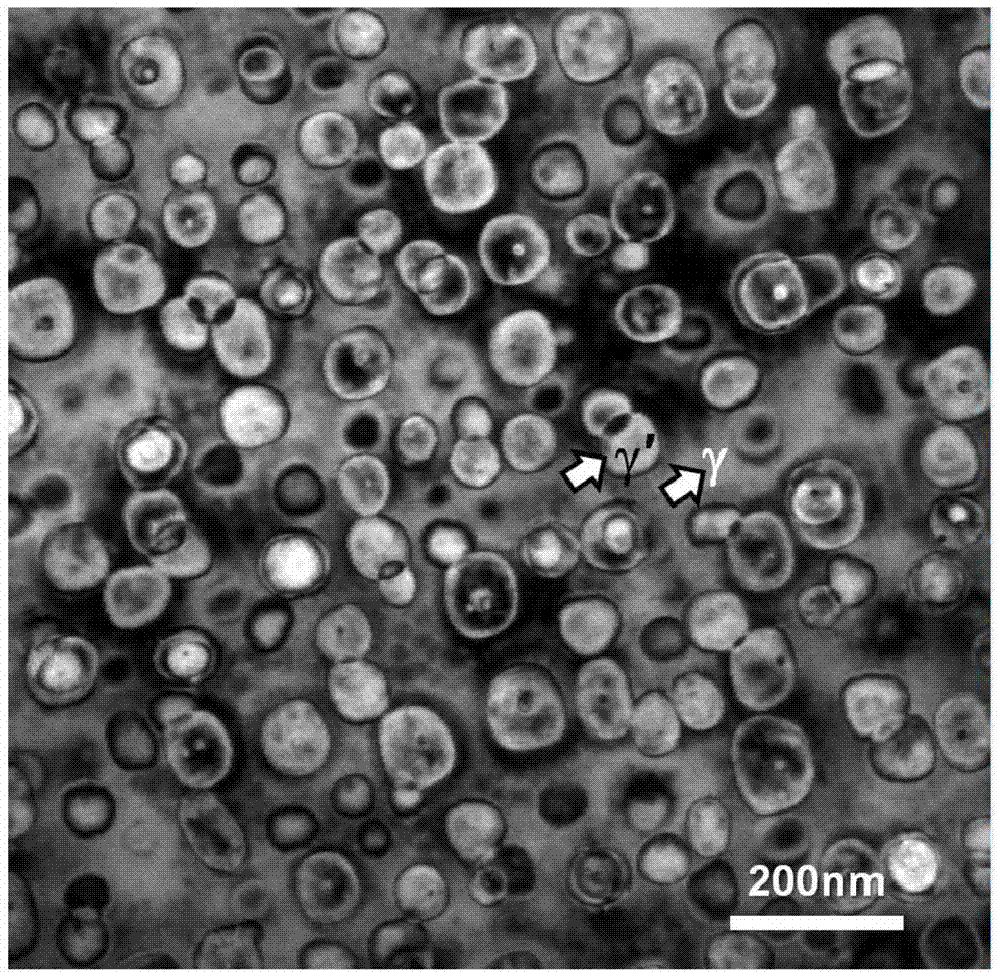
Low-expansion antioxidative Ni-Fe-Cr-based high temperature alloy and preparation method thereof
A ni-fe-cr, superalloy technology, applied in the field of metal structural materials, can solve the problems of poor oxidation resistance and hot corrosion resistance, low high temperature strength, poor hot formability, etc., to improve hot workability, improve high temperature strength, cost reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-6
[0039] 1. The composition of the alloy
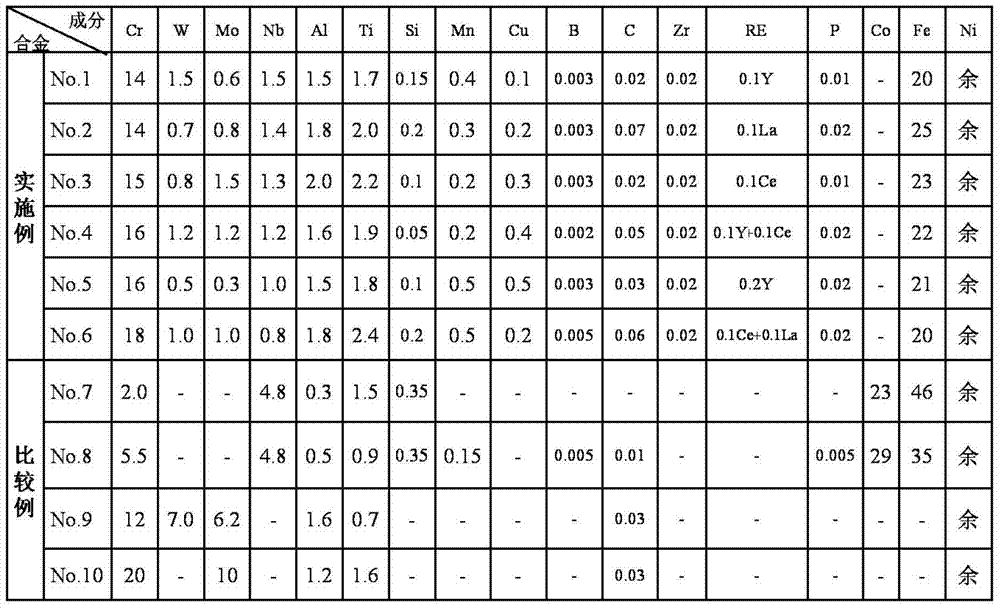
[0040] Table 1 provided the chemical composition of Examples 1-6 of the present invention. As comparative materials, No.7 (existing Fe-based low-expansion alloy In929C), No.8 (existing high-temperature low-expansion Ni-Fe-Cr-based alloy Thermo-Span), No.9 (existing High-temperature and low-expansion Ni-Mo-W-based alloy LTES700R) and No.10 (existing high-temperature and low-expansion Ni-Mo-based alloy USC141).
