Process for manufacturing coated substrates
A substrate and coating technology, which is applied in the directions of copying/marking methods, devices for coating liquids on surfaces, and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of increasing extra cost, inability to effectively retain solubility and fine properties, and hindering dehydration of paper webs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0128] 1. Materials
[0129] base : Standard uncoated 80 gm-2 wood-free copy paper (PlanoJet; Papyrus AB, Sweden).
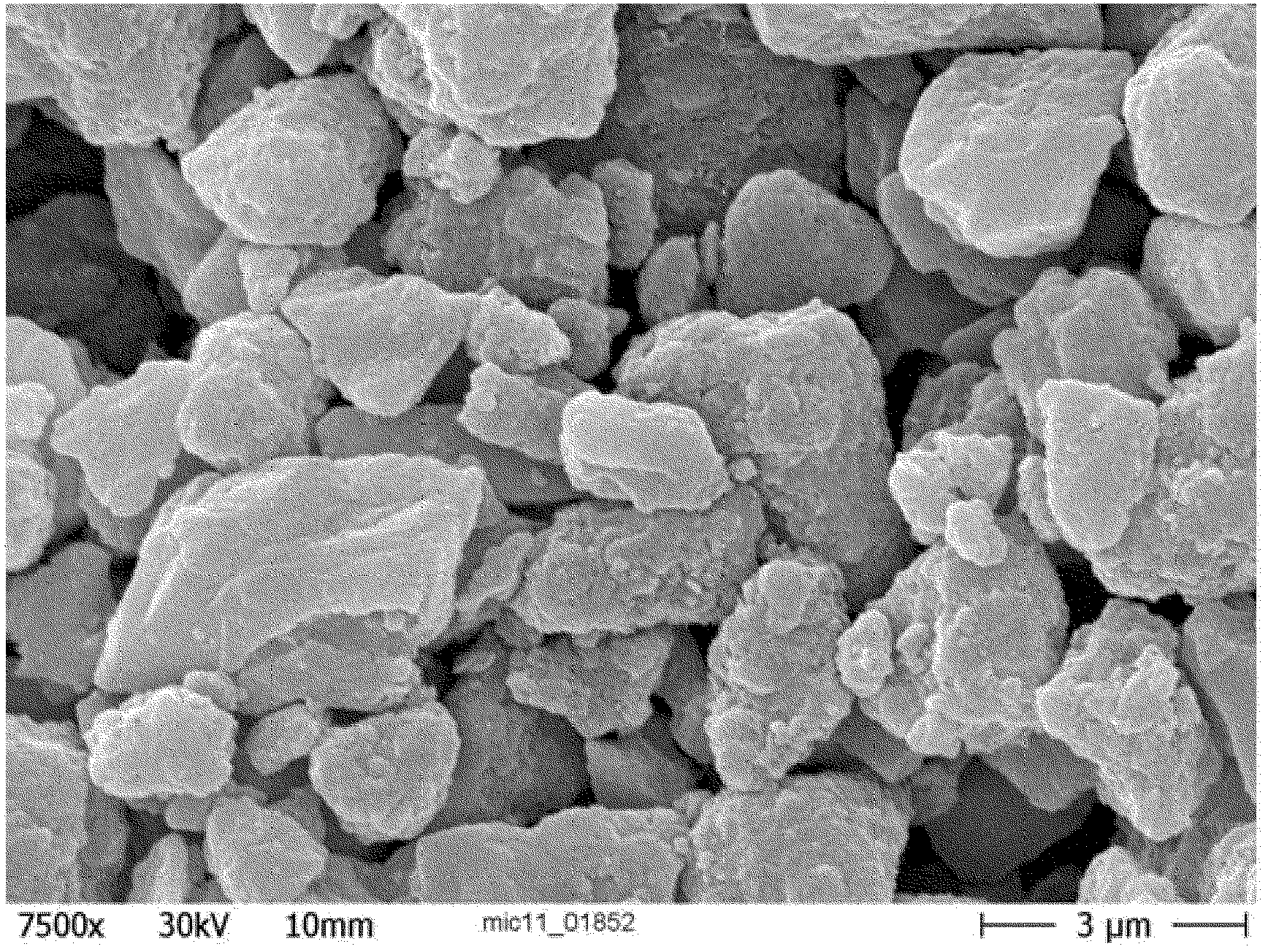
[0130] mineral material : surface-reacted natural ground calcium carbonate (Omyajet B6606; Omya AG, Oftringen, Switzerland; see figure 1 ); weight median particle size d 50 =2.70μm (Sedigraph5100); specific surface area=56m 2 / g; in the form of an aqueous slurry with a solids content of 50% by weight with respect to the mineral material;
[0131] The mineral material was mixed and diluted with 10 wt% styrene acrylate latex binder (Acronal S360D; BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany) based on the amount of mineral material to obtain a total solids content of 40 wt%.
