Resource utilization method of residual sludge from petrochemical organic wastewater biological treatment
A technology for excess sludge and organic wastewater, applied in the field of solid waste resource utilization, can solve problems such as limiting the output of ceramsite filter materials, and achieve the effect of saving fuel consumption, high content, energy saving and emission reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] (1) Drying of raw materials
[0025] The remaining petrochemical sludge, clay, and river sediment were dried at 105°C, and then pulverized in a planetary ball mill, sieved through 100 mesh, and collected for later use. Fly ash was dried at 105°C and passed through a 100-mesh sieve for later use. The civil building waste glass is mechanically crushed to less than 5mm, then placed in a planetary ball mill to crush, sieved through 100 mesh, and collected for later use.
[0026] (2) Raw material mixing, granulation and drying
[0027] Weigh 20g of petrochemical and biochemical residual sludge, 30g of fly ash, 40g of river sediment, and 10g of glass powder, mix well, add 25-30g of water to granulate to obtain sludge raw meal particles, and the particle size of the raw meal particles is controlled At 4-7mm; and place it in an oven to dry at 105°C.
[0028] (3) Calcination of filter material
[0029] Place the dried sludge raw meal particles in a tubular sintering furnace,...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The difference between Example 2 and Example 1 lies in the reduction of residual petrochemical sludge and the increase of river sediment, the preheating temperature and preheating time are increased, and other operating conditions remain unchanged. The difference between Example 3 and Example 1 is that the amount of petrochemical residual sludge and fly ash is reduced, the amount of river sediment is increased, the preheating temperature is increased and the preheating time is extended, and other operating conditions remain unchanged. . Example 4 is similar to Example 1 in that the amount of petrochemical residual sludge, fly ash, and river sediment is reduced, the amount of clay is increased, the preheating temperature is increased and the preheating time is extended, and other operating conditions constant.
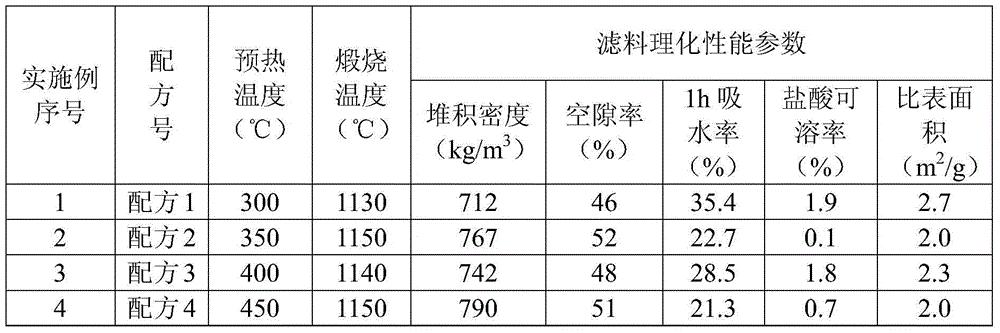
[0033] The concrete raw material ratio of embodiment 1-4 is shown in Table 1, and the physical and chemical performance index of the filter material product of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voidage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com