Acoustic optical modulator-based high-stability laser frequency scanning device
An acousto-optic modulator and frequency scanning technology, applied in the field of laser spectroscopy, can solve problems affecting spectral accuracy and stability, and achieve the effects of flexible stability, high spatial stability and power stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
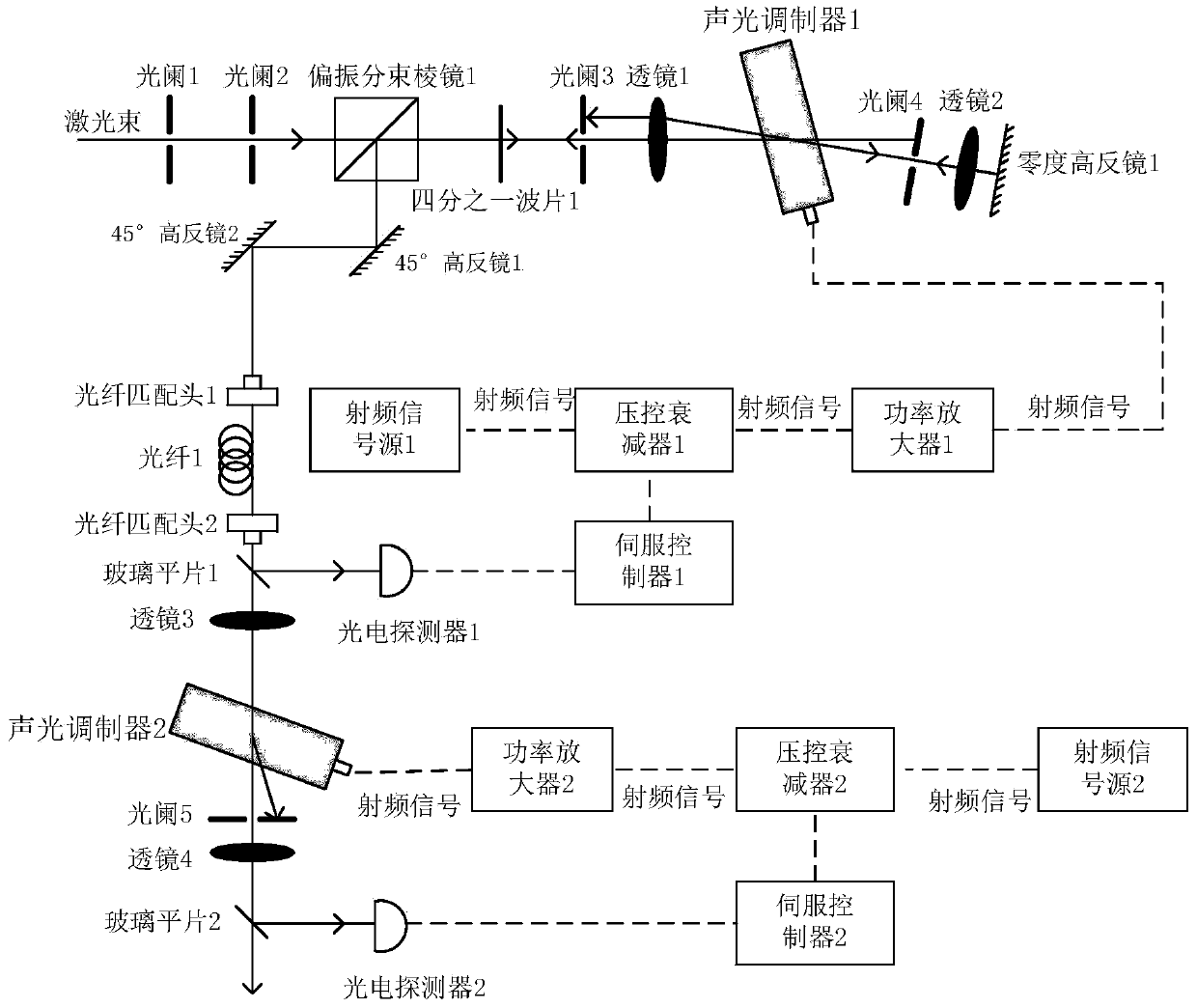
[0026] 1. Laser double-pass acousto-optic modulation
[0027] see figure 1, a 689nm parallel laser beam with a stable frequency and a polarization direction parallel to the paper surface (horizontal), passes through the centers of aperture 1 and aperture 2 in sequence, and the laser beam propagates along the optical path fixed by the system. Since the incident light is horizontally polarized, the laser light passes through the polarization beam splitter prism 1 . After the horizontally polarized light passes through the quarter-wave plate 1, it becomes circularly polarized light. The parallel light beam passes through the aperture center of the diaphragm 3 and is focused by the lens L1. The focal point of the lens L1 is located at the crystal center in the AOM 1 and diffracted in the AOM 1. The angle of the acousto-optic modulator 1 is adjusted so that the diffraction efficiency of the negative first-order diffracted light reaches more than 80%. Adjust the position of the a...
