Method and system for non-invasive detection of fetal chromosomal aneuploidy
A chromosome and Y chromosome technology, applied in the field of medical testing, can solve problems that affect the accuracy of the final result, do not consider the sequence preference between chromosomes, and construct an optimization model for sex chromosome data.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
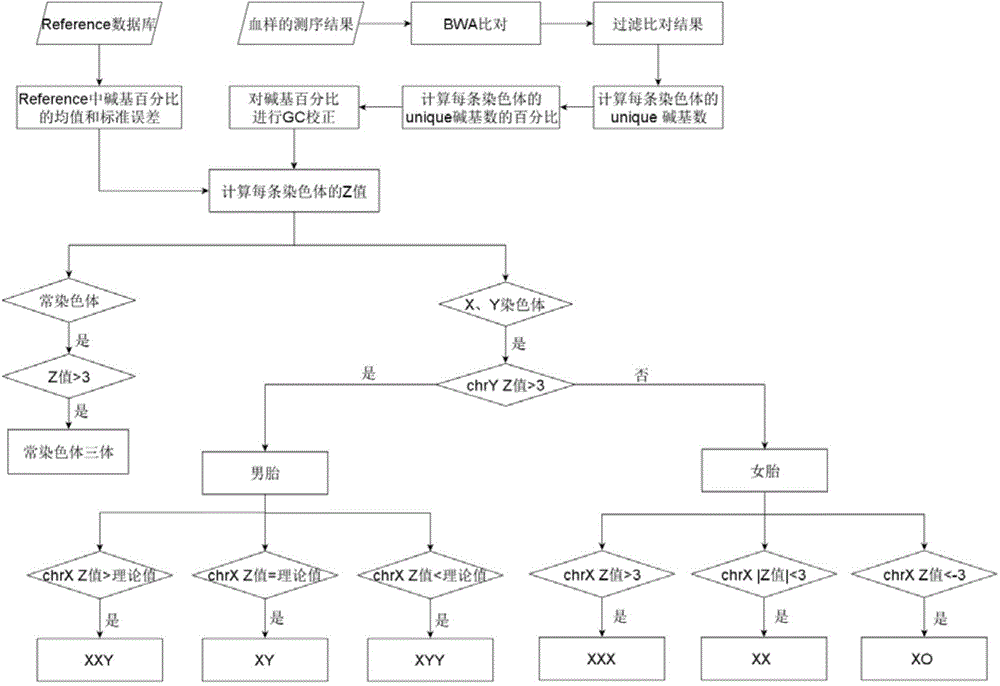
[0094] Example 1: Building a reference database
[0095] 1. Select control blood samples
[0096] 500 peripheral blood samples from pregnant women whose gestational age was greater than or equal to 12 weeks and had no chromosomal abnormalities in karyotype analysis were selected to form the control blood samples in the reference database A (ReferenceA). Among them, the blood samples of 200 pregnant women with normal female fetuses constitute the control blood samples in the reference database B (ReferenceB).
[0097] 2. Accurate positioning of sequencing data
[0098] Compare the sequencing data with the human genome standard sequence hg19 to determine the exact position of the base sequence on the chromosome.
[0099] 3. Quality control of sequencing data
[0100] In order to ensure the quality of the sequencing results and avoid the interference of some repetitive sequences, low-quality sequences were eliminated, and the bases located in the tandem repeat and transposable...
Embodiment 2
[0107] Example 2: Construction of determination parameters and threshold ranges for X chromosome aneuploidy in male fetuses
[0108] 1. Calculate the Z value of X and Y chromosomes in male fetuses
[0109] Using ReferenceB as a reference database, calculate the Z values of fetal X and Y chromosomes in the blood samples of pregnant women carrying normal male fetuses according to formula 1, that is, Z X and Z Y .
[0110] Z i =(x i -μ i ) / σ i (Formula 1)
[0111] i: chromosome number;
[0112] x i : Unique base percentage of chromosome i in the analysis data;
[0113] mu i : The average value of the Unique base percentage of chromosome i in the reference database;
[0114] b i : The standard error of the Unique base percentage of chromosome i in the reference database.
[0115] 2. Construct Z in male fetus X and Z Y relationship model between
[0116] According to the calculation formula of Z value, Z X and Z Y Both are related to the concentration of fetal D...
Embodiment 3
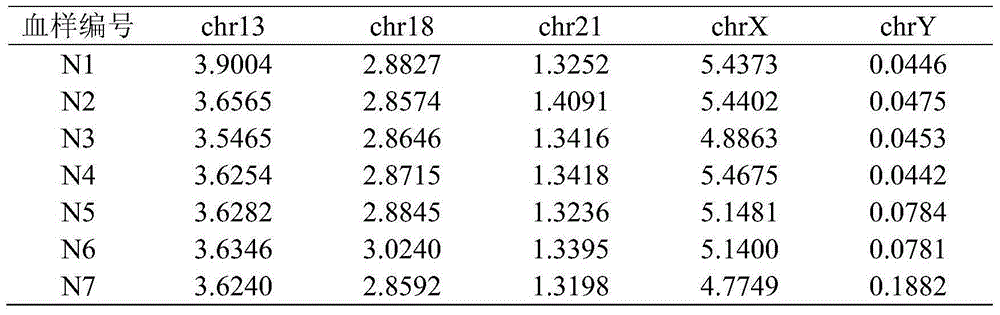
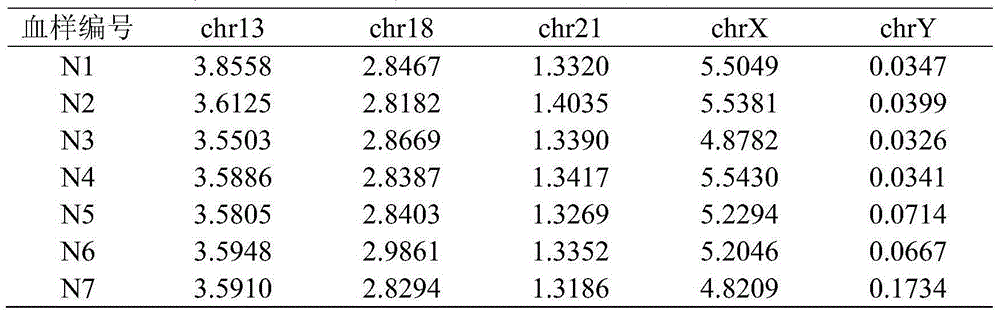
[0126] Embodiment 3: detection of the blood sample to be tested
[0127] 1. Whole genome sequencing of blood samples to be tested
[0128] Seven pregnant volunteers participated in this test, and the blood samples were numbered N1-N7. The results of karyotype analysis showed: 1 fetus with trisomy 21, 1 fetus with trisomy 13, 1 fetus with trisomy 18, and 1 male fetus with an extra Y chromosome , 1 pregnant with a female fetus lacking one X chromosome, 1 pregnant with a normal female fetus, and 1 pregnant with a normal male fetus.
[0129] The peripheral blood of each pregnant woman was drawn, centrifuged to obtain plasma, and then DNA was extracted from the plasma, using the IonProton of Life Company TM Sequencers perform large-scale, high-throughput sequencing. The above blood samples were collected by Guangzhou Women and Children's Medical Center.
[0130] 2. Count the percentage of Unique bases in chromosomes in the blood sample to be tested
[0131] By comparing and fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com