Homogenization heat treatment process of large-size magnesium alloy ingot
A technology for homogenizing heat treatment and magnesium alloys, applied in the field of magnesium alloy material preparation, can solve problems such as difficulty in handling large-size magnesium alloy ingots, and achieve the effects of facilitating later deformation and heat treatment, avoiding local over-burning, and being uniformly heated.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Charge the Mg-Al-Zn magnesium alloy semi-continuous ingot cold furnace with a diameter of Φ300mm and a height of 650mm, and rapidly raise the temperature from room temperature to 320°C at a rate of 30°C / min for 10 minutes. After reaching 320°C, The heating rate was 12°C / h, and the temperature was raised for 7.5 hours. After reaching 410°C, the temperature was kept for 20 hours, and then the furnace was blown to cool with a cooling rate of 2°C / min to obtain a finished product.
Embodiment 2
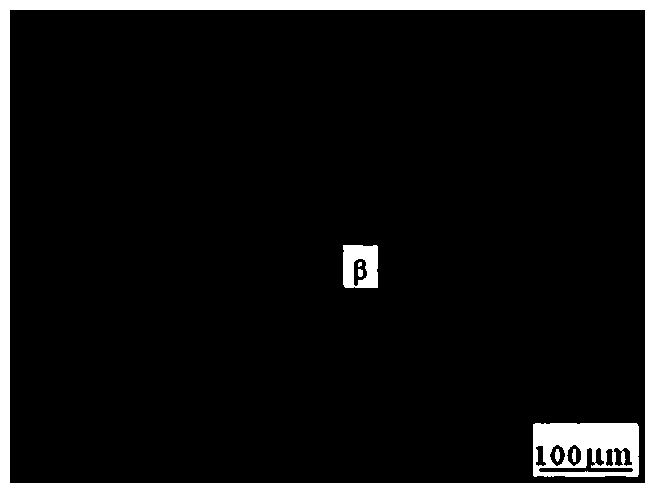
[0028] Charge a Mg-Al-Zn magnesium alloy semi-continuous ingot cold furnace with a diameter of Φ350mm and a height of 650mm, and rapidly raise the temperature from room temperature to 350°C at a rate of 15°C / min for 23 minutes. After reaching 350°C, The heating rate was 17.5°C / h and the temperature was raised for 4 hours. After reaching 420°C, the temperature was kept for 25 hours, and then cooled by blasting with the furnace at a cooling rate of 7°C / min; the finished product was obtained. The metallographic structure of the finished product is as image 3 shown by image 3 It can be seen that after homogenization treatment, the as-cast structure of the alloy basically disappears, and clear grain boundaries appear.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Charge the Mg-Al-Zn magnesium alloy semi-continuous ingot cold furnace with a diameter of Φ350mm and a height of 700mm. Rapidly raise the temperature from room temperature to 350°C at a rate of 20°C / min for 15 minutes. After reaching 350°C, The heating rate was 25°C / h, and the temperature was raised for 3.2 hours. After reaching 430°C, the temperature was kept for 30 hours, and then cooled by blasting with the furnace, and the cooling rate was 9°C / min; the finished product was obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com