Method for sintering neodymium iron boron magnets
A sintering method and NdFeB technology, applied in the manufacturing of magnetic objects, magnetic materials, inductors/transformers/magnets, etc., can solve the problems of rising machining costs, dimensional deformation, green body oxidation, etc., and achieve convenient machining and reduce The effect of machining allowance and reduction of sintered deformation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] In this embodiment, the specific content of each of the aforementioned steps is:
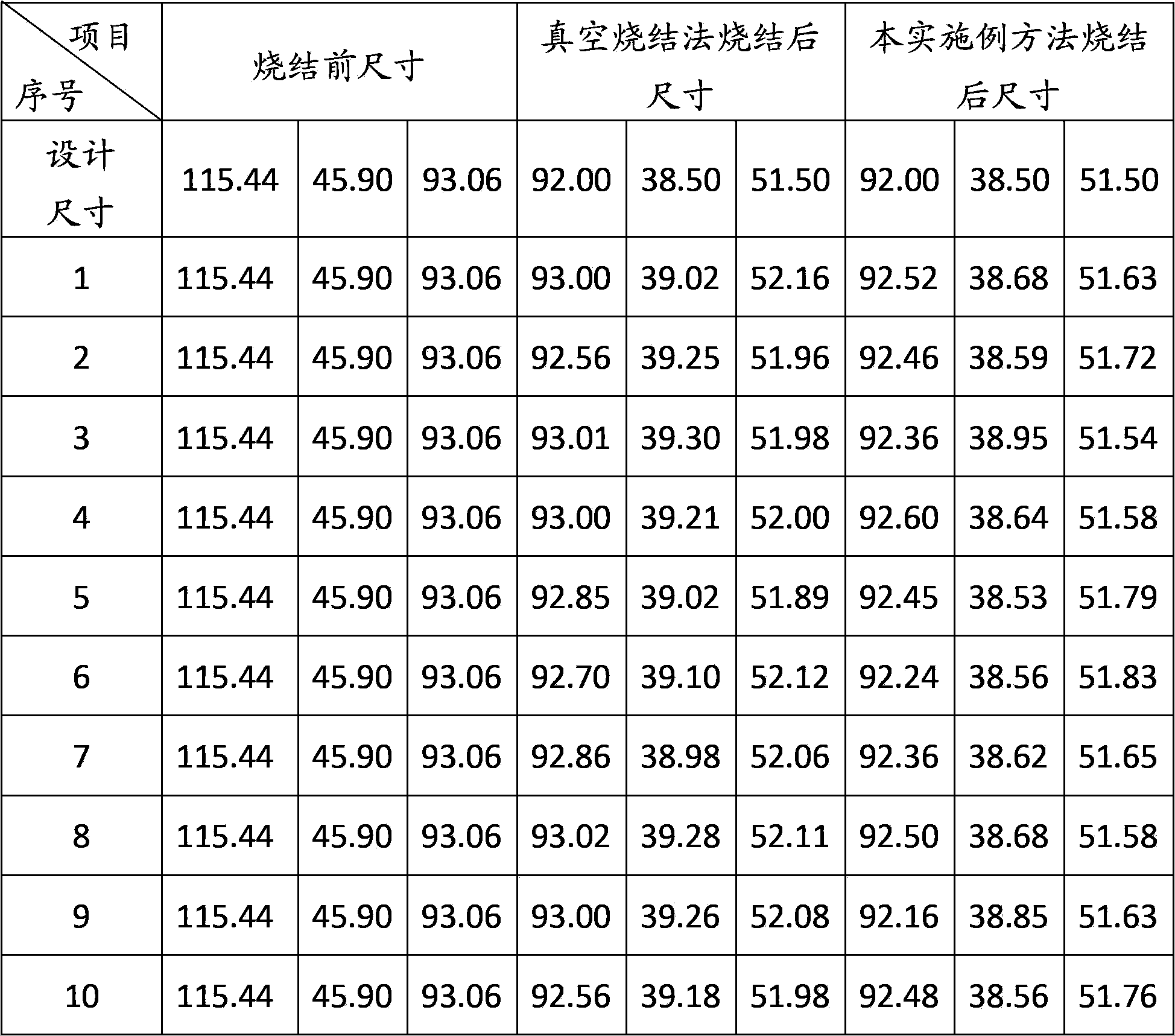
[0029] Preparation steps: Place the NdFeB green body in a graphite tray with at least one small grid, place at least one NdFeB green body in each small grid, and use high temperature resistant powder with a particle size range of 10-60μm The NdFeB green body is fully buried to isolate the air. The space in the small cell should be completely filled with high-temperature-resistant powder, so that not only can the air be isolated, but also the NdFeB green body can be well positioned in the small cell, and the position will not be easily moved. If the size of the NdFeB green body is very small, two or more NdFeB green bodies can be placed in a small cell, but it is necessary to ensure that any two NdFeB green bodies in the same small cell are separated from each other. The intervals are well spaced with high temperature resistant powder. In order to avoid bonding impurities on the surface ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] This embodiment is based on the previous embodiment, and uses a flat graphite material tray without small grids to contain the NdFeB green body and high-temperature-resistant powder, and the rest of the technical content is consistent with the previous embodiment. Since the thermal conductivity of high-temperature-resistant powder (graphite powder, alumina powder, magnesium oxide powder, or high-temperature-resistant ceramic powder) is worse than that of the graphite tray, the neodymium iron in this embodiment The heating condition of the boron green body during sintering is worse than that of the previous embodiment, but as long as the furnace temperature and sintering time are properly adjusted, the sintered size with the same statistical effect as in Table 1 can still be obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0039] In this embodiment, on the basis of the first and second embodiments, the selection scheme of the high temperature resistant powder is changed. In this embodiment, at least two of the powder materials such as graphite powder, alumina powder, magnesium oxide powder and high temperature resistant ceramic powder can be mixed with each other before being put into use. Since the above several powders do not react with each other at high temperature, the requirements of the technical solution of the present invention can be met. However, since different powders have certain differences in thermal conductivity, after mixing two or more powders, the surface heating uniformity of the NdFeB green body during the sintering process will be slightly reduced, but will not Obvious shape deformation of the NdFeB magnet can be obtained, and the sintered size similar to the statistical effect shown in Table 1 can be obtained, which can meet the requirements of the invention objective of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com