[0041] Table 1 The chemical composition (weight %) of the embodiment of the present invention and comparative example
[0042]
[0043] 2. Alloy melting and thermal deformation
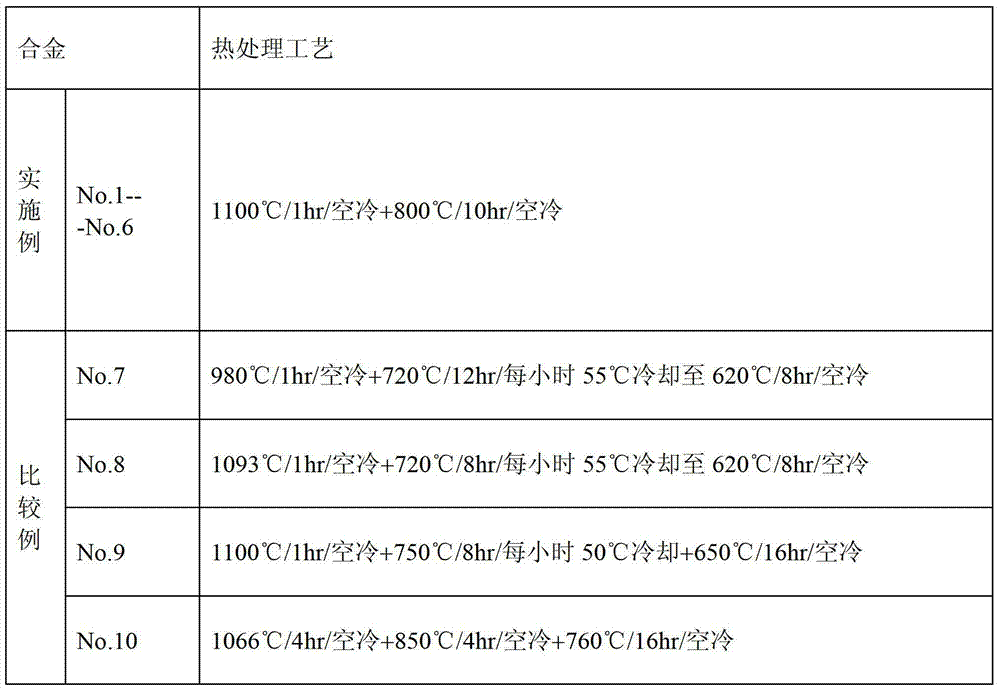
[0044] Each element of each embodiment in Table 1 was added into a vacuum induction furnace for melting, and cast into a master alloy ingot. Homogenize the master alloy ingot at 1150-1200°C for 20-40 hours. The homogenized master alloy ingot is subjected to hot deformation (hot rolling or hot extrusion) at 1000-1150°C, with a maximum deformation o...
Embodiment 7
[0057] Step 1: By weight percentage, 22% Fe, 16% Cr, 1.8% Al, 1.8% Ti, 1.2% Nb, 1.0% Mo, 1.5% W, 0.05% Si, 0.1% Mn, 0.2% of Cu, 0.05% of C, 0.005% of B, 0.01% of Zr, 0.01% of P, 0.1% of Y, and the balance of Ni is added to the vacuum induction furnace for melting and casting into master alloy ingots;
[0058] Step 2: Homogenize the master alloy ingot at 1180°C for 20 hours;
[0059] Step 3: hot deforming the homogenized master alloy ingot at 1130°C;
[0060] Step 4: The hot-deformed alloy is subjected to solution treatment at 1150° C. for 1 hour, then air-cooled, and then treated at 850° C. for 24 hours, and then air-cooled to obtain a low thermal expansion and oxidation-resistant superalloy. The coefficient of thermal expansion of the alloy between 20°C and 700°C is 14.9×10 -6 / °C.
Embodiment 8
[0062] Step 1: By weight percentage, 20% Fe, 17% Cr, 2.0% Al, 2.5% Ti, 0.5% Nb, 0.3% Mo, 1.5% W, 0.3% Si, 0.7% Mn, 0.3% of Cu, 0.04% of C, 0.008% of B, 0.005% of Zr, 0.005% of P, 0.2% of Ce, and the balance of Ni is added to the vacuum induction furnace for melting and casting into master alloy ingots;
[0063] Step 2: Homogenize the master alloy ingot at 1150°C for 40 hours;
[0064] Step 3: hot deforming the homogenized master alloy ingot at 1100°C;
[0065] Step 4: The hot-deformed alloy is subjected to solution treatment at 1050° C. for 4 hours, then air-cooled, and then treated at 750° C. for 24 hours, and then air-cooled to obtain a low thermal expansion and oxidation-resistant superalloy. The coefficient of thermal expansion of the alloy between 20°C and 700°C is 14.8×10 -6 / °C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal expansion coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal expansion coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com