Mushroom dreg fermentation bed and manufacturing method thereof
A fermentation bed and fermentation bed bacterial strain technology, applied in the field of animal husbandry, can solve the problems that the bacteria residue particles are not as uniform as sawdust, stimulate the respiratory tract of pigs, and the bacteria residue cannot completely replace sawdust, etc., so as to reduce the cost of litter, reduce stimulation, expand The effect of the amount added
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
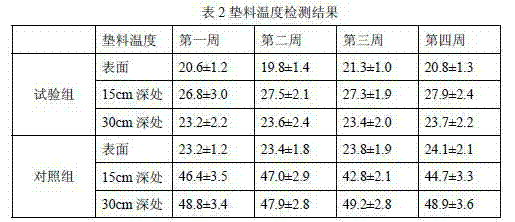
[0021] The production of the fermentation bed of fungus residue in the test group and the feeding of pigs. On July 21, 2013, a fermentation bed of 100 square meters and 0.6 meters thick was made at the pig farm in Shanghe County. According to 35% of rice husk, 65% of mushroom residue (volume ratio of Flammulina velutipes mushroom residue to Pleurotus eryngii mushroom residue 1:1), and oil bran 0.3 kg / m 3 , Fermentation bed bacteria (Bacillus live bacteria content 2.5*10 7 piece / g) 200 g / m 3 The ratio is to take the raw materials for later use. First, mix the oil bran and fermentation bed bacteria, and then use the TMR mixer to mix the mixture of rice husk, fungus residue and oil bran bacteria, and do not add feces and urine water during the mixing process. Then the litter after mixing the rice husk fungus residue is filled in the fermentation tank. When the bedding is mixed and filled to a thickness of 0.42 meters, spread out the bedding and evenly spray 0.21 cubic meters ...
example 2
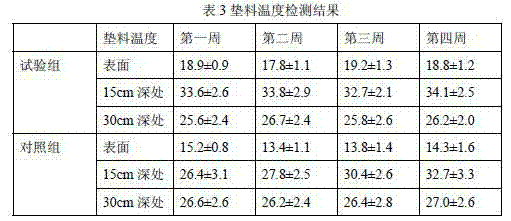
[0028] The production of the fermentation bed of fungus residue in the test group and the feeding of pigs. On December 15, Pingyin Pig Farm made a fermentation bed of 110 square meters and 0.9 meters thick. 30% of rice husk, 70% of mushroom residue (volume ratio of Flammulina velutipes mushroom residue to white jade mushroom residue of 0.9:1), oil bran 0.3 kg / m 3 , Fermentation bed bacteria (Bacillus live bacteria content 2.0*10 7 piece / g) 250 g / m 3 The ratio is to take the raw materials for later use. Firstly, the oil bran and the strain of the fermentation bed are mixed evenly, and secondly, the mixture of the rice husk, the fungus residue and the strain of the oil bran is mixed manually, and no excrement water is added during the mixing process. Then the litter after mixing the rice husk fungus residue is filled in the fermentation tank. When the mixed litter is filled to 0.72 meters, the litter is spread out and paved, and 0.79 cubic meters of pig manure and urine are ...
example 3
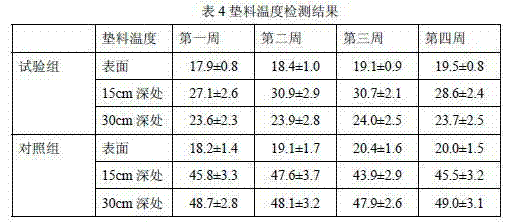
[0035] The production of the fermentation bed of fungus residue in the test group and the feeding of pigs. On May 12, a pig farm in Huaiyin District, Jinan City made a fermentation bed with a thickness of 0.8 meters and an area of 150 square meters. 32% of rice husk, 68% of mushroom residue (volume ratio of Flammulina velutipes mushroom residue to Pleurotus ostreatus mushroom residue 1.1:1), oil bran 0.3 kg / m 3 , Fermentation bed bacteria (Bacillus live bacteria content 2.2*10 7 piece / g) 220 g / m 3 The ratio is to take the raw materials for later use. Firstly, the oil bran and the strain of the fermentation bed are mixed evenly, and secondly, the mixture of the rice husk, the fungus residue and the strain of the oil bran is mixed manually, and no excrement water is added during the mixing process. Then the litter after mixing the rice husk fungus residue is filled in the fermentation tank. When the mixed litter is filled into a thickness of 0.64 meters, the litter is spre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com