Method for disposing waste water by using enhanced polyhydroxy ferrous compound
A polyhydroxy ferrous and waste water treatment technology, applied in the direction of reductive water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of complex process and slow speed, and achieve the effect of less dosage, convenient operation and flexible dosing method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
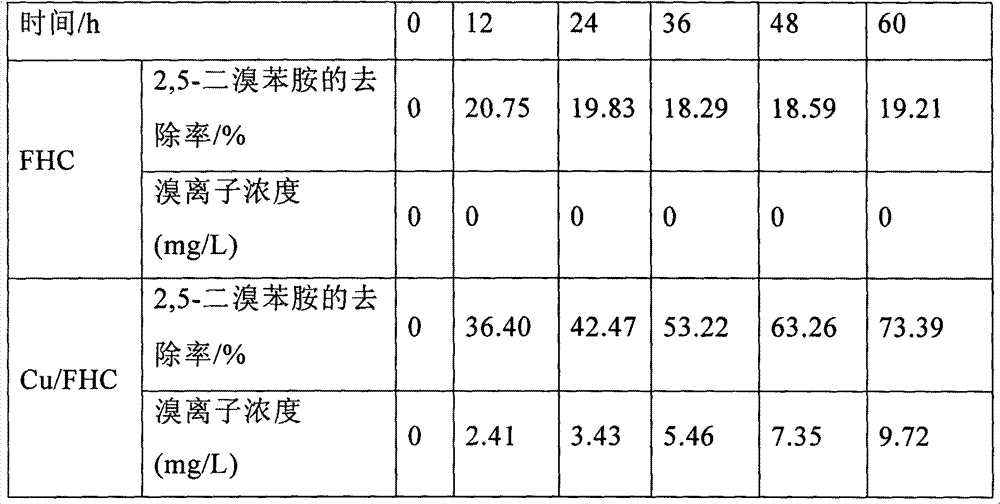
[0031] Preparation of Cu / FHC: use 0.75×10 -4 mol / L ascorbic acid solution, add the cetyltrimethylammonium bromide anaerobic aqueous solution 1ml of 3% mass concentration, then add the NaOH of 5mol / L dropwise to this solution, make [Fe (II)]: [OH -]=0.5, stir and mix evenly, add 0.8mol / L CuSO while stirring 4 , so that the mixed solution contains copper ions and iron ions with a molar ratio of Cu / Fe=0.14. The preparation method of ordinary FHC is to use anaerobic distilled water to configure 1mol / L FeSO 4 aqueous solution, and then add 5 mol / L NaOH dropwise to the solution to make [Fe(II)]:[OH-]=0.5, stir and mix evenly to form precipitate FHC. .
[0032] Take 250mL of 2,5-dibromoaniline stock solution with a concentration of 50mg / L and add it to a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask with a stopper, add 1.6g / L of Cu / FHC and FHC respectively, stir, and regularly take samples to analyze 2,5- Dibromoaniline reduction product.
[0033] Table 1 shows that when only FHC is added, the removal...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Preparation and use of Cu / FHC: get six parts of 250mL concentration and add 2,5-dibromoaniline stock solution of 50mg / L into the 250mL Erlenmeyer flask with stopper respectively, add 1g / L of FHC (according to Example 1) Cu / FHC preparation method by preparing ascorbic acid solution and adding dispersant, but without adding Cu 2+ ), add a certain amount of 1mol / L CuCl to the bottle while stirring 2 Make the molar ratio of Cu / Fe up to 3.5×10 -3 ~0.3, after 60 hours of reaction, samples were taken to analyze the reduction products of 2,5-dibromoaniline. Table 2 shows that with the increase of Cu(II) dosage, the removal rate of 2,5-dibromoaniline and the bromide ion concentration gradually increase.
[0038] Table 2 Differences in the removal of 2,5-dibromoaniline under different Cu(II) dosage conditions
[0039] Molar ratio of Cu / Fe
Embodiment 3
[0041] Six parts of 250mL concentration is the 2,5-dibromoaniline stock solution of 50mg / L to adjust pH=13, add the ferrous sulfate of 0,0.5,1,1.6,3.2,5g / L respectively (in the iron content in the solution, hereinafter the same), and add 0.5ml of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide anaerobic aqueous solution of 3% mass concentration, add a certain amount of 0.1mol / L Cu(NO 3 ) 2 Make Cu / Fe=0.03, and take a sample to analyze the reduction product of 2,5-dibromoaniline after 60 hours of reaction. Table 3 shows that when the dosage of FHC is greater than or equal to 1.6g / L, the promotion effect of FHC on the reduction of pollutants is weak.
[0042] Table 3 Effects of different FCH dosages on the removal of 2,5-dibromoaniline
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com