A culture substrate for promoting cross-infection of truffle mycorrhizal seedlings and its application method
A technology for cultivating substrates and mycorrhizal seedlings, which is applied in the directions of seed and rhizome treatment, botanical equipment and methods, cultivation, etc. species, the availability of raw materials, and the effect of shortening the time required for infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1 Preparation of Culture Substrate
[0031] The volume ratios of peat soil and perlite were 2:1, 7:3 and 3:1, respectively, and the two were evenly mixed to obtain three kinds of culture substrates, which were numbered No. 1, No. 2 and No. 3 respectively.
[0032] Take the above medium and add rooting powder, mix well, and control the quality of rooting powder to account for 0.1%~1% of the total mass of the culture medium. A series of culture substrates containing rooting powder were obtained, wherein the volume ratio of peat soil and perlite was 7:3, and the quality of rooting powder accounted for three types of culture substrates with a percentage of 0.01%, 0.05%, and 0.1% respectively in the total mass of the culture substrate. The culture substrates were numbered No. 4, No. 5 and No. 6 respectively.
[0033] Take the above two series of culture substrates containing rooting powder and without rooting powder, add water-retaining agent, mix evenly, control th...
Embodiment 2
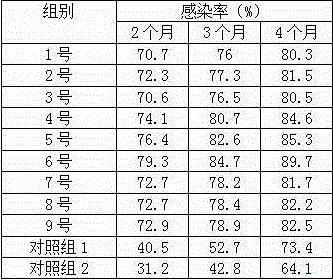
[0036] The culture described in Example 1 is used for the cross-infection inoculation of truffle mycorrhizal seedlings, and No. 1-9 culture substrates are taken as 9 experimental groups respectively, and river sand: vermiculite: perlite=1:1:1 are taken respectively (volume ratio) mixed substrate and pure peat soil as control group 1 and control group 2, and each group was operated according to the following specific steps:
[0037] 1) Collection and processing of host plant seeds: collect and select high-quality host plant (Pine yunnanensis in this example) seeds for cleaning and sterilization;
[0038] 2) Collection and processing of truffle strains: collect mature truffle fruiting bodies, wash and sterilize, add water and crush into spore suspension;
[0039] 3) Sterilization of the culture medium: sterilize the above culture medium at 126°C for 3 hours, cool it down naturally, and place it in a sterile environment for one week before use. If it has been sterilized during pr...
Embodiment 3
[0047] According to the operation steps described in Example 2, in the step 2), the spore suspension is mixed with the water-retaining agent that has been made into water, and then sterile water is continuously added until the water-retaining agent reaches saturated water absorption capacity, so that the spores are suspended The liquid will be evenly adsorbed to the surface of the water retaining agent. In step 4) of No. 6 culture substrate, the pine species and the water-retaining agent that adsorbed the spore suspension were mixed and sown in the culture substrate, and the rest of the operations were the same as in Example 2. The statistical results of the infection rate show that the adoption method can increase the infection rate by 2-3% on the basis of the infection rate corresponding to each time period of No. 6 culture substrate in Example 2.
[0048] In the method described in this example, if step 4) is adjusted to: lay a 5 cm thick sterile culture substrate in a seed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com