Turbine with moving blades with pits at blade tops
A technology of moving blades and turbines, which is applied to the supporting elements of blades, engine elements, machines/engines, etc., which can solve the problem of increasing the heat transfer coefficient of the local area of the blade tip, increasing the unevenness of heat transfer at the blade tip, and ineffective control of gap leakage. It can achieve the effect of good applicability of attack angle change, reducing gap leakage and reducing rigidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
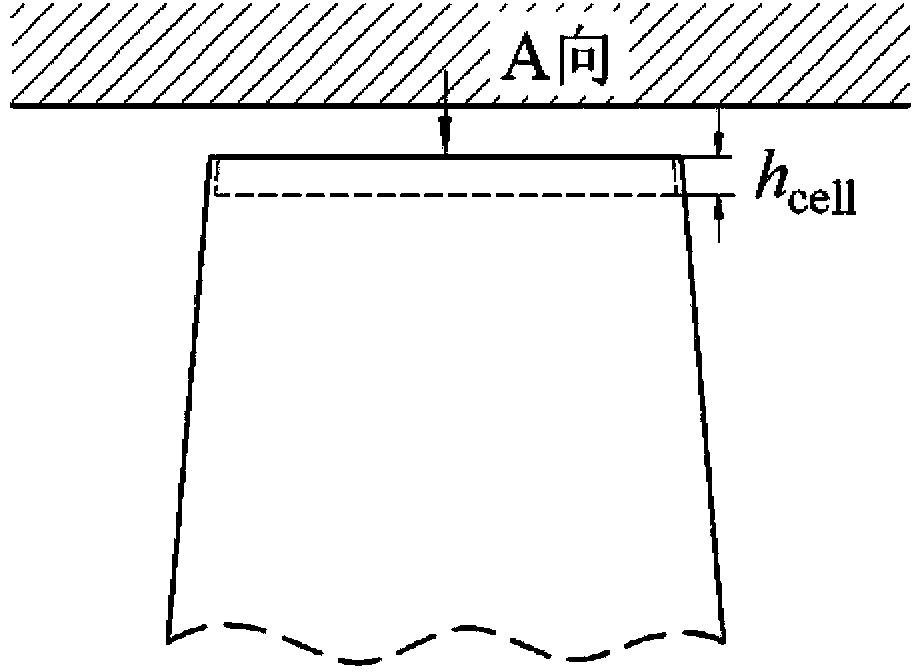
[0021] With reference to Figures 2 to 3, to manufacture the turbine blades with holes on the tip of the present invention, the gas turbine blades are first designed by traditional design methods. For a given blade load distribution and operating conditions, the specific structural parameters of the tip honeycomb (the honeycomb core size d cell And honeycomb depth h cell ) Can be obtained by simulation or experiment with existing computational fluid dynamics software, and then the honeycomb structure as shown in Figure 3(a) is processed on the tip surface of the blade. The ratio of the honeycomb core cell size to the maximum thickness of the blade tip is 0.1-0.5, the ratio of the honeycomb depth to the maximum thickness of the blade tip is 0.1-0.5, and the honeycomb depth is not less than the size of the honeycomb core cell. Those skilled in the art should understand that for turbine blades for specific applications, the honeycomb structure parameters of the blade tip are selecte...
Embodiment approach 2
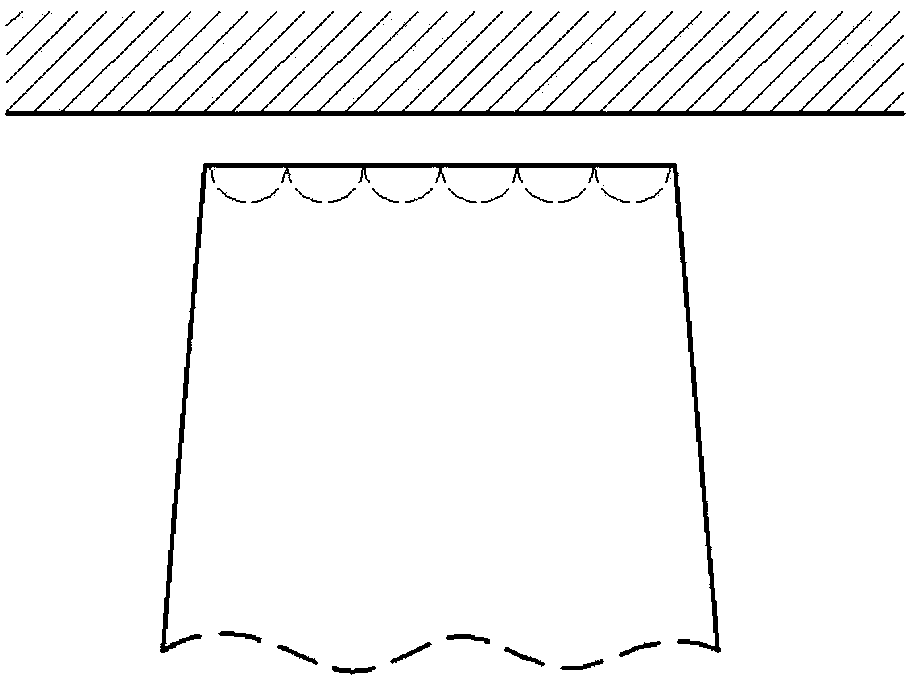
[0026] Such as Figure 3c , Figure 3d As shown, the shape of the tip hole is a ball socket, and the ratio of the diameter of the ball socket to the maximum thickness of the tip is 0.1-0.5, and the others are the same as in Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com