Method for determining activity of alpha-amylase inhibitor by colorimetric method via resin de-coloring
A technology of amylase inhibitor and colorimetry, which is applied in the direction of color/spectral characteristic measurement, etc., can solve the problems of vacancy and inaccurate determination of active ingredients, and achieve the effect of reducing loss, reducing color interference, and good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Resin decolorization is used for the method of colorimetric assay α-amylase inhibitor activity:
[0035] Weigh 10.00g of black tea powder, add 100mL distilled water, extract in 90°C water bath for 30min, filter, add 80mL distilled water to medicinal residues, extract in 90°C water bath for 30min, filter, add 60mL distilled water to extract in 90°C waterbath for 30min, filter, three times The filtrates were combined, and the volume was adjusted to 250mL (concentration is equivalent to 0.04g crude drug per 1ml). Take 30mL of the filtrate and centrifuge (4000r / min) for 10min, and take 20mL of the supernatant as the sample solution.
[0036]Take D101 macroporous resin after conventional treatment. Take a certain amount of D101 macroporous resin and use filter paper to absorb the surface moisture, then weigh 8.00g of the macroporous resin to remove the surface moisture, and put it into a 2cm*15cm chromatography column with a column volume of about 13mL. Take the centrifuge...
Embodiment 2
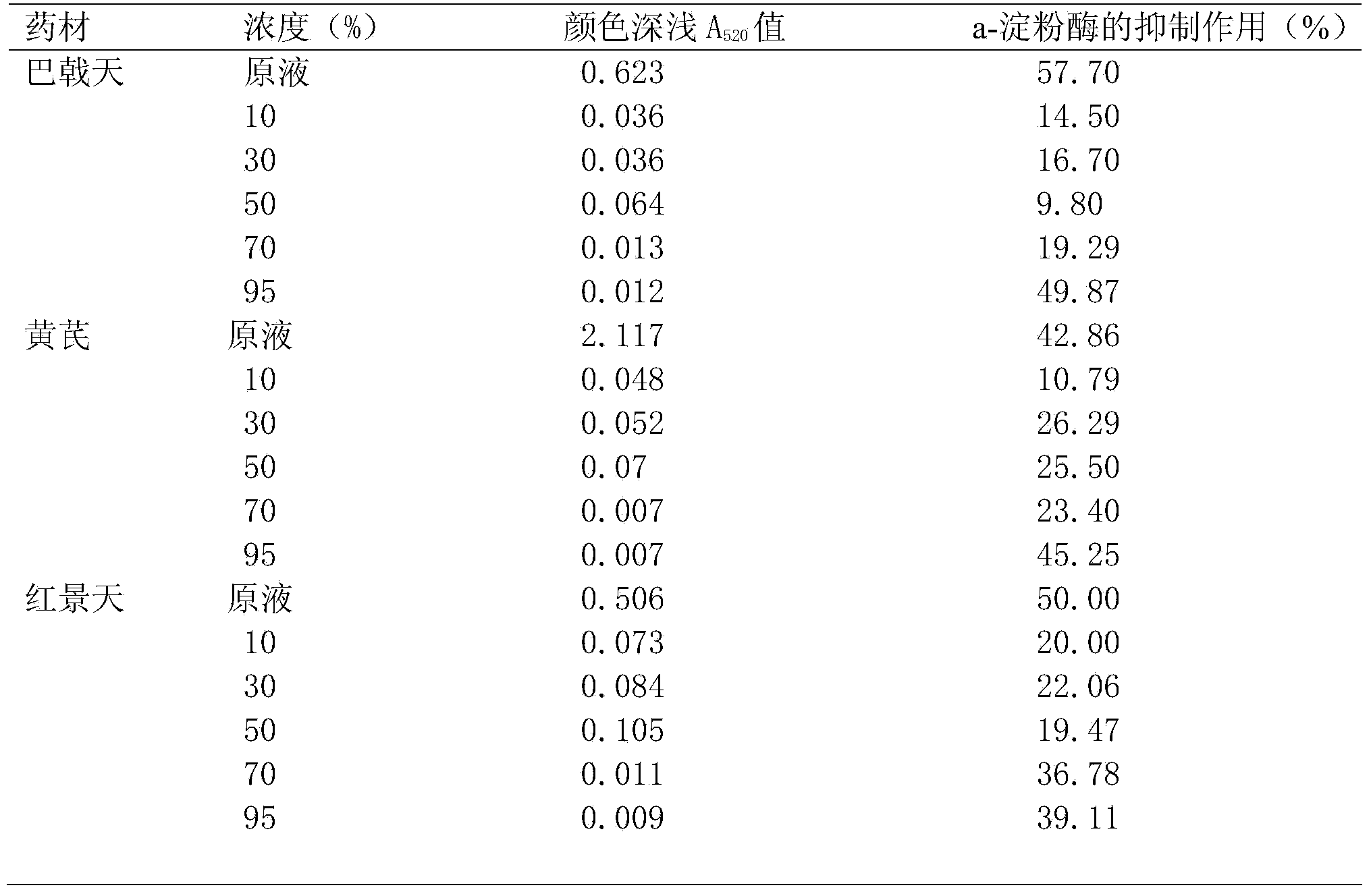
[0042] According to the operation method of Example 1, Morinda officinalis, Radix Astragali, and Rhodiola were decolorized with D101 macroporous resin, and the fractions after decolorization were collected. Comparison of the color depth of the elution fractions of different gradients, determination of A 520 The results are shown in Table 4.
