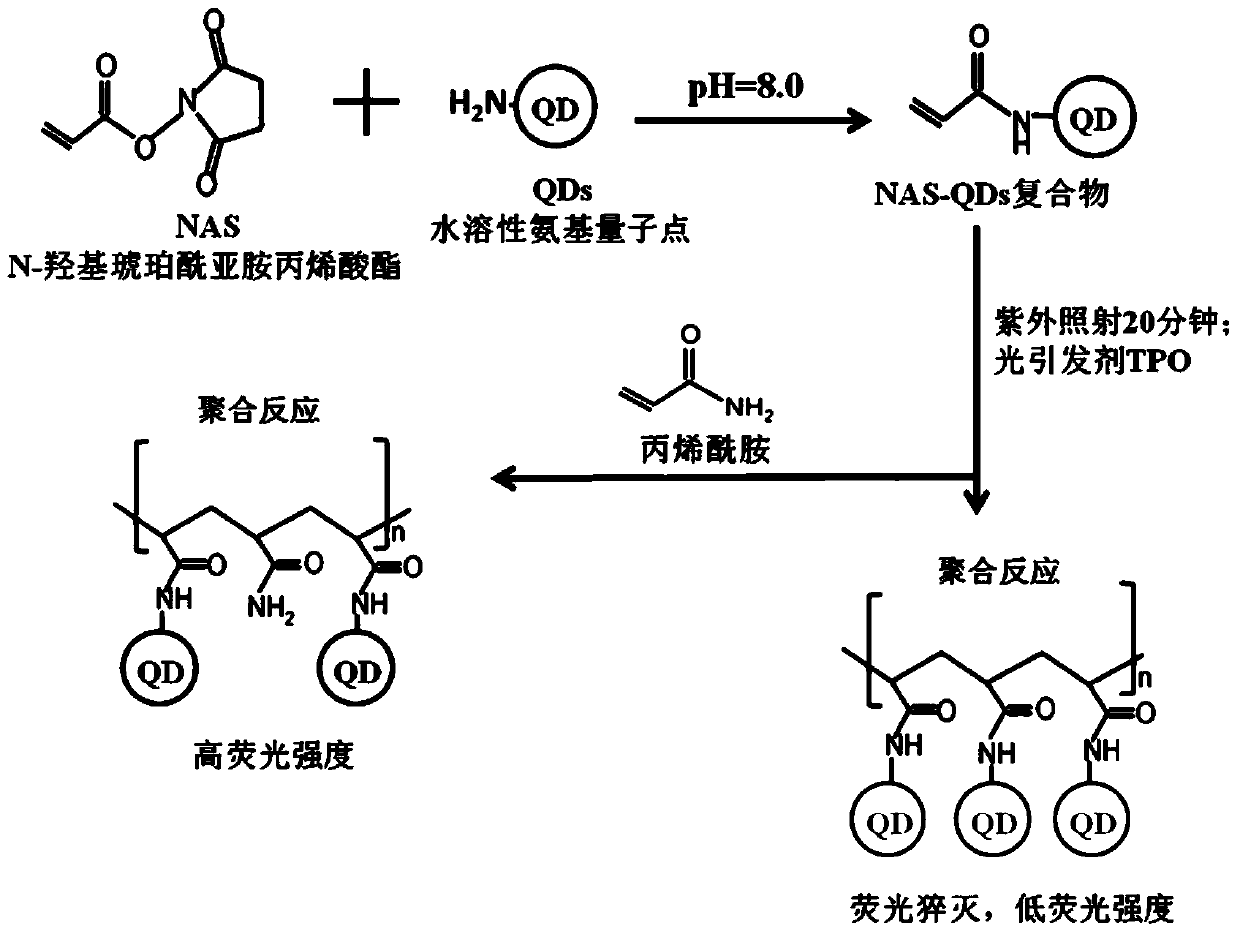
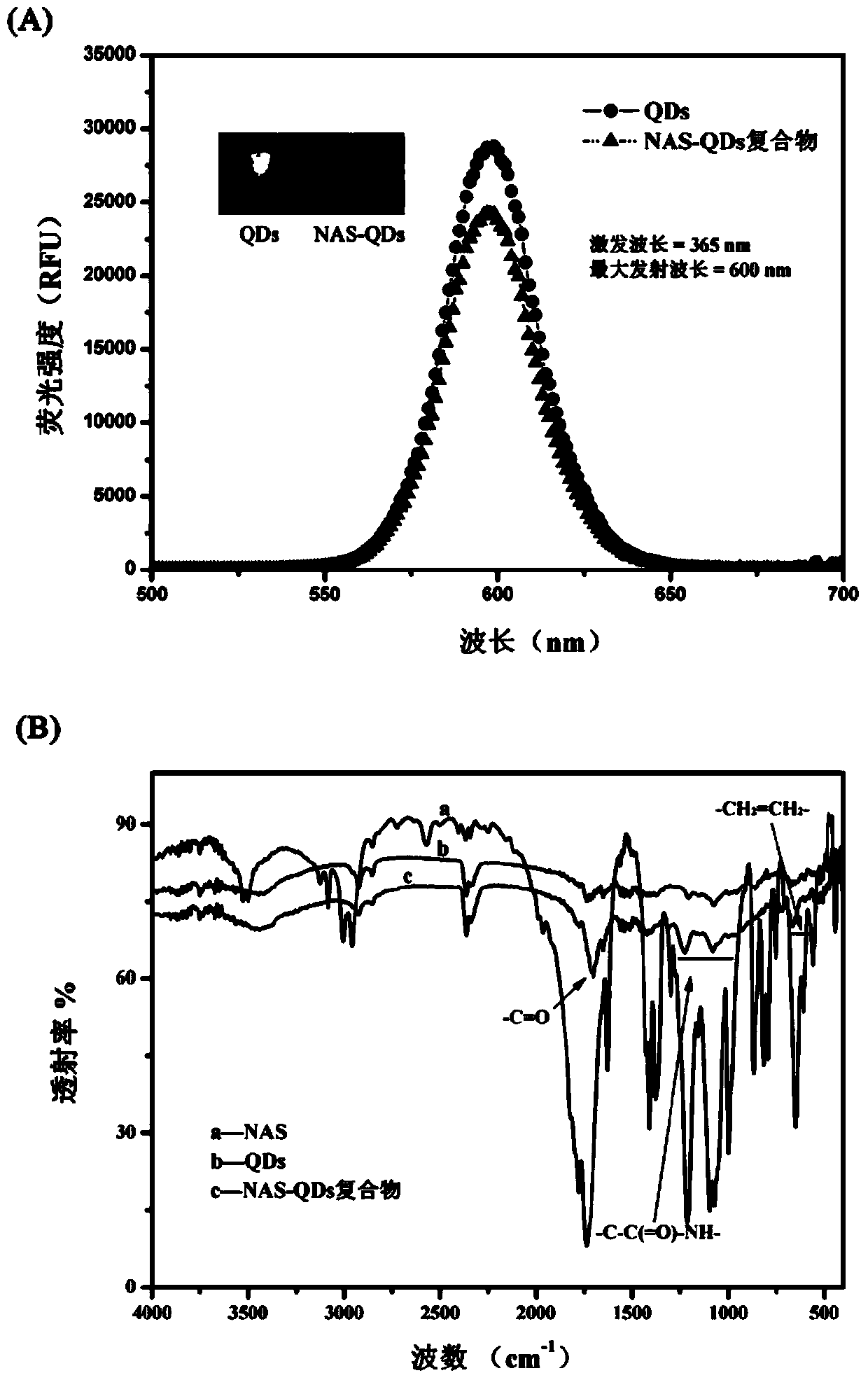
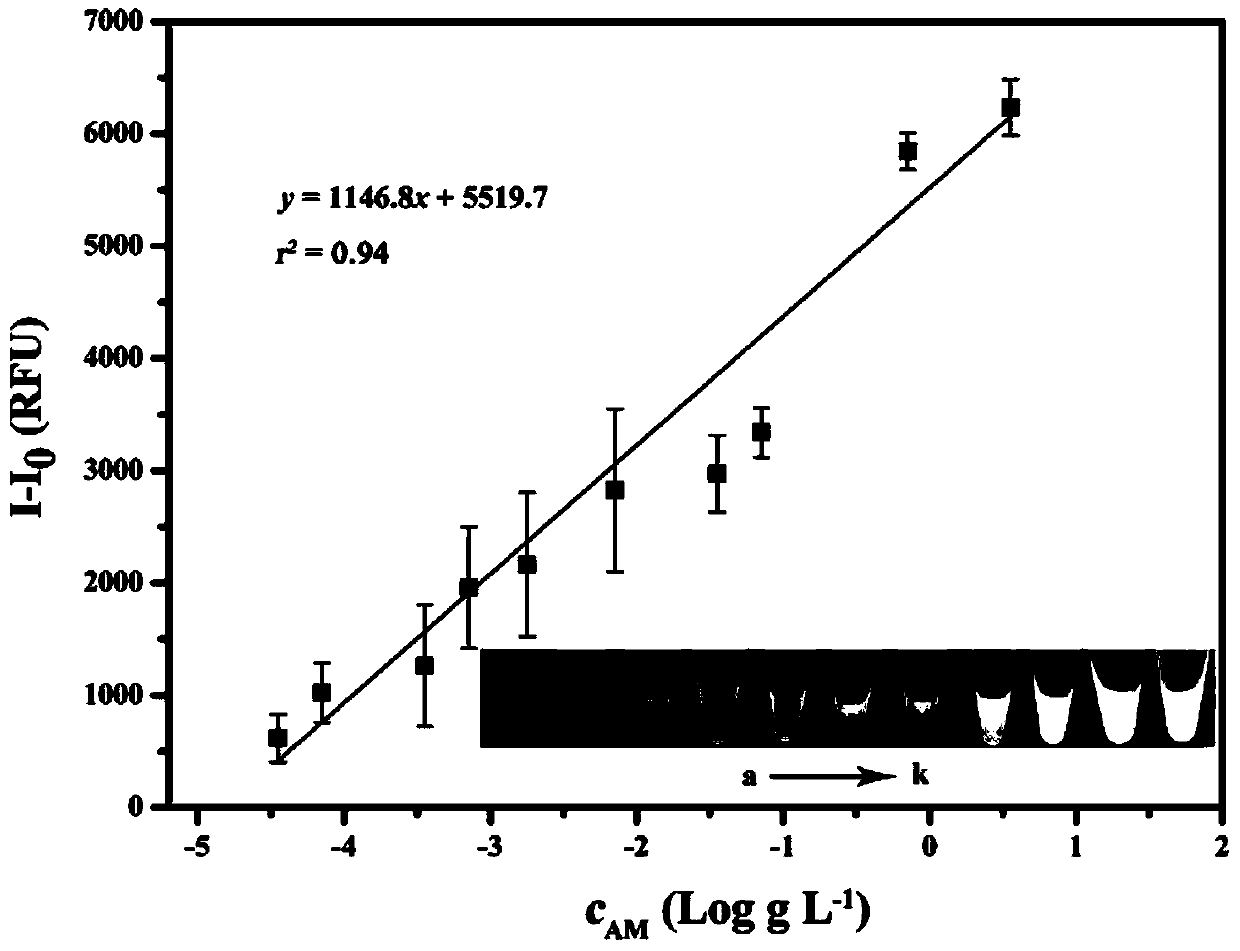
Method for detecting acrylamide in thermal processed foods by using fluorescence method based on quantum dots
A technology of acrylamide and quantum dots, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of poor accuracy and achieve the effects of low detection cost, short detection time, and novel principles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Embodiment 1. A method for detecting acrylamide in heat-processed food based on quantum dot fluorescence method, using commercially available potato chips as the heat-processed food to be tested, the following steps are carried out in sequence:
