Absolute fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primer pair, probe and method for determining growth titer of mycoplasma hyopneumoniae
A technique for mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and fluorescence quantification, which is applied in the field of molecular biology and can solve the problems of time-consuming, fast detection and poor accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1 Absolute fluorescence quantitative PCR measures the growth titer of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae
[0029] The steps of the following method describe in detail the preparation of the plasmid, the determination of the concentration of the plasmid, the establishment of a standard curve for the amplification of the plasmid, and the determination of the fermentation liquid sample of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae to be tested. Taking the determination of the titer of the Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae fermentation broth after one fermentation as an example, the absolute fluorescence quantitative PCR method of the present invention is used to detect its copy number, that is, the growth titer of the Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae fermentation broth.
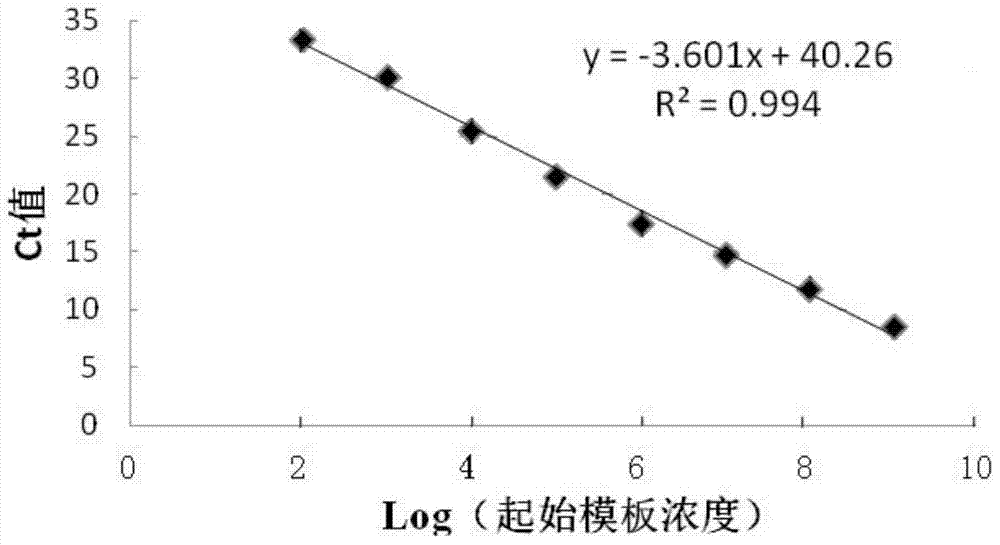
[0030] 1) The Primer express software was used to design common PCR primer pairs at the 16S rRNA conserved sequence of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (GB︱AE017243.1︱), and the common PCR primer pairs were synthesized by Invitrogen. The common P...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2 Absolute fluorescence quantitative PCR repeatability experiment
[0047] Using the absolute fluorescence quantitative PCR method in Example 1, standard plasmids with different concentration gradients were used as templates, and the standard plasmids with different concentration gradients were measured 5 times in the same reaction, and the coefficient of variation (CV) of each repeated sample was calculated. The experimental results showed (Table 2) that the coefficient of variation of the Ct value of each dilution gradient repeated sample was less than 2%, showing that the absolute fluorescence quantitative PCR of the present invention has good reproducibility.
[0048] Table 2 Fluorescent quantitative PCR repeatability experiment
[0049] copy
[0050] ×10 -5
Embodiment 3
[0051] Embodiment 3 Absolute fluorescence quantitative PCR primer pair specific experiment
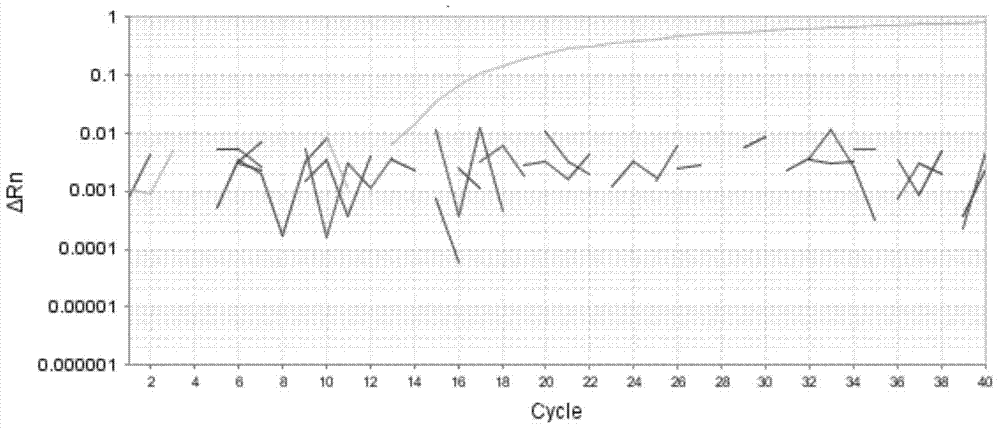
[0052] Use the bacterial genomic DNA extraction kit to extract the genomic DNA of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae as a positive control, and simultaneously extract the DNA of Mycoplasma hyorhina, Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Bacillus subtilis, and Staphylococcus aureus for specific detection, using the absolute fluorescent quantitative PCR in Embodiment 1 Primer pair and probe and method, the result all does not have amplification curve except positive control, illustrates that the absolute fluorescence quantitative PCR primer pair of the present invention has good specificity, see image 3 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com