Detection or assisted detection method for bacterial strains to be detected based on species specific sequence
An auxiliary detection and genome sequence technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electronic digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems affecting the prevention and control of infectious diseases, the long time-consuming period, and the easy contamination of PCR, etc., to achieve rapid Identification and detection, good species specificity, good effect of specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
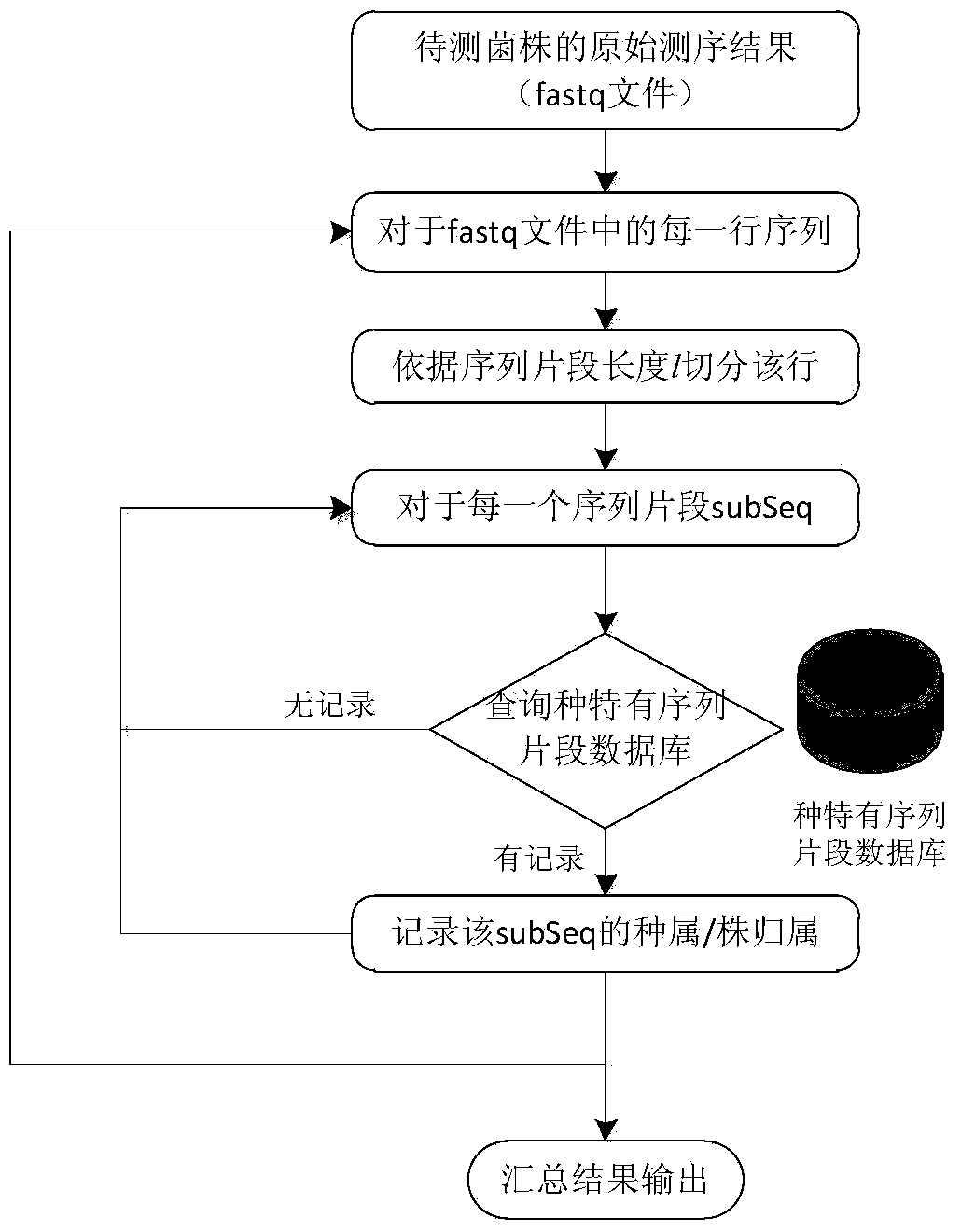
[0041] Example 1, Bacterial Pathogen Detection Method Based on Species-Specific Fingerprint Sequence
