Preparation method, application, device and detection method of disposable microbial film sensor capable of rapidly detecting water biotoxicity
A technology of microbial film and biological toxicity, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problem of insensitivity of acute toxicity detection of poisons, and achieve good biocompatibility, simple and convenient operation, and rapid field analysis.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
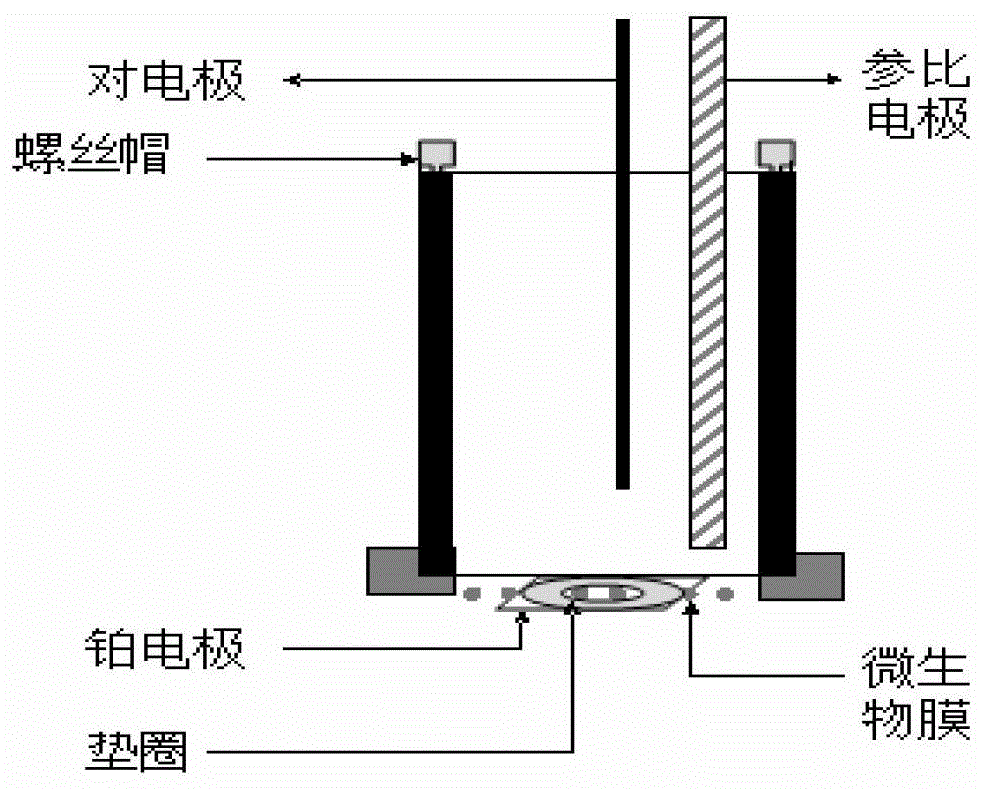
[0054] A disposable microbial film sensor for rapid detection of water biotoxicity:
[0055] 1. Preparation of disposable microbial film
[0056] Using yeast as the test microorganism, inoculate Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S.cerevisiae) in the liquid medium, the composition of the liquid medium is (mass concentration): yeast extract (1%), peptone (2%), glucose (2%) , grown for 24 hours, centrifuged to obtain wet bacteria, suspended in phosphate buffer solution and stored at 4°C until use.
[0057] In order to improve the analytical sensitivity, the cell wall of the yeast can be pretreated with 30% methanol or ethanol for 12-24 hours to achieve the effect of partially removing the cell wall while maintaining the normal life activities of the microorganism.
[0058] Take 100 μL of the treated yeast liquid and add it to 1 mL of dissolved mixed sol (the mixing volume ratio of polyvinyl alcohol sol (5%) and sodium alginate sol (1%) is 1:0.2), mix well, and drop-coat on On a clean p...