[0132] polysaccharide material :
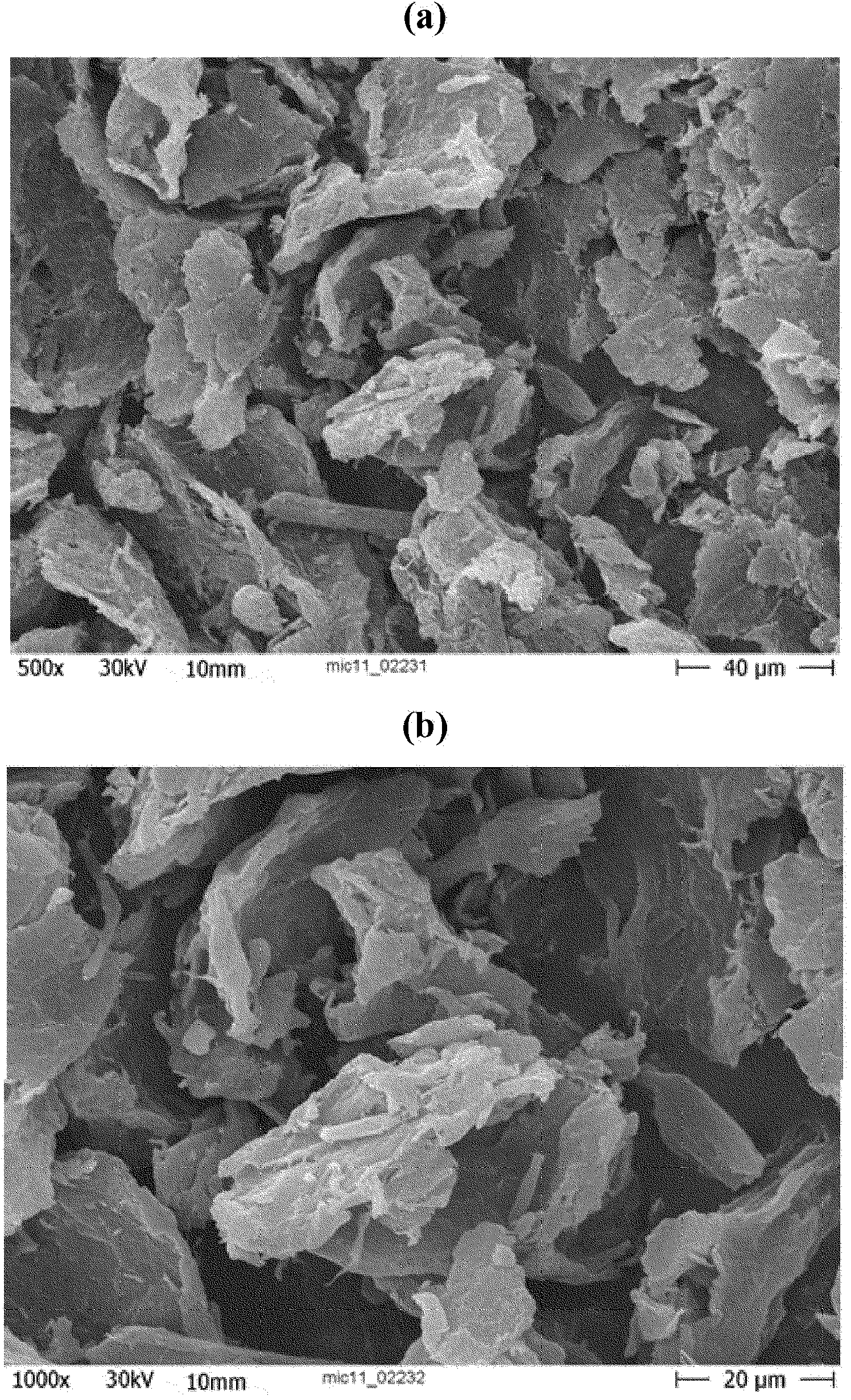
[0133] PM1: ARBOCEL MF40-10 (J. Rettenmeyer und GmbH & Co. KG, Rosenberg, Germany), nanodispersed cellulose with a solids content of 10 wt%, a median particle (fiber) diameter figure 2 ).
[0134] PM2: Nanofibrillar cellulose gel formed using dissolution dis...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com