[0043] Table 4. Comparison of deliquified colors of Morinda officinalis, Astragalus, and Rhodiola and their inhibitory effects on a-amylase
[0044]
[0045] The results showed that the medicinal material became lighter in color after being eluted by D101 macroporous resin, and the inhibitory effect on α-amylase was concentrated in the 70% and 95% fractions with lighter color.
Embodiment 3
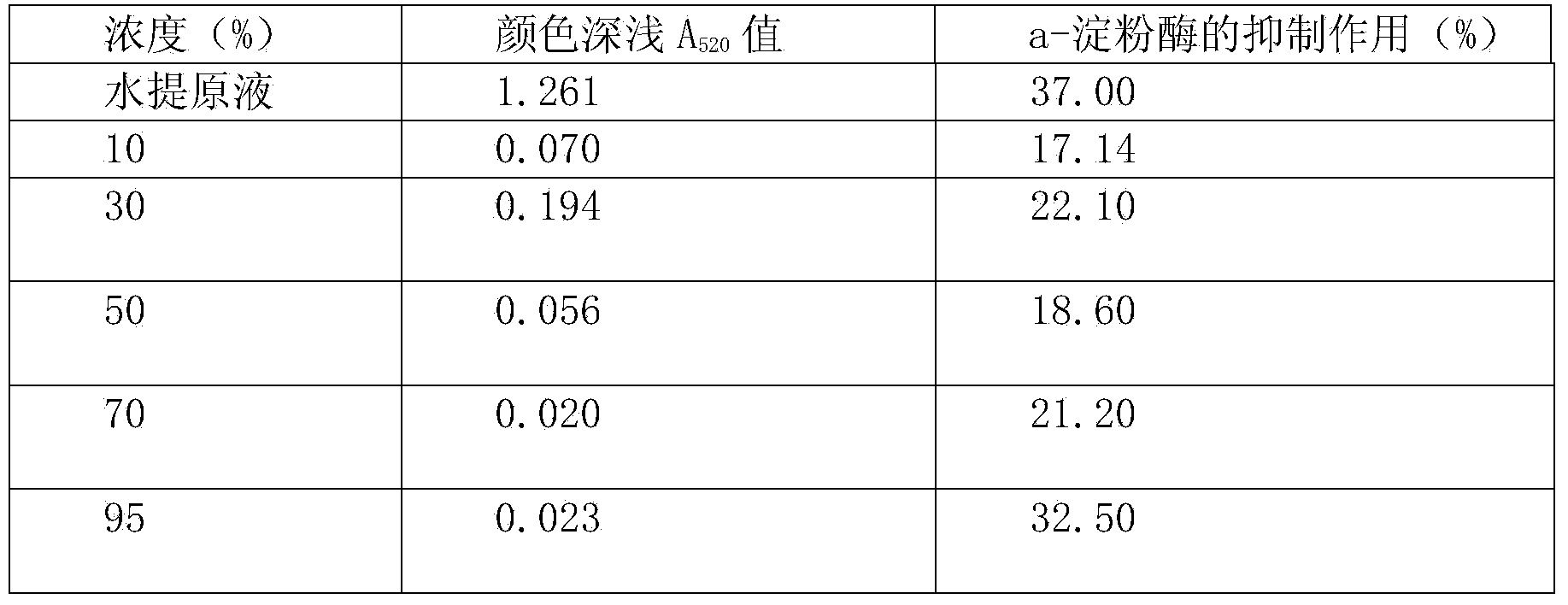
[0047] Resin decolorization is used for the method of colorimetric assay α-amylase inhibitor activity:
[0048] Accurately weigh 10.00g of Prunella vulgaris powder, add 100mL of deionized water, extract in a 93°C water bath for 30min, filter, add 80mL of deionized water to the residue, extract in a 93°C water bath for 30min, filter, add 60mL of deionized water to the residue in a 93°C water bath Extract for 30 minutes, filter, combine the three filtrates, and dilute to 250mL (concentration: 0.04g / mL). Take 30mL of the filtrate and centrifuge (4000r / min) for 15min, and take 20mL of the supernatant as the sample solution. Accurately weigh 8.00 g of D101 macroporous resin (the same batch of pre-treated D101 macroporous resin as in Example 1) after removing the moisture on the surface of the resin, and put it into a chromatographic column with a specification of 2cm*15cm. The column volume is about 13mL. Take the centrifuged supernatant and load the sample, control the flow rate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com