Embodiment 2
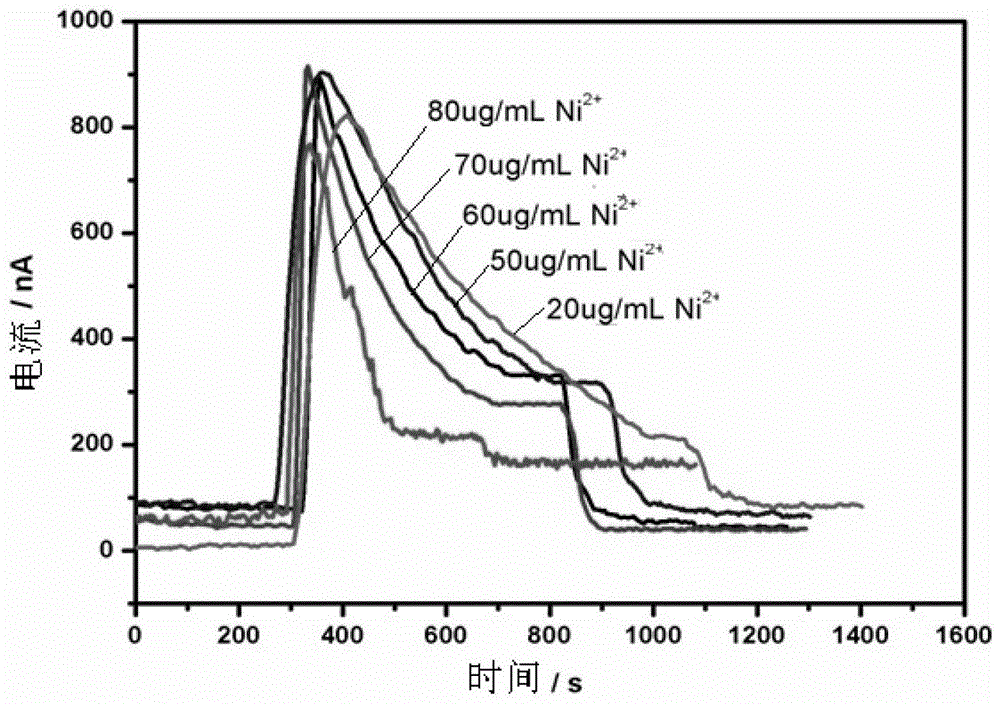
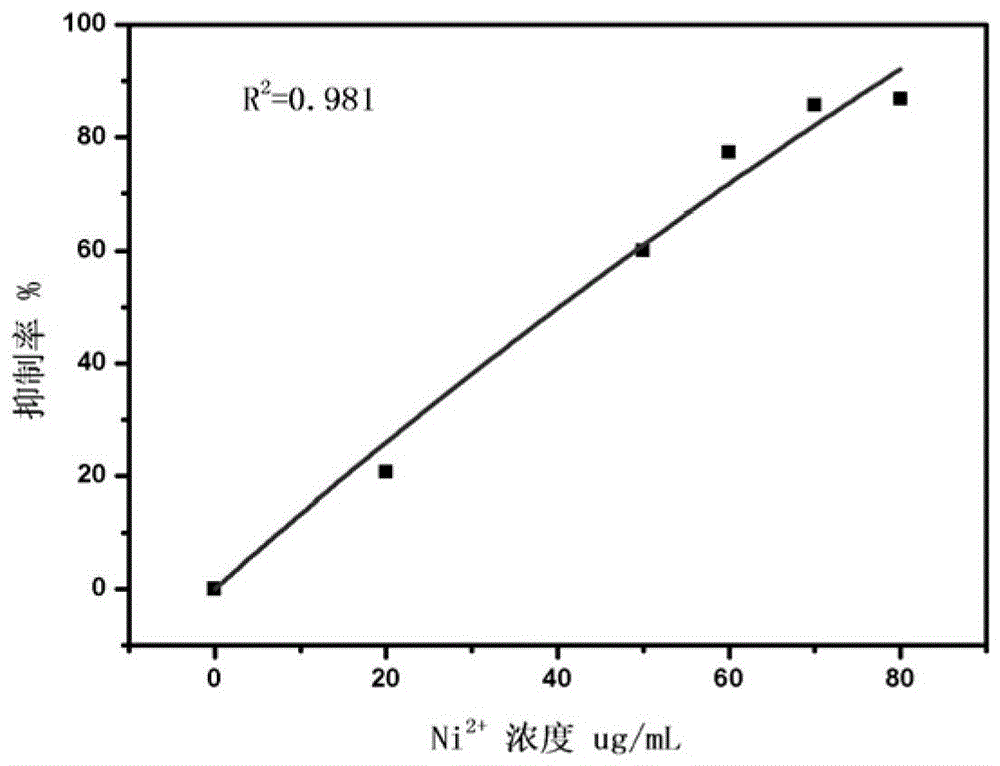
[0067] The operation method and steps are the same as those in Example 1 to evaluate the biological toxicity of heavy metal ions. The only change is: the test solution 3,5-dichlorophenol (DCP) solution with different concentrations is configured as the test solution to carry out the water quality acute biological toxicity test , DCP is often used as a reference in international toxicity tests. The results showed that the DCP current decreased in varying degrees after adding toxic substances, which indicated that DCP had obvious toxic effects on yeast. The dose-effect curve is calculated by fitting the hyperbolic function based on the Miman equation, such as Figure 4 As shown, the EC50 value of DCP was 11.45 μg / mL. Compared with the results of the mixed bacteria inspection in Example 5, the sensitivity was significantly improved.
Embodiment 3
[0069] The operation method and steps are the same as those in Example 1 for evaluating the biotoxicity of heavy metal ions, the only change being: preparing organic matter solutions of different concentrations such as the pesticide acephate as the tested solution for water quality acute biotoxicity testing. The results showed that the current decreased to varying degrees after adding the toxic substance acephate, which indicated that the pesticide acephate had obvious toxic effects on yeast. The dose-effect curve is calculated by fitting the hyperbolic function based on the Miman equation, such as Figure 5 Shown, the EC50 value of pesticide acephate is 52.58 μ g / mL. Compared with the results of the E. coli test in Example 4, the sensitivity was remarkably improved.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com