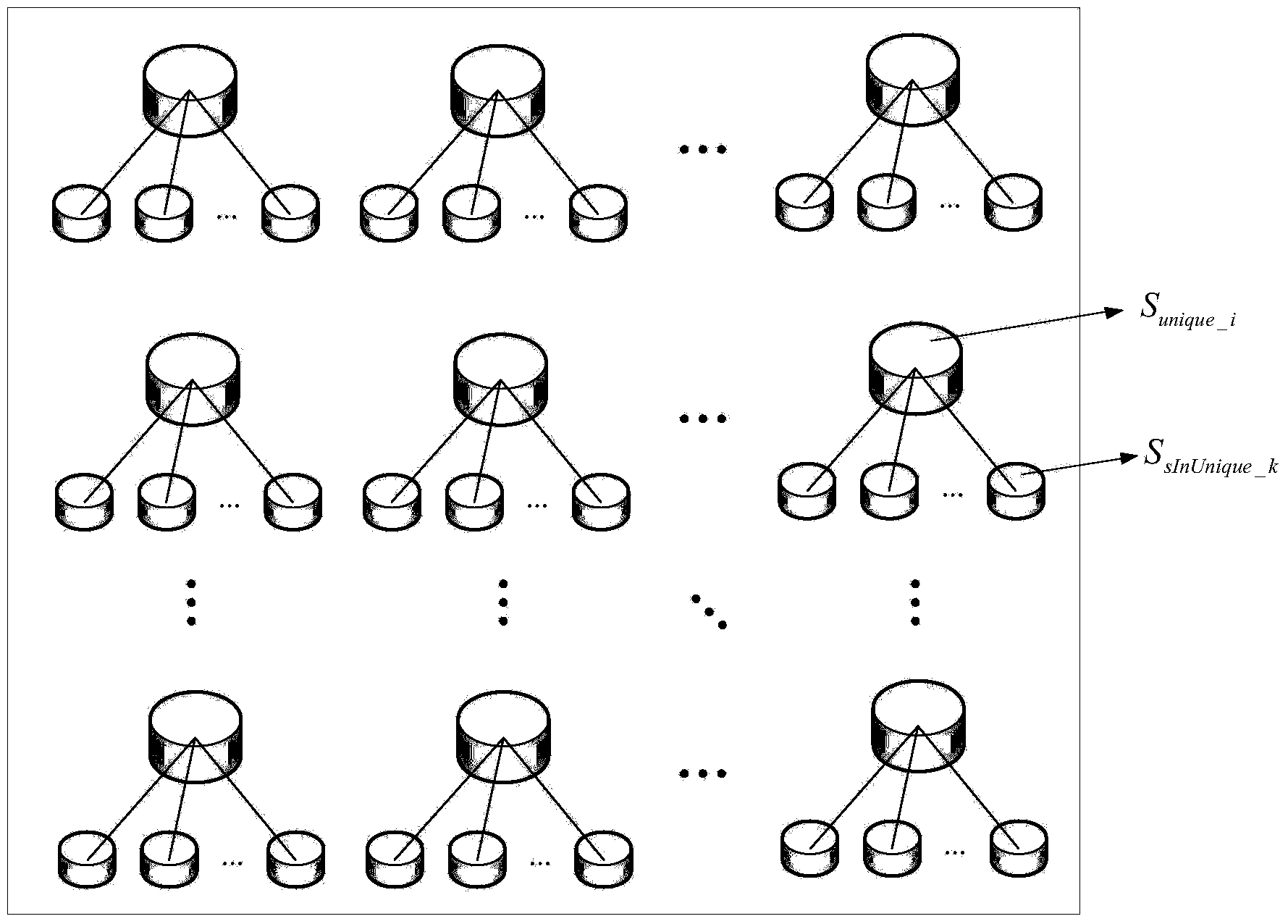
[0042] 1. Acquisition of the strain's species-specific gene fragment database
[0043] 1. Download NCBI bacterial genome sequence data
[0044] Log in to NCBI's ftp server (ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), download the whole genome sequence of strains that have completed whole genome sequencing (the server is all genome sequencing, and the downloaded bacteria are all bacteria), and generate a download file , download the file to record the genome sequence of each strain;
[0045] In this example, a total of 2349 strains were downloaded from the NCBI database on 2013-05-11 to complete the whole genome sequence of the strains whose genomes were sequenced.
