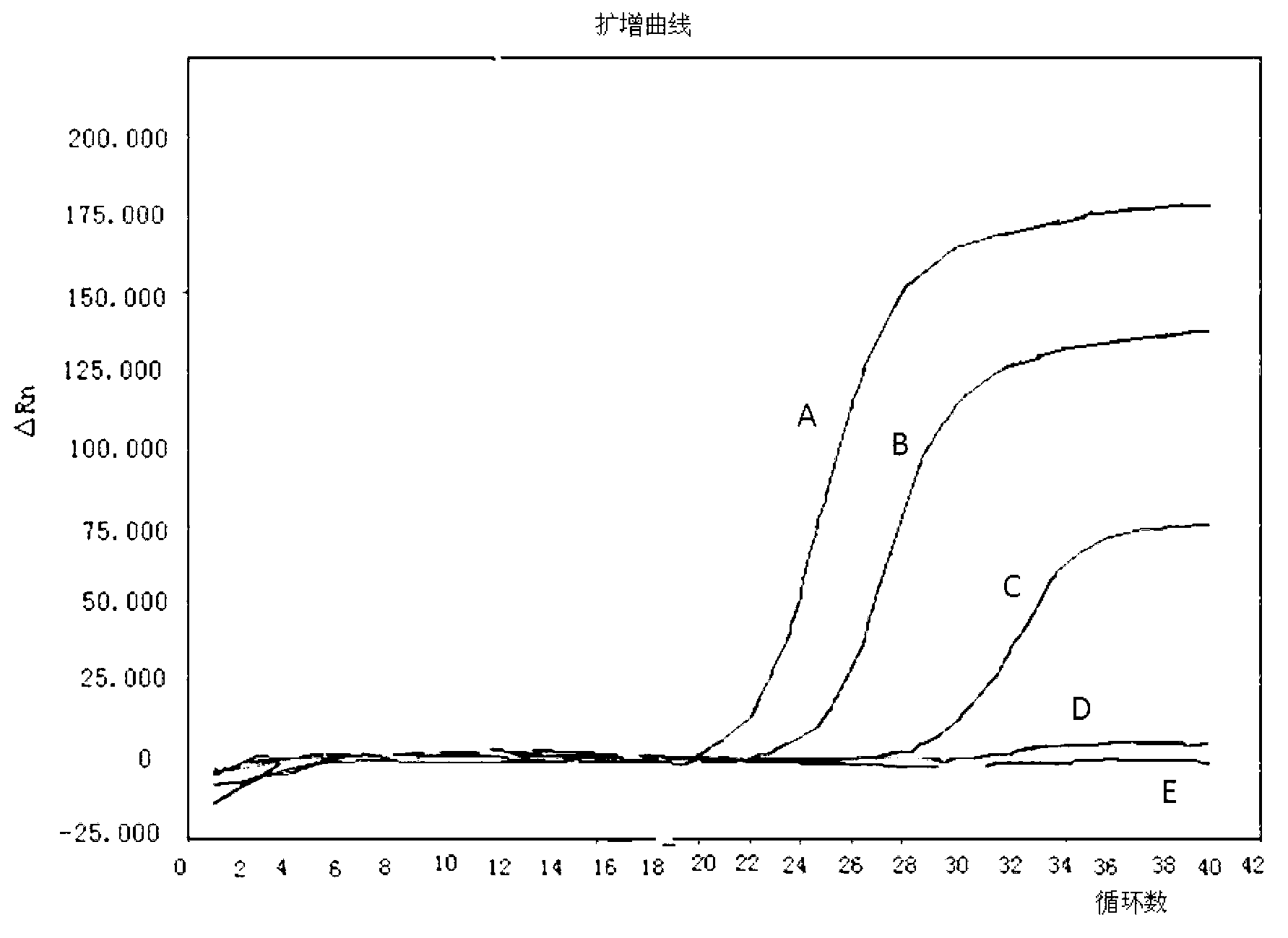
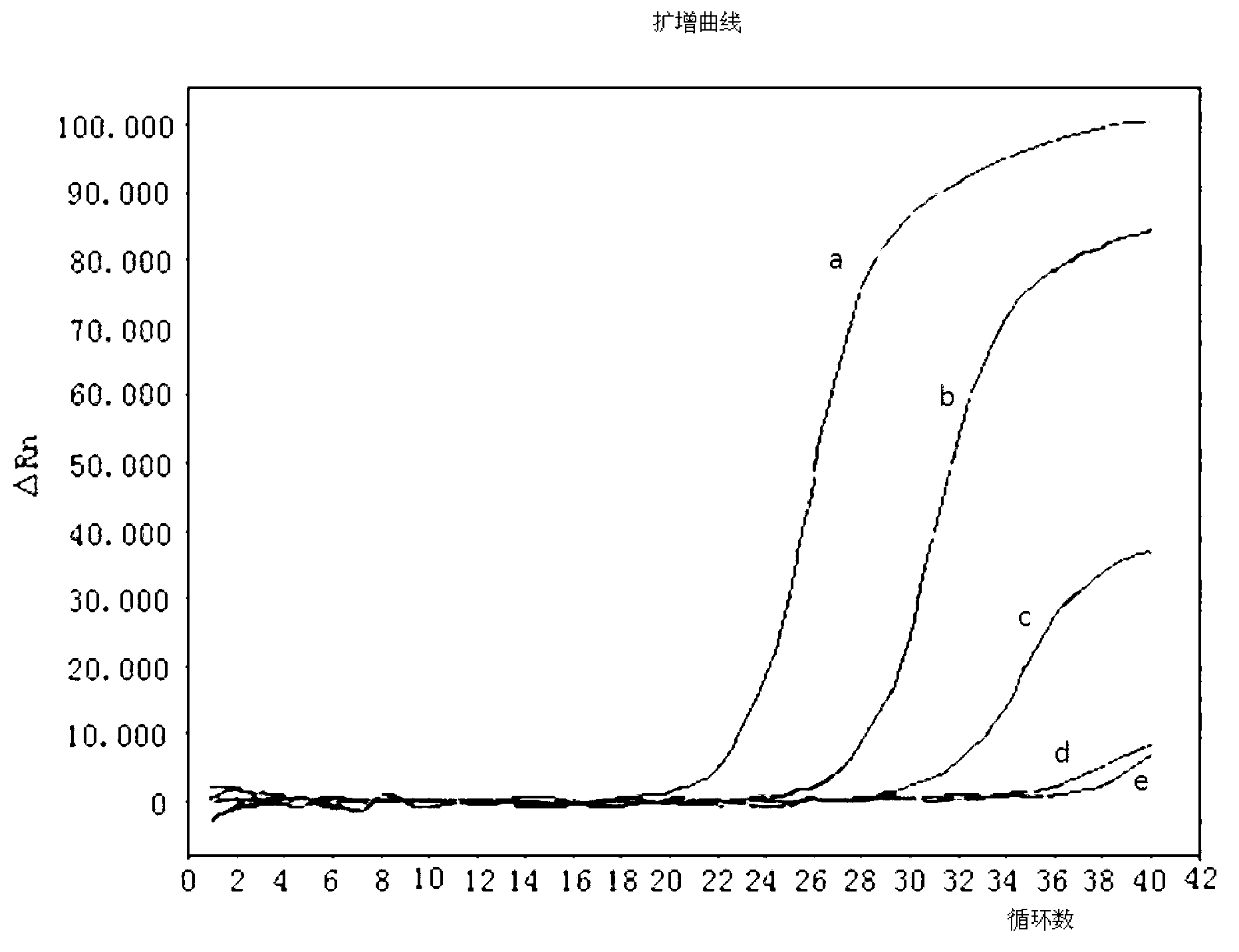
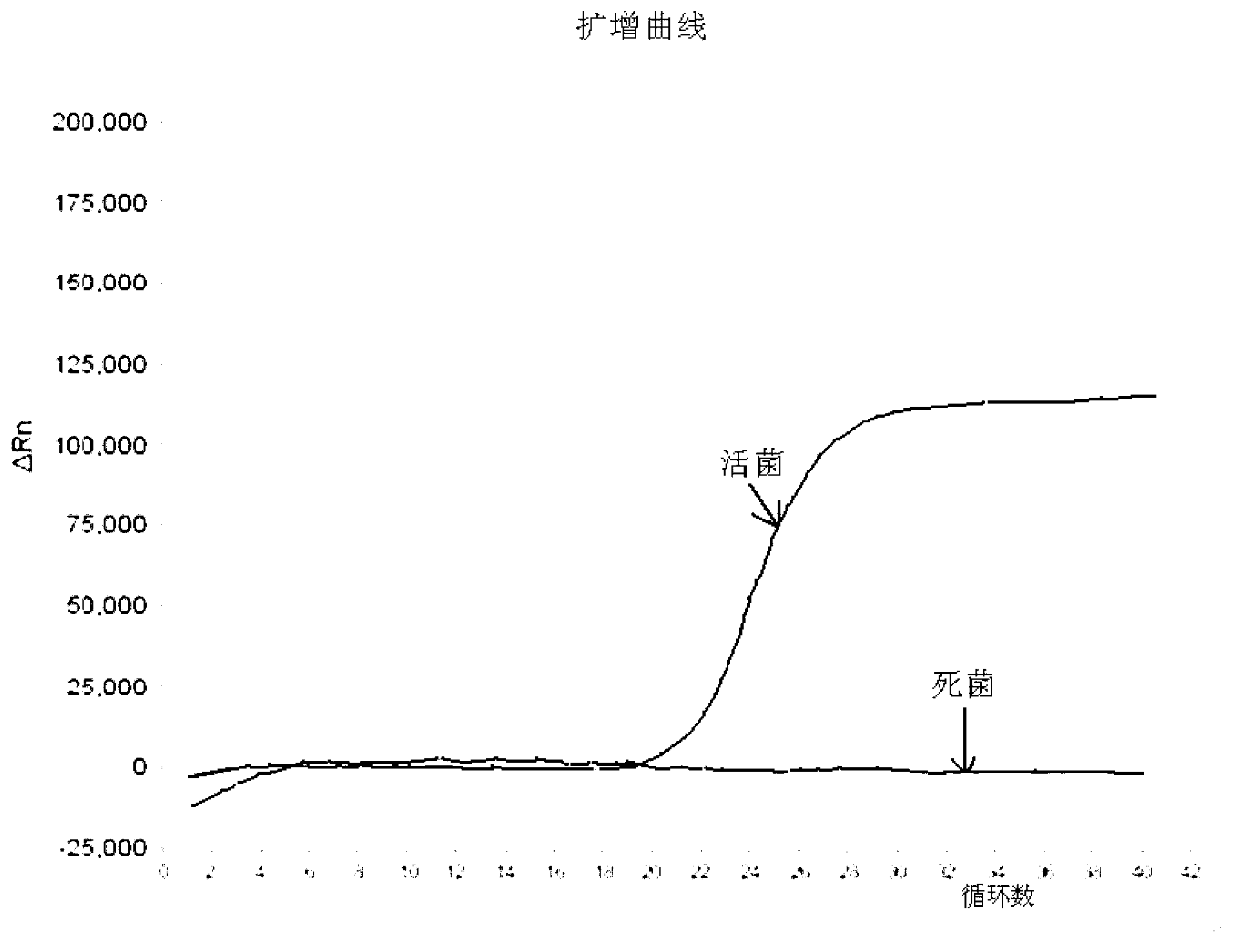
Method for detecting live enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli O157: H7
A technology of Escherichia coli and O157, applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial determination/inspection, etc. Viable bacteria and other problems, to achieve the effect of shortening the detection period, short detection period, and eliminating interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] A method for detecting enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli O157:H7 viable bacteria, carried out according to the following steps:
[0025] (1) Pretreatment of the sample to be tested: use an inoculation loop to dip the bacterial solution of the sample to be tested stored in a glycerol tube, streak on the LB solid medium, and incubate in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C for 24 hours. Pick a single colony and inoculate it in 50 mL of liquid LB medium, and cultivate it on a shaker at 37°C and 180 rpm until the logarithmic growth phase (OD600≈1.0). Adjust the OD600 value to 1.0 with sterile LB medium, in which the bacterial concentration is 10 9 CFU / mL. Draw 1mL of the bacterial