Method for analyzing and detecting solid solubility of tungsten in cemented carbide binding phase
A technology of cemented carbide and detection method, which is applied in the field of quantitative analysis of solid solution tungsten element content in cemented carbide binder phase by X-ray energy spectrum, can solve the problems of inability to quantitatively analyze the content of tungsten element, unable to use separation, etc., and achieve intuitive The effect of accurate reference data, improved accuracy, and high detection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Analysis and detection of the solid solubility of tungsten in the bonding phase Co in WC-Co cemented carbide
[0028] First, prepare a smooth metallographic polished surface from the WC-Co cemented carbide sample to be tested; (the following examples are the same)
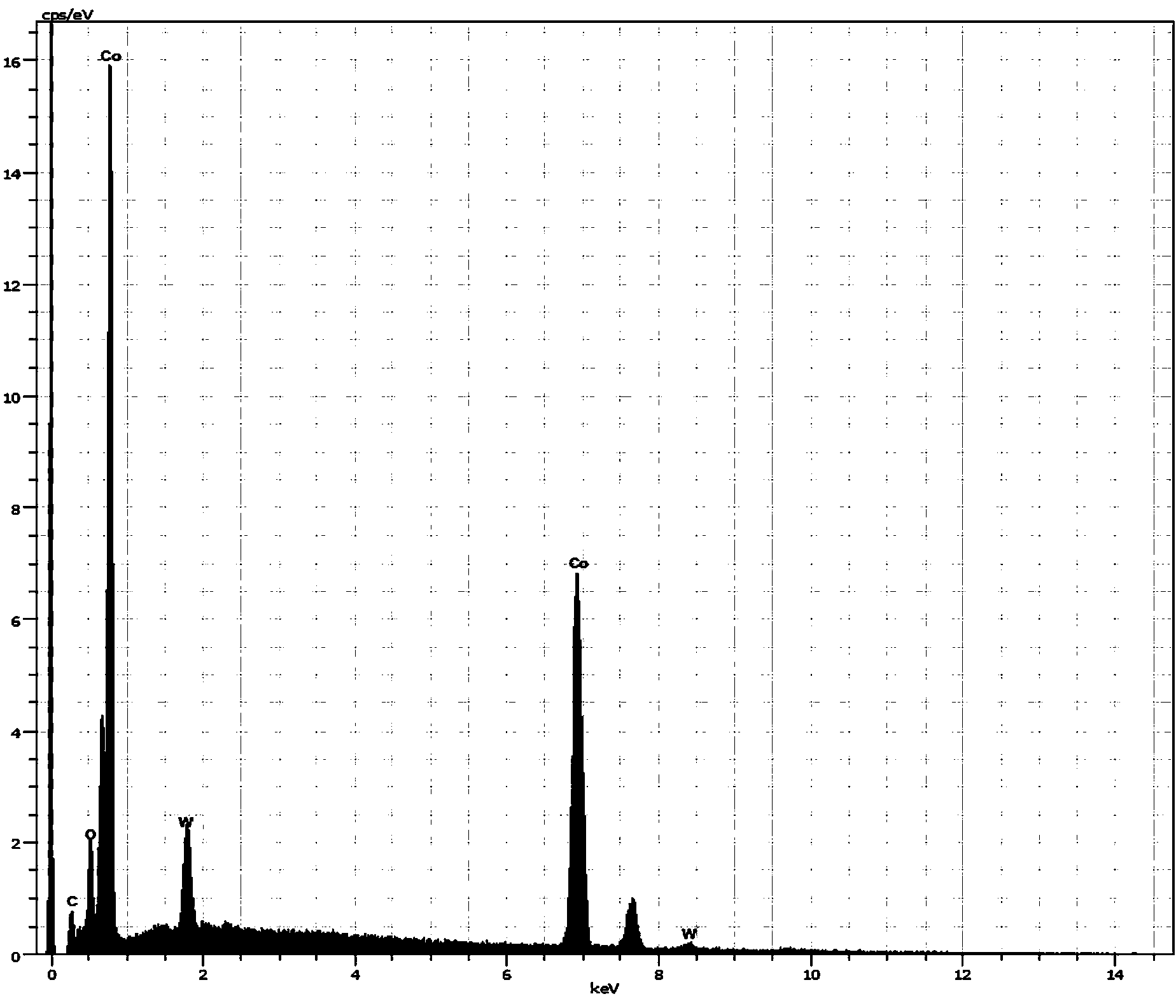
[0029] Then, the hard phase WC on the metallographic polished surface is peeled off by using electrolytic separation, a chemical separation technology. The electrolyte solution for electrolytic separation is NaOH or KOH strong alkali solution with a mass percentage of 20-40%. The electrolytic current is controlled at 0.1-0.5A. The electrolytic anode is made of hard alloy, and the cathode is made of pure titanium plate. After the electrolysis is completed, the impurities and oxide layer on the sample surface are removed, and the sample to be tested that has been stripped of the hard phase is prepared on the metallographically polished surface, (the following examples are the same); Analysis showed...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: Analysis and detection of the solid solubility of tungsten in the binder phase (Co+Ni) in WC-(Co+Ni) cemented carbide, where a small amount of Cr is added to the (Co+Ni) binder phase
[0039] First, the sample to be tested is prepared with a smooth metallographic polished surface. Then the hard phase WC is peeled off, and the sample surface impurities and oxide layer are removed, and the sample to be tested is prepared; observation and X-ray energy spectrum analysis have no obvious oxide layer and precipitates, such as Figure 4 As shown in , it shows that the hard phase WC on the metallographic polishing surface has been completely stripped from the bonding phase (Co+Ni).
[0040] Next, optimize the calibration settings of the X-ray energy spectrometer by using the pure Co binder phase standard sample, and save it at the same time;
[0041] Then select a cobalt-based cemented carbide sample with a known mass percentage of 5% W+95% Co as the standard sample ...
Embodiment 3
[0045]Example 3: Analysis and detection of the solid solubility of tungsten in the binder phase (Co+Ni) in WC-(Co+Ni) cemented carbide, including a small amount of Ni in the (Co+Ni) binder phase 3 Al phase
[0046] First, the sample to be tested is prepared with a smooth metallographic polished surface. Then the hard phase WC is peeled off, and the sample surface impurities and oxide layer are removed, and the sample to be tested is prepared; observation and X-ray energy spectrum analysis have no obvious oxide layer and precipitates, such as Figure 4 As shown in , it shows that the hard phase WC on the metallographic polishing surface has been completely stripped from the bonding phase (Co+Ni).
[0047] Next, the X-ray spectrometer calibration settings were optimized using pure Co standard samples and saved at the same time.
[0048] Then select a cobalt-based cemented carbide sample with a known mass percentage of 5% W+95% Co as the standard sample for X-ray energy spectru...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com