Desynchronization resistant lightweight RFID bidirectional authentication protocol
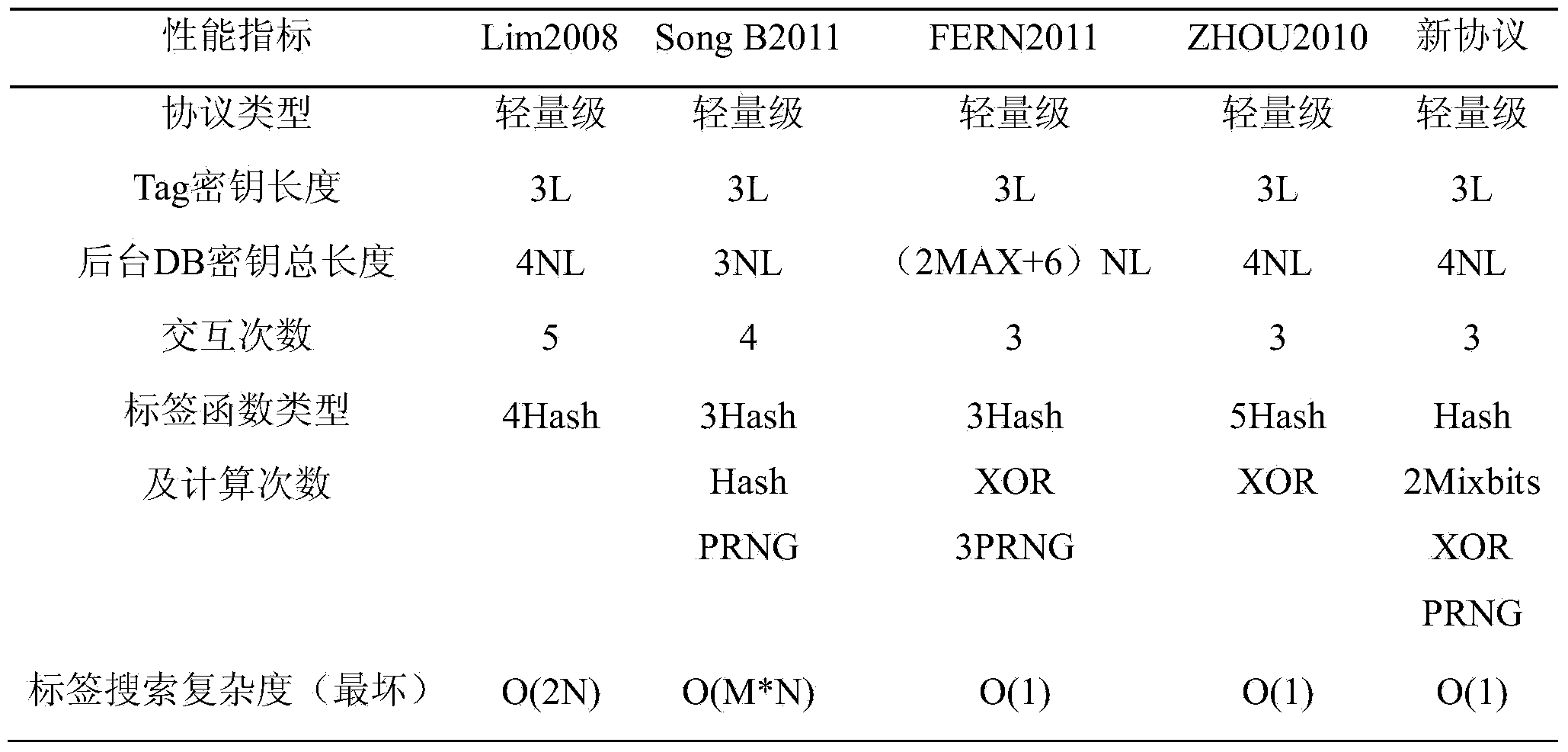
A two-way authentication and lightweight technology, applied to key distribution, can solve problems such as desynchronization attacks, lack of trusted freshness, etc., achieve low key length, improve trustworthiness and real-time performance, and tag search complexity low effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] (1) Implementation steps
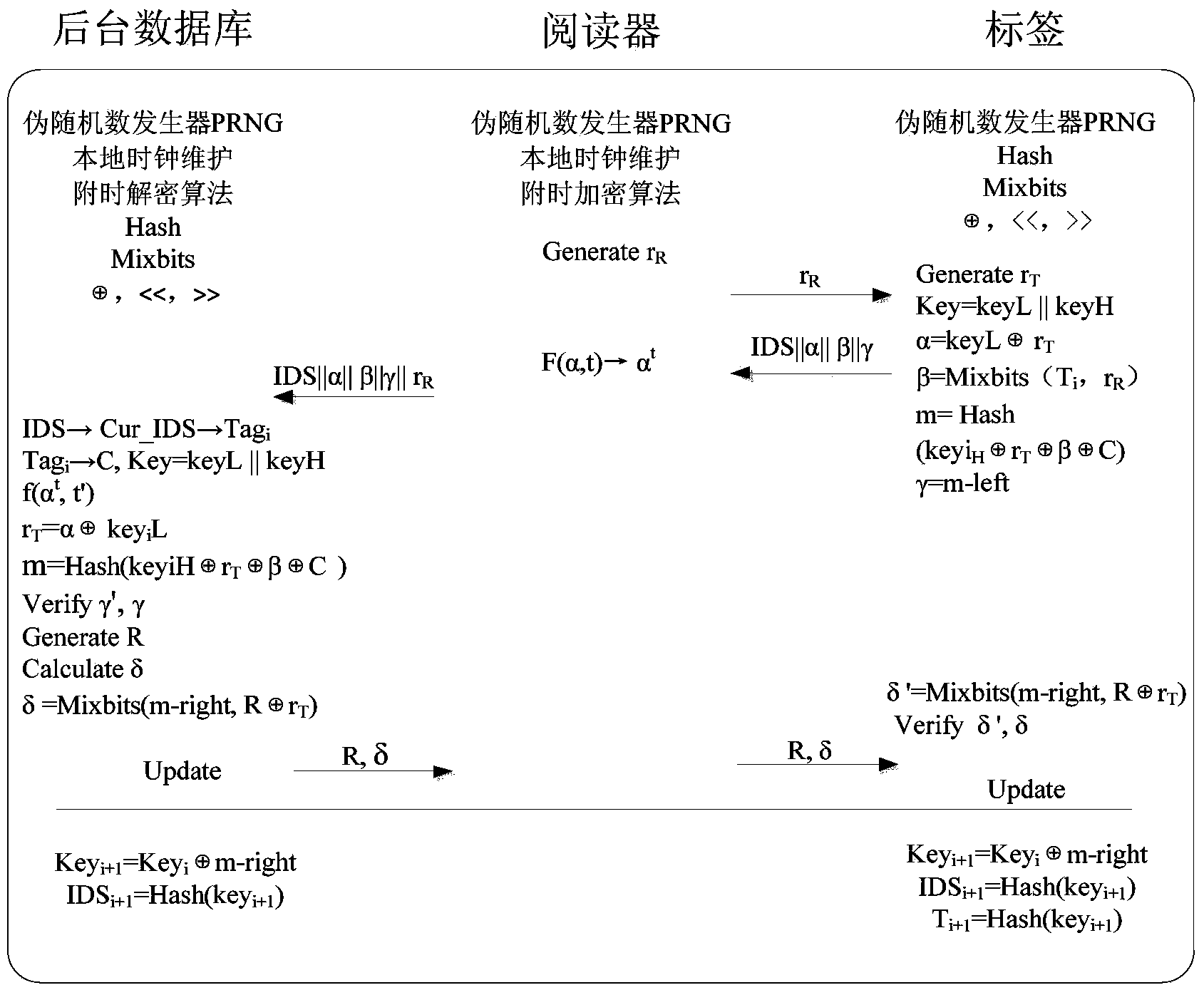