culture solution in the logarithmic phase into a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, treat it in a boiling water bath for 50s, and immediately place it on ice to cool it, which is the heat-killed Escherichia coli. Through this treatment, the cell wall and cell membrane are damaged to varying degrees to ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A method for detecting enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli O157:H7 viable bacteria, carried out according to the following steps:
[0037] (1) Pretreatment of the sample to be tested: use an inoculation loop to dip the bacterial solution preserved in the glycerol tube, streak on the LB solid medium, and incubate in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C for 24 hours. Pick a single colony and inoculate it in 50 mL of liquid LB medium, and cultivate it on a shaker at 37°C and 180 rpm until the logarithmic growth phase (OD600≈1.0). Adjust the OD600 value to 1.0 with sterile LB medium, in which the bacterial concentration is 10 9 CFU / mL. Draw 1mL of the bacterial culture solution in the logarithmic phase into a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, treat it in a boiling water bath for 50s, and immediately place it on ice to cool it, which is the heat-killed Escherichia coli. Through this treatment, the cell wall and cell membrane are damaged to varying degrees to achieve the purpose of...
Embodiment 3
[0047] (1) Pretreatment of the sample to be tested: use an inoculation loop to dip the bacterial solution preserved in the glycerol tube, streak on the LB solid medium, and incubate in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C for 24 hours. Pick a single colony and inoculate it in 50 mL of liquid LB medium, and cultivate it on a shaker at 37°C and 180 rpm until the logarithmic growth phase (OD600≈1.0). Adjust the OD600 value to 1.0 with sterile LB medium, in which the bacterial concentration is 10 9 CFU / mL. Draw 1mL of the bacterial culture solution in the logarithmic phase into a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, treat it in a boiling water bath for 50s, and immediately place it on ice to cool it, which is the heat-killed Escherichia coli. Through this treatment, the cell wall and cell membrane are damaged to varying degrees to achieve the purpose of damaging the bacteria.
[0048] (2) For a concentration of 10 9 CFU / mL live bacteria or heat-treated dead bacteria samples were centrifu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com