Embodiment 2
[0043] In this embodiment, the positive first-order diffracted light of the AOM 1 is used.
[0044] see figure 1 , a 689nm parallel laser beam with a stable frequency and a polarization direction parallel to the paper surface (horizontal), passes through the centers of aperture 1 and aperture 2 in sequence, and the laser beam propagates along the optical path fixed by the system. Since the incident light is horizontally polarized, the laser light passes through the polarization beam splitter prism 1 . After the horizontally polarized light passes through the quarter-wave plate 1, it becomes circularly polarized light. The parallel light beam passes through the aperture center of the diaphragm 3 and is focused by the lens L1. The focal point of the lens L1 is located at the crystal center in the AOM 1 and diffracted in the AOM 1. The angle of the acousto-optic modulator 1 is adjusted so that the diffraction efficiency of the positive first-order diffracted light reaches more ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] In this embodiment, the positive first-order diffracted light of the acousto-optic modulator 2 is used, and Step 1, Step 2, and Step 3 are the same as Embodiment 1.
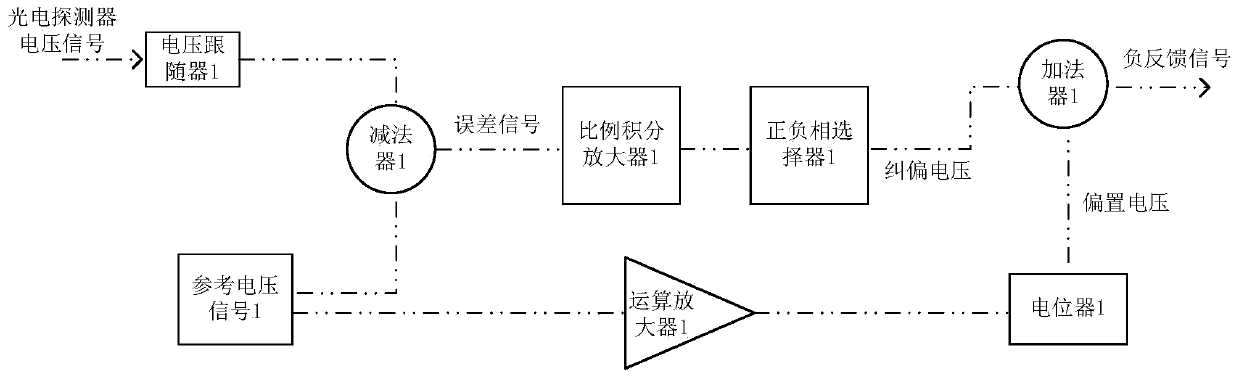
[0048] see figure 1 , similar to the primary stabilization of the laser power, the RF signal source 2, the voltage-controlled attenuator 2, the power amplifier 2, the acousto-optic modulator 2, the flat glass plate 2, the photodetector 2 and the servo controller 2 form another power stabilization The closed loop of , its working principle is similar to the primary stabilization of laser power. The lens 3 and the lens 4 are two lenses with the same focal length, and the two lenses are confocal, and the center of the AOM 2 is located on the focal point. Let only the positive first-order diffraction order pass through the aperture 5, and no longer scan the laser frequency. The frequency value of the RF signal source 2 is a fixed value, such as 100MHz, the laser frequency will increase by 100MHz, and the powe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com