Method for simultaneously detecting AZA1, AZA2 and AZA3 in bivalve aquatic products
A technology for aquatic products and bivalves, which is applied in the field of determination of various protopolyformic acid shellfish toxins in bivalve aquatic products, and can solve the problem of time-consuming, inability to determine the specific components of various toxins, and sample processing operations cumbersome and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving the efficiency of detection and analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
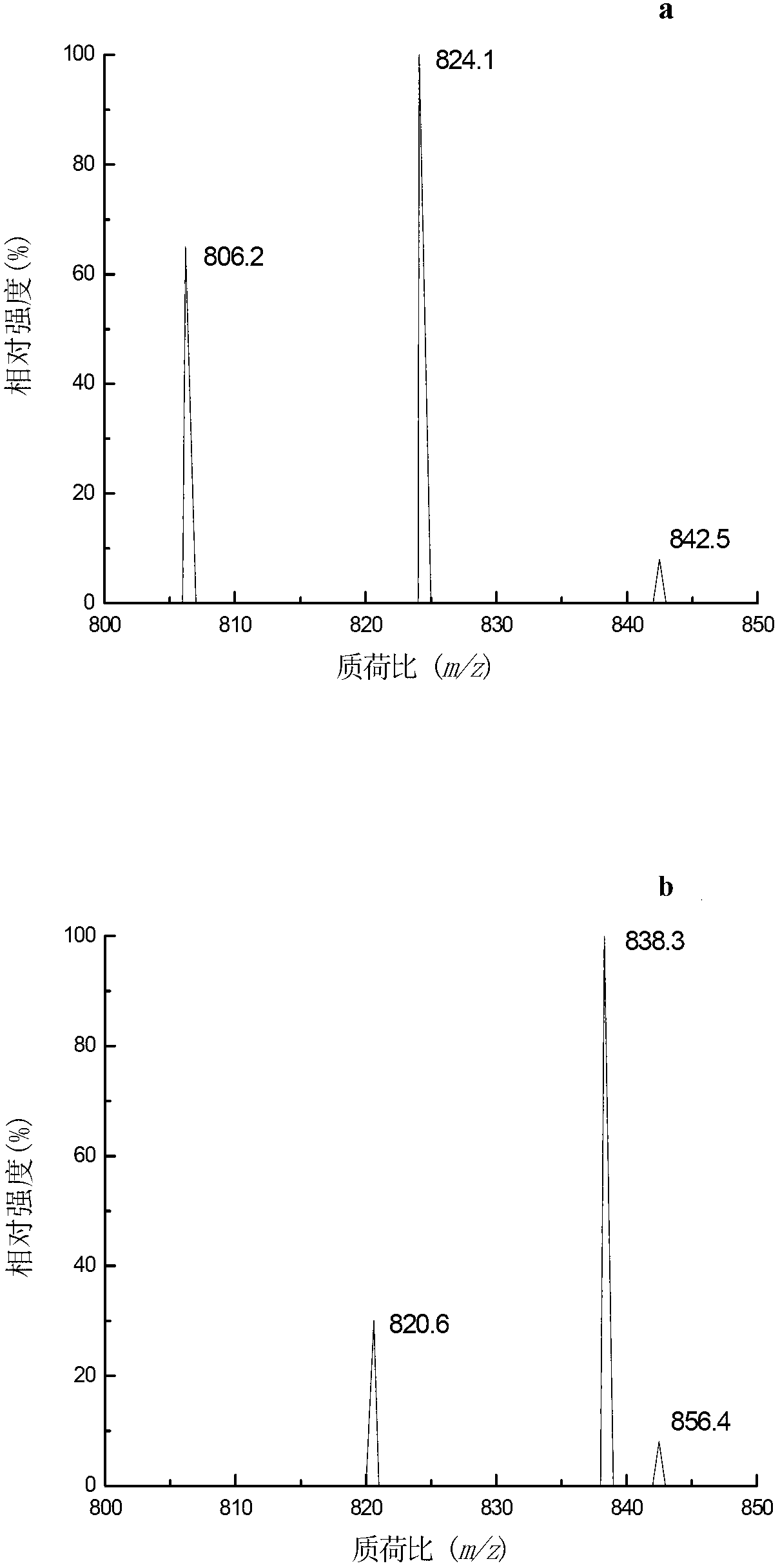
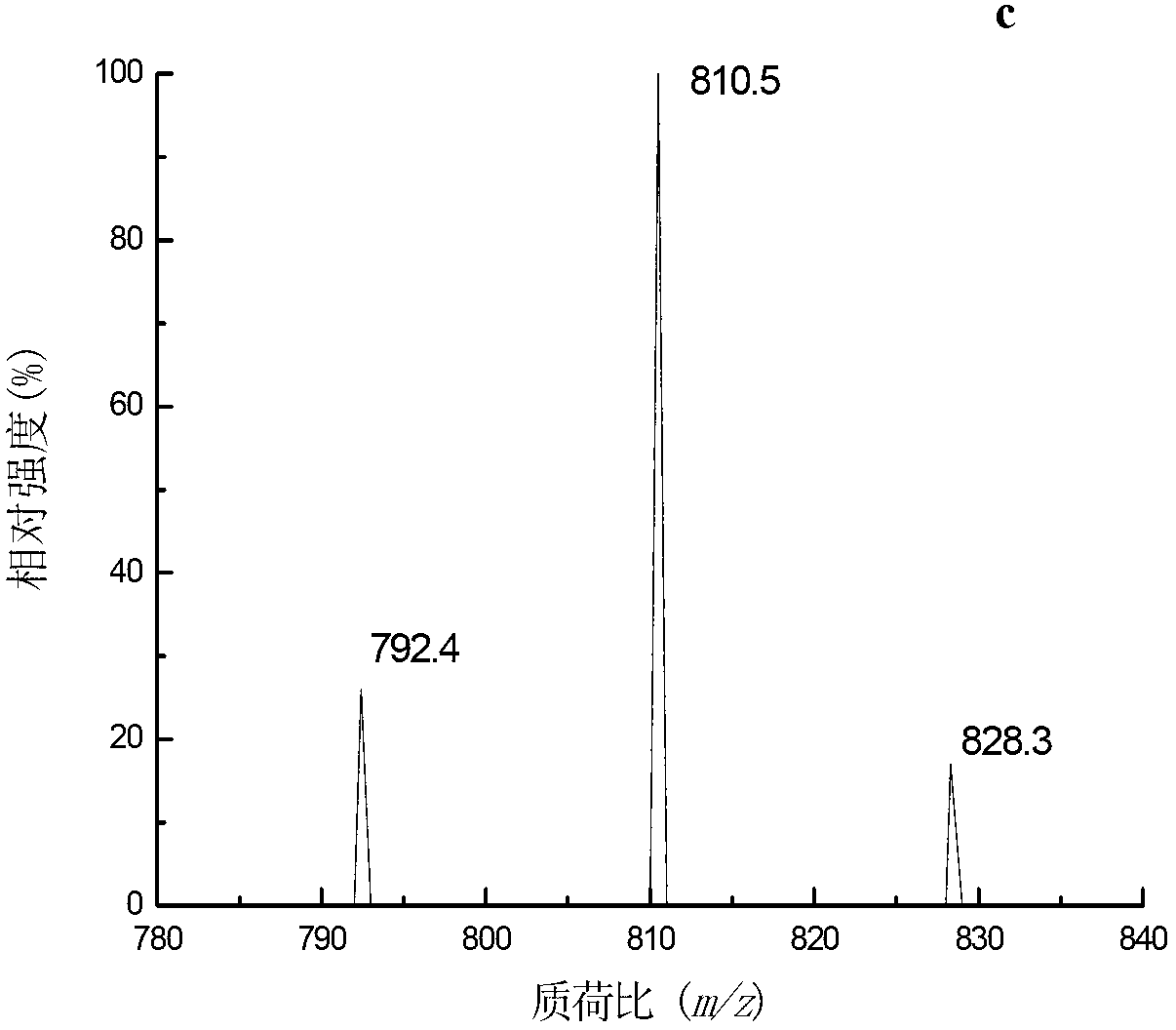
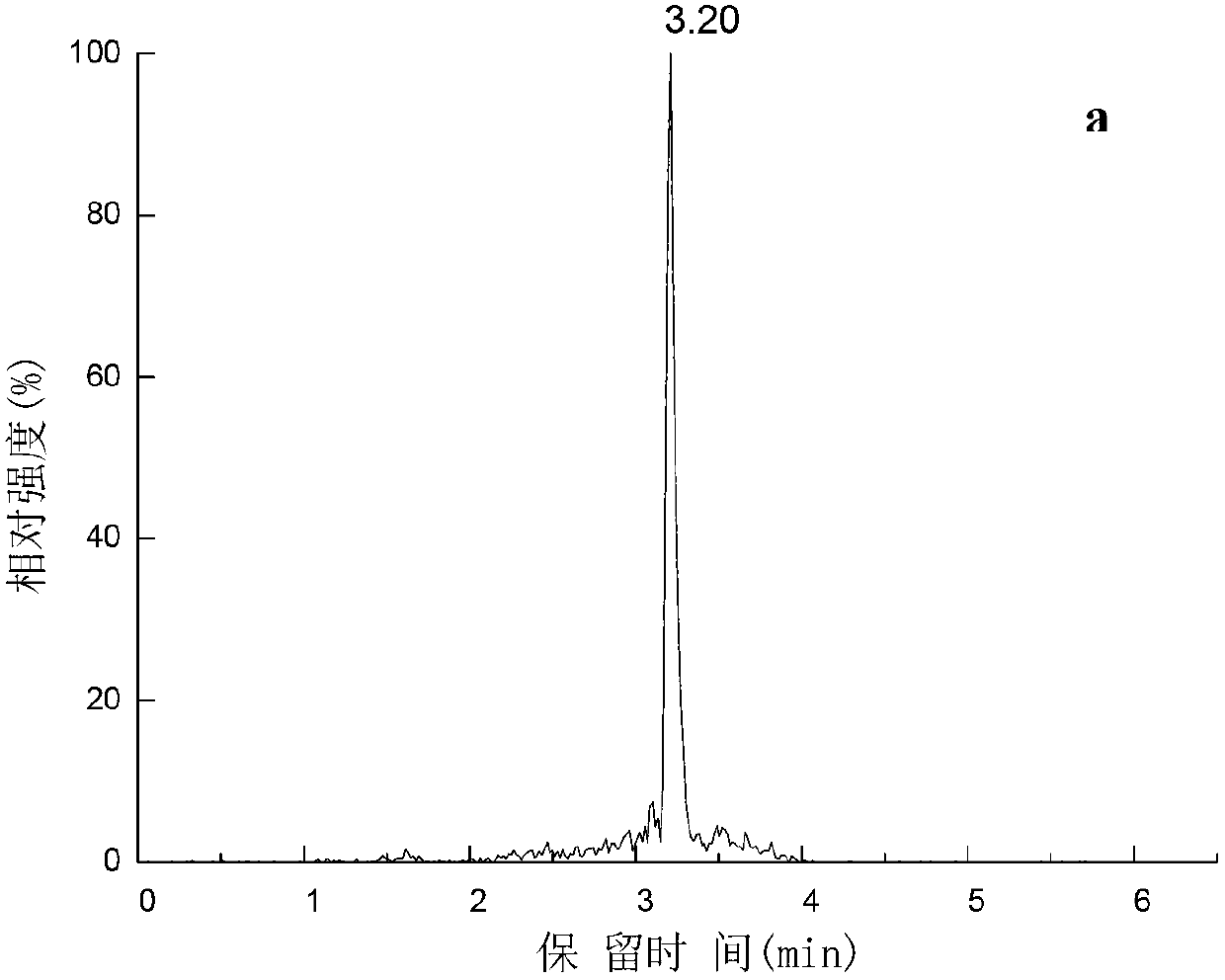
[0049] Extraction: Take scallops, oysters, and variegated clams, which are representative bivalve aquatic products, as the research objects. Weigh 100g of the edible parts of the three samples, wash and homogenize at 9500r / min for 5min for sample preparation. Weigh 2 g of the homogeneous sample to be tested (accurate to 0.01 g) and place it in a 50 mL plastic centrifuge tube with a stopper, add 8 mL of 80% (V / V) methanol aqueous solution, vortex extract for 2 min, and extract at 8000 r / min at 4 °C Centrifuge for 5 minutes, transfer the supernatant to another centrifuge tube, add 8 mL of 80% (V / V) methanol aqueous solution to the residue and re-extract once, combine the supernatant; add 5 mL of n-hexane to the supernatant, and vortex at 1500 r / min Extract for 1 min, remove the n-hexane layer after static layering, and obtain extract I; add 15 mL of chloroform to extract I, vortex extract at 1500 r / min for 2 min, centrifuge at 8000 r / min at 4 °C for 2 min, remove the supernatant,...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Embodiment 2. Application to actual sample detection
[0066] Using the detection method established in Example 1, 50 actual samples of bivalve aquatic products sold in the market were tested, and no AZAs shellfish toxins were detected. It is reported that AZA1 has been detected in shellfish samples in Dalian sea area with a content of 99.6pg / g, but a single AZA1 measurement result cannot be used as a basis for judging whether AZAs in bivalve aquatic products exceed the standard. According to the European Union's detection requirement that the total amount of AZAs does not exceed 160 μg / kg, the present invention does not pursue a lower detection limit too much, and can fully meet the requirements of AZAs in bivalve aquatic products under the detection limit of LOQ=1.5 μg / kg. The need for routine testing and monitoring of shellfish toxins.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| correlation coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com