Method for preparing novel competent cell and transformation step thereof
A competent cell, a new type of technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of decreased sensory effect, reduced experimental efficiency, cumbersome transformation process, etc., and achieves the effect of increasing permeability, high application value, and good repeatability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
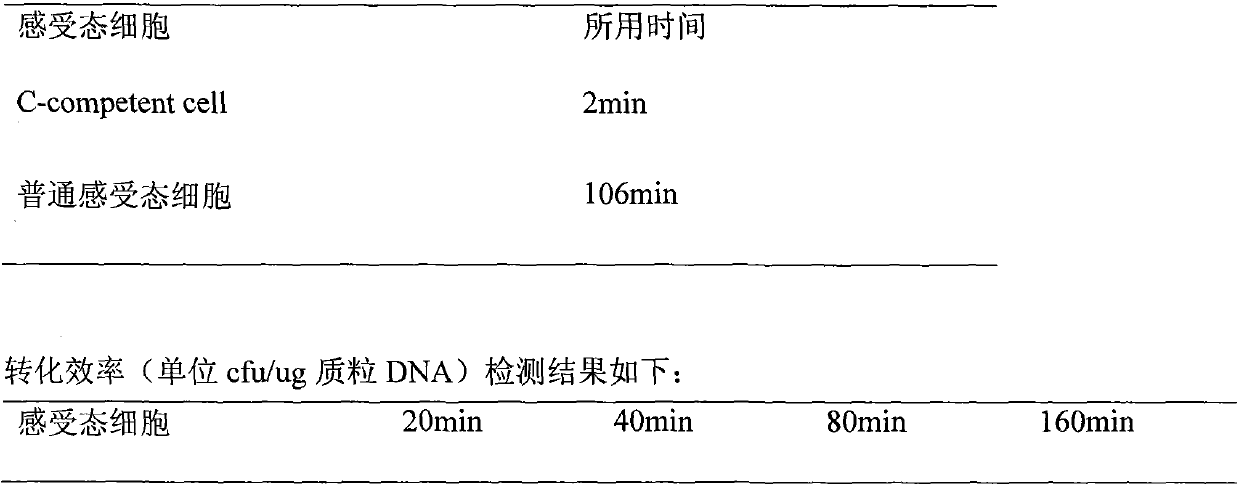
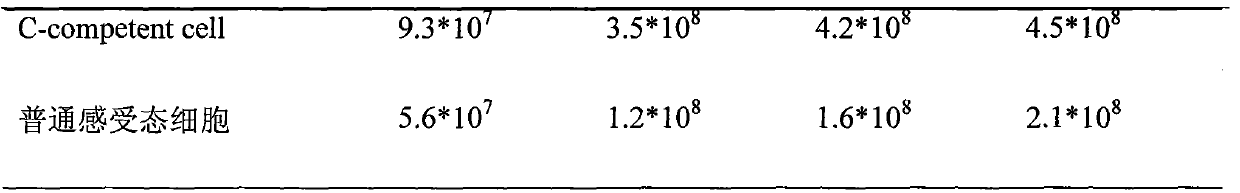
[0021] Example 1: Detection of the conversion time and conversion efficiency of the C-competent cell described in the present invention.
[0022] Materials and reagents used in this embodiment are as follows:
[0023] Materials: pUC18 plasmid, recipient strain DH5α
[0024] Reagents: LB liquid medium: 10 grams of protein, 5 grams of yeast extract, 10 grams of sodium chloride, 2.4 grams of magnesium sulfate, distilled water to 1000ml, pH 7.0, sterilized at 121°C for 20 minutes.
[0025] Buffer washing solution 1 is an aqueous solution containing the following components: 50 mM magnesium chloride, 20 mM potassium chloride, 100 mM calcium chloride, 1% glucose, 20 mM 4-hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid, and the pH is adjusted to pH 6.5.
[0026] Buffer washing solution 2 is an aqueous solution comprising the following components: 30 mM calcium chloride, 50 mM sodium chloride, 30 mM ferric chloride, 10% DMSO, adjusted to pH 7.0.
[0027] The preparation process of C-compe...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 Common Competent Cell Preparation Method Transformation and Transformation Efficiency Detection
[0035] Materials and reagents used in this embodiment are as follows:
[0036] Materials: pUC18 plasmid, recipient strain DH5α
[0037] Reagents: LB liquid medium: 10 grams of protein, 5 grams of yeast extract, 10 grams of sodium chloride, 2.4 grams of magnesium sulfate, distilled water to 1000ml, pH 7.0, sterilized at 121°C for 20 minutes, 0.1mol / L CaCl 2 (contains 15% glycerin)
[0038] The preparation process of ordinary competent cells (prepared by calcium chloride method) is as follows (for the steps, refer to the Molecular Biology Experiment Manual, as a comparison of C-competent cells):
[0039] Spread Escherichia coli DH5α preservation solution on an antibiotic-free LB plate, and culture overnight at 37°C; pick up monoclonal bacteria to 5ml LB medium and shake overnight at 37°C; inoculate into 100ml LB medium at a ratio of 1% (v / v) In medium, shake vigo...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3 conversion influence factors
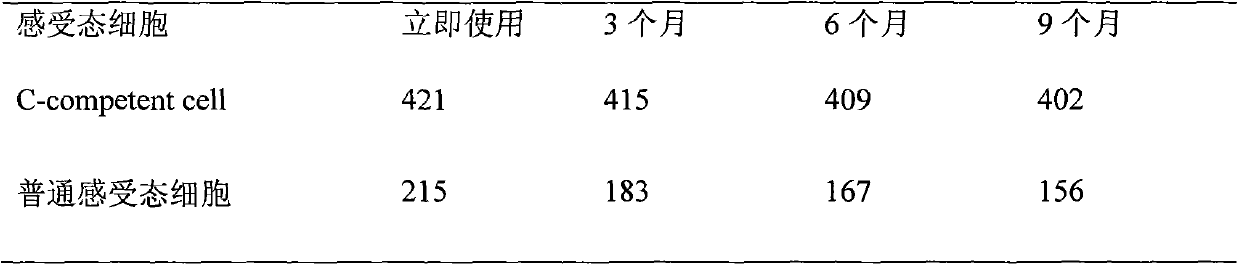
[0046] Comparing the C-competent cell described in the present invention and ordinary competent cells in the four time points of immediate use, frozen storage (-80°C) for 3 months, frozen storage for 6 months, and frozen storage for 9 months, the same plasmid pUC18 was used to carry out bacterial For the difference in transformation efficiency, the C-competent cells and ordinary competent cells at the above four time points were selected for transformation, and the clones were counted after successful transformation.
[0047] The result is as follows:
[0048]
[0049] Conclusion: From the above, it can be seen that the C-competent cells described in the present invention have no obvious changes when they are stored for 9 months, while the number of clones of ordinary competent cells decreases with the prolongation of time.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com