[0070] 1) Pretreatment of potato chip samples:
[0071] The potato chips were fully pulverized into powder by a pulverizer, and stored at -20°C for later use. Weigh 1±0.1g potato chip powder into a 50mL centrifuge tube, add 10mL0.3% (volume%) formic acid solution, vortex and mix for 1min, centrifuge at 10000rpm, 4℃ for 10min, and divide into 3 layers after centrifugation: White grease layer at the top, supernatant at the middle layer, and sediment at the bottom.
[0072] Discard the white grease layer and take the supernatant. Repeat the above extraction step once (that is, repeat the above process with the precipitate instead of potato chip powder), and combine the supernatant obtained twice (about 20ml in total) as the samp...
Embodiment 2
[0113] Embodiment 2, change the potato chips in embodiment 1 into another brand of potato chip samples, and all the other are equal to embodiment 1.
[0114] The linear equation is y=1.8633x+604.95(r 2 =0.96), let y=0, the absolute value of x is the content of acrylamide in the sample to be tested, 324.67μg L -1 , therefore, the content of acrylamide in potato chips is 1.082mg kg -1 .
[0115] Verification test: the potato chips sample described in Example 2 was detected by LC-MS / MS method, and the acrylamide content was 1.143 mg kg -1 , is basically consistent with the result obtained in Example 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com