[0019] The protocol includes three stages of initialization, authentication, and update. The specific interaction process between the background-reader and the tag in the protocol is described as follows:
[0020] 1. Initialization phase
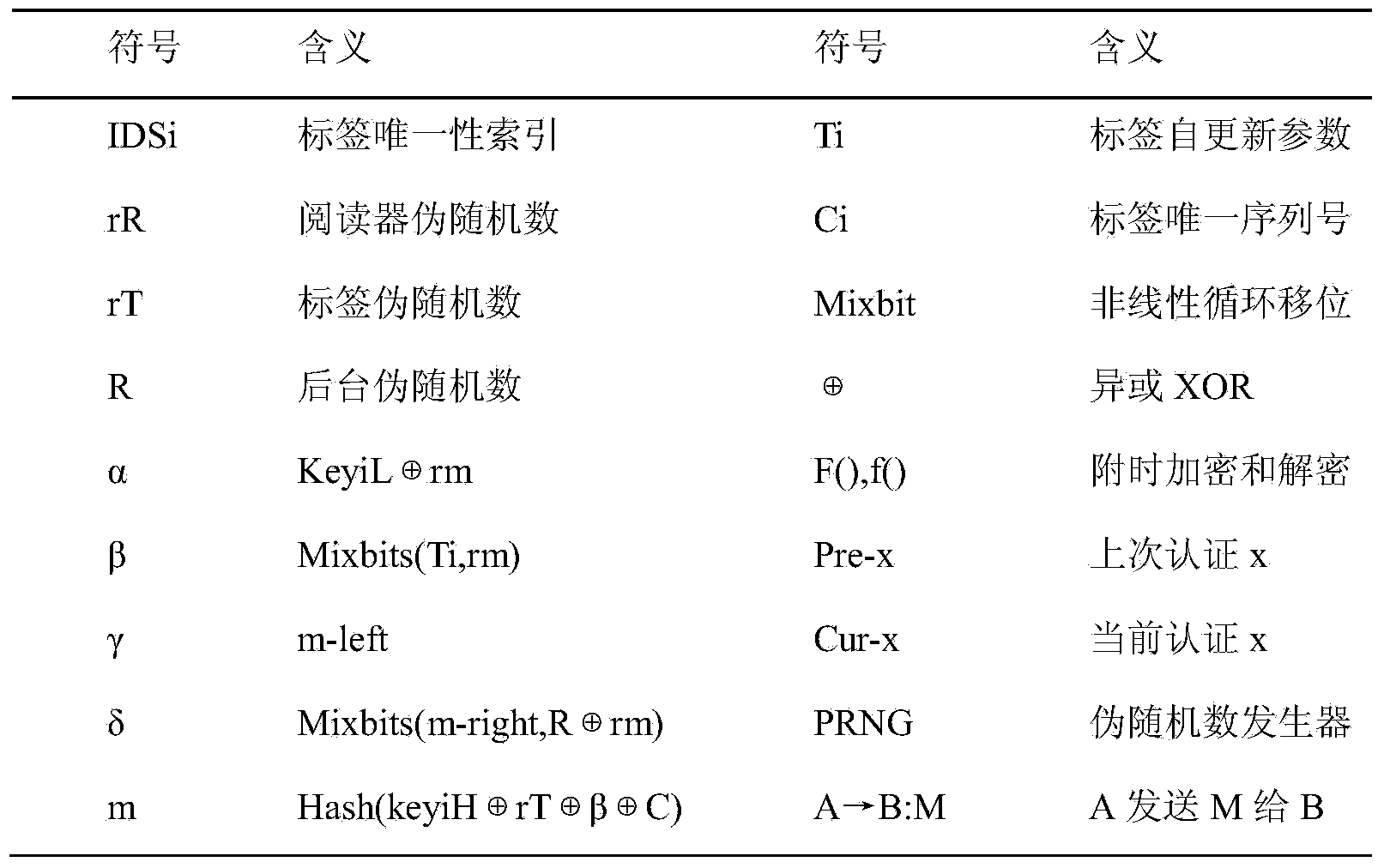
[0021] The RFID system generates a unique serial number C for each tag Tag i , self-updating parameter T i , and share the key group with the database (key i L, key i h). The tag party saves its unique search name and key group, and the storage unit is (IDS, keyL, keyH, T i , C); background database storage directory (Pre-IDS i , Pre-key i ;Cur-IDS i , Cur-key i ; C), where the Cur key unit of the database (Cur-IDS i , Cur-key i ) is the same as (IDS, key) for tags. The reader side and the background database each maintain a local clock t.
[0022] 2. Authentication stage
[0023] 2.1) Step1Reader→Tag(Challenge Message):r R
[0024] The reader generates a random number r R And send it to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com