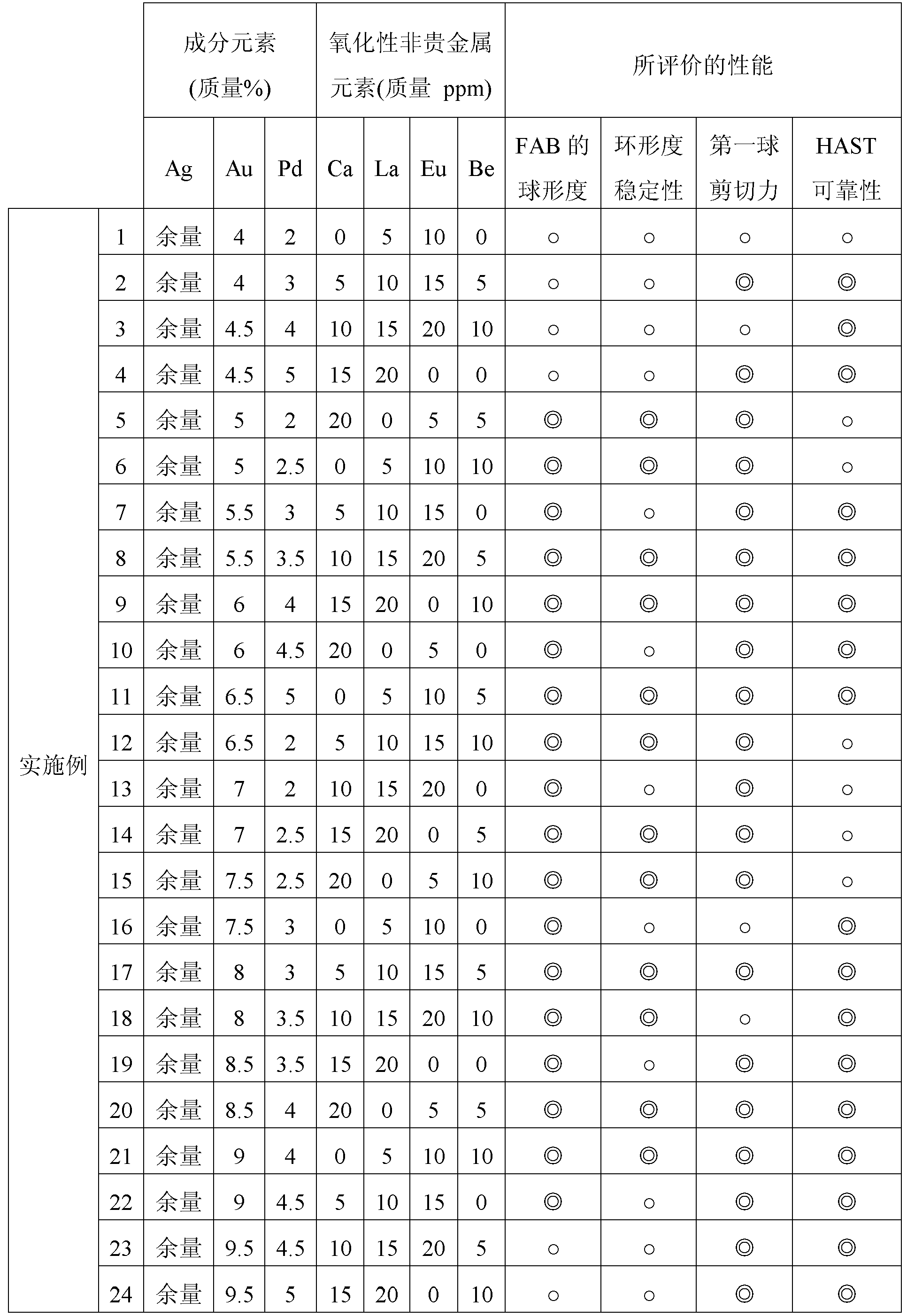
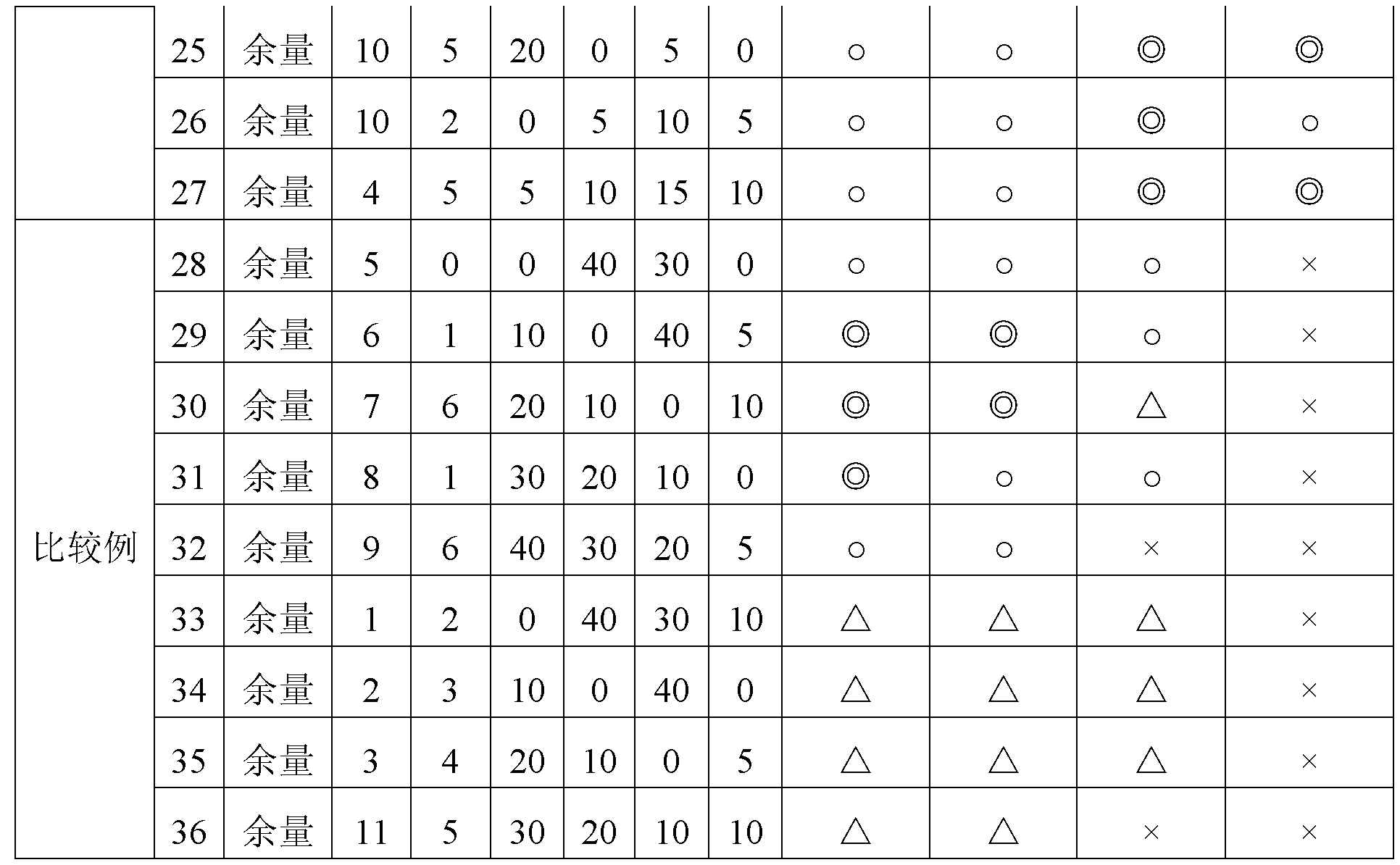
[0041] The Ag-Au-Pd alloy having the element composition shown in the left half of Table 1 was prepared by melt casting, and the wire of 10 mm diameter was elongated to 3 mm diameter and annealed at 600 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes, and then the wire was drawn Grow to 0.1mm diameter and annealed at 600 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes. After that, by performing the final wet continuous stretching, the inventors prepared 20-micrometer-thick bonding wires 1-27 (hereinafter referred to as invention wires) made of the Ag-Au-Pd alloy according to the present invention and used more than the original Invented bonding wires 28-36 made of Ag-Au-Pd alloy in the composition range (hereinafter referred to as comparison wires). These invention wires 1-27 and comparison wires 28-36 were placed on a wire bonder (trade name: Maxμm Ultra) manufactured by Kulicke & Soffa, and bonded to a semiconductor IC chip mounted in an atmosphere of purging nitrogen. On the 50 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com