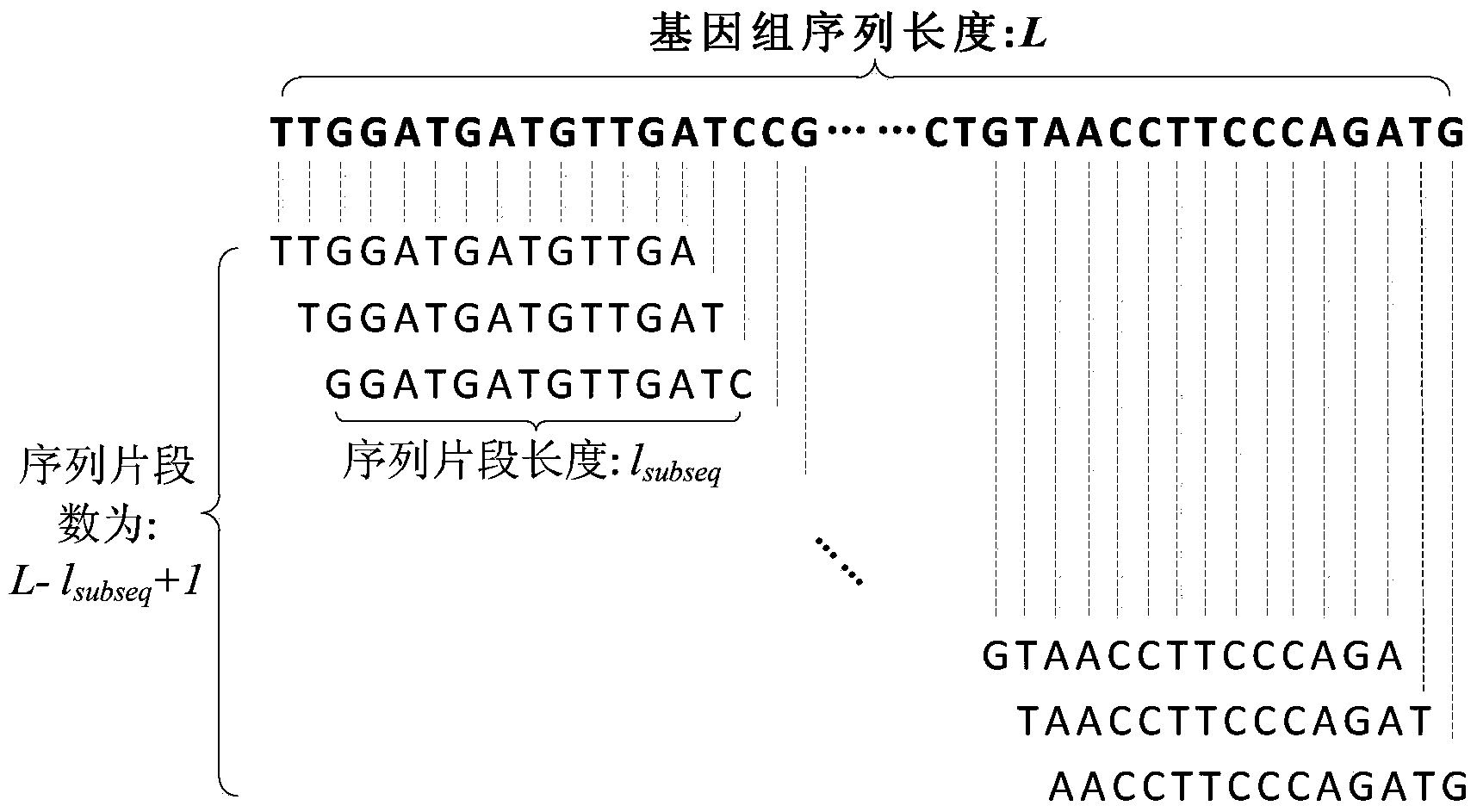
[0046] 2) Segment genome data
[0047] Find the longest gene sequence in the downloaded bacterial genome sequence, that is, find the length of the longest genome sequence in the genome sequences of all strains downloaded, set its l...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Embodiment 2, construction of intraspecific phylogenetic tree traceability of strains to be tested
[0078] According to the bacterial species-specific gene fragment set to which the strain to be tested belongs and the strain-to-be-tested gene fragment set, the contribution of the strain to be tested to the species-specific gene fragment set to which the strain to be tested is calculated according to step (5) of Example 2 , to obtain the set of species-specific gene fragments of the strain to be tested;
[0079] The species-specific gene fragment set of the strain to be tested and the set of species-specific gene fragments of each strain in the species to which the strain to be tested belong are used as markers to construct a phylogenetic tree to realize the traceability of the strain to be tested.
[0080] details as follows:
[0081] The strains to be tested belonged to 58 strains in Escherichia coli, and the number of specific gene fragments was 20509. When construct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com