Method for preparing basic magnesium carbonate and coproducing hydrochloric acid by mineralizing CO2 (carbon dioxide) via magnesium chloride
A technology of magnesium chloride and magnesium carbonate, applied in the direction of chlorine/hydrogen chloride, cells, electrolysis process, etc., can solve the problems of long process flow, long production cycle, large equipment investment, etc., and achieve the effect of simple process, short production cycle and large output
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
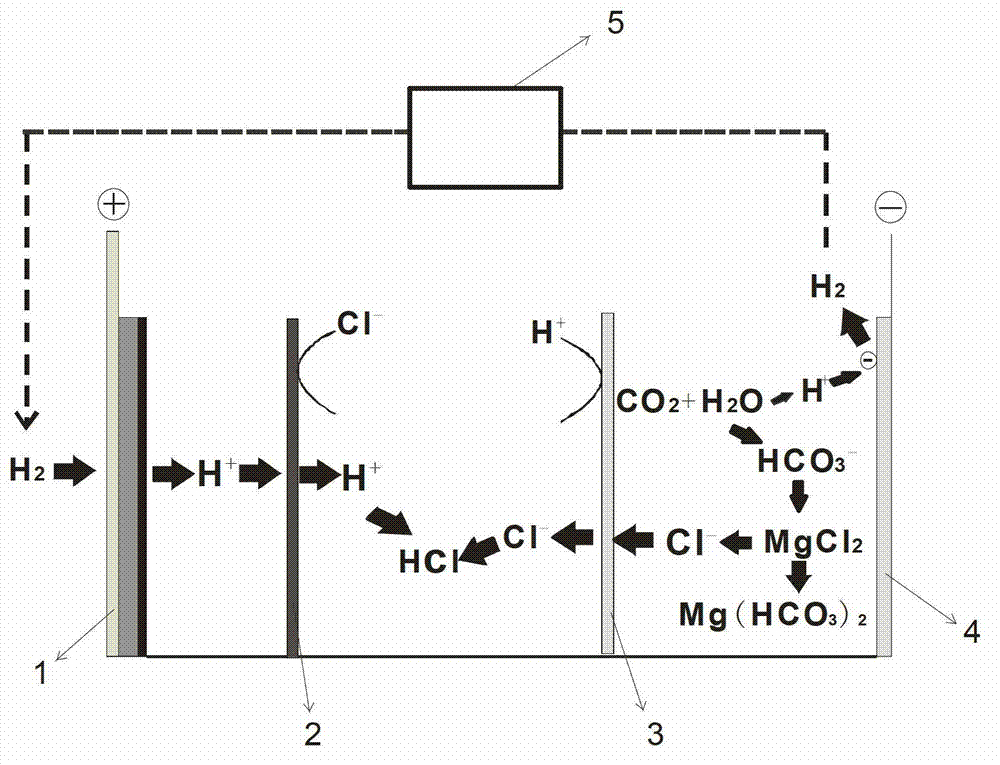
[0029] The mineralization process of the present embodiment is as attached figure 1 shown. The electrolytic cell is divided into three parts: a positive electrode area, an intermediate area and a negative electrode area by a cation exchange membrane 2 which only allows cations to pass through but can prevent anions from passing through, and an anion exchange membrane 3 which only allows anions to pass through but can prevent cations from passing through. area. Add 2mol / L of H 2 SO 4 solution to the positive electrode electrolyzer as the positive electrode electrolyte, add 1.2mol / L of MgCl 2 The solution is used as the negative electrode electrolyte in the negative electrode electrolyzer, and the hydrochloric acid of 0.4mol / L is added in the intermediate chamber. The gas diffusion electrode 1 is used as the positive electrode, and the platinum electrode 4 is used as the negative electrode. The CO bubbled in at the bottom of the negative electrode electrolyzer 2 The flow r...
Embodiment 2
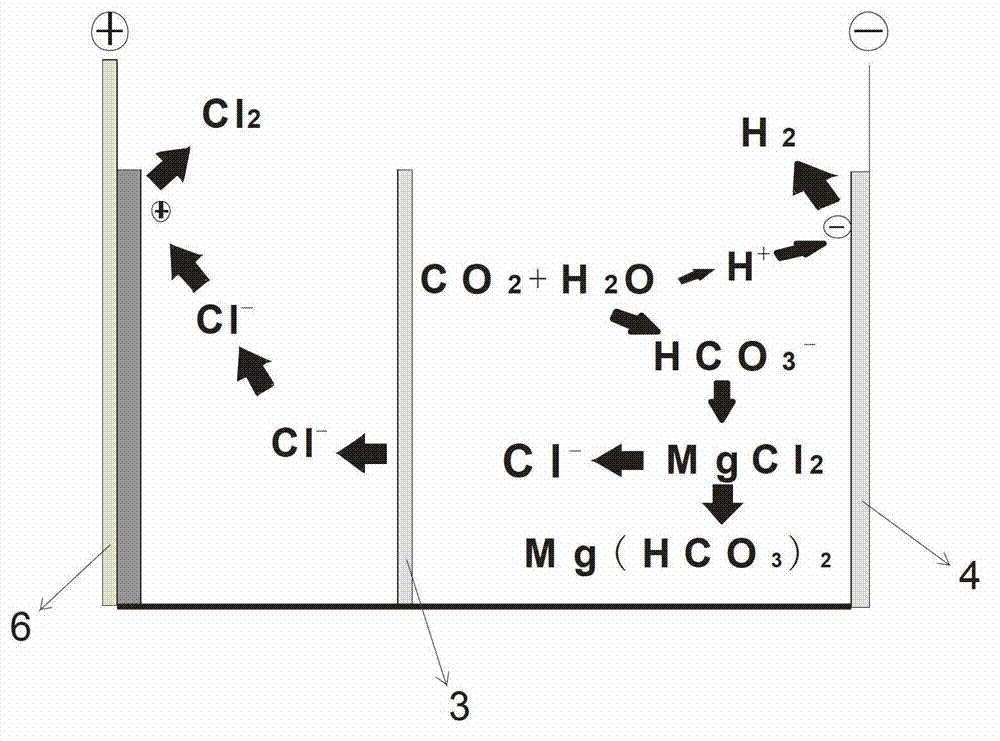
[0031] The mineralization process of the present embodiment is as attached figure 2 shown. The electrolytic cell is divided into positive and negative areas by an anion exchange membrane 3 that only allows anion to pass through but can prevent cation from passing through. Add 2 mol / L HCl solution to the positive electrode electrolytic cell as the positive electrode electrolyte, and add 2 mol / L MgCl2 solution to the negative electrode electrolytic cell as the negative electrode electrolyte. The metal titanium iridium electrode 6 is used as the positive electrode, and the metal nickel electrode 4 is used as the negative electrode. The CO bubbled in at the bottom of the negative electrode electrolyzer 2 The flow rate was 20 ml / min, and the electrolysis reaction was carried out at a voltage of 2.6 V for 1 h. Heat the liquid in the negative electrode electrolyzer to obtain 2 The mineralization product of basic magnesium carbonate solid. The current efficiency of producing bas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com