An Optical Wavefront Error Improvement System Based on Discrete Pupil Gating
A wavefront error and wavefront technology, which is applied in the field of optical wavefront error improvement system, can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining, high cost, and complex wavefront corrector, and achieve cost reduction and cost reduction, high real-time performance, and easier product The effect obtained
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
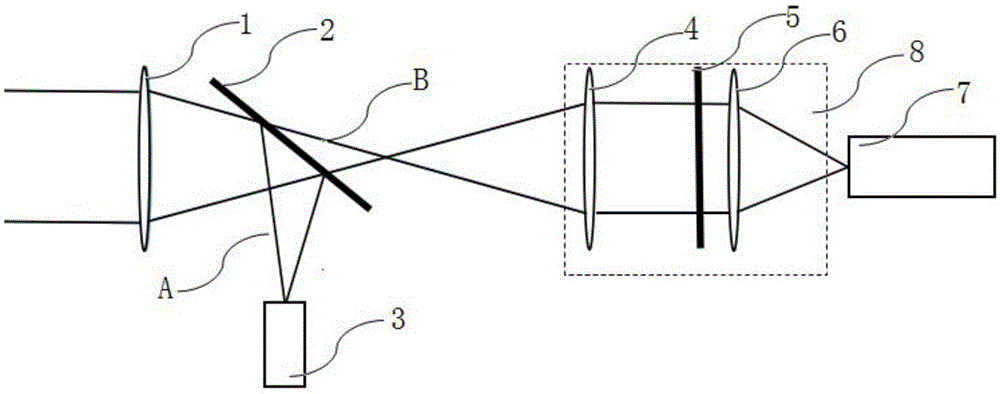
[0021] like figure 1 As shown, an optical wavefront error improvement system 10 based on pupil discrete gating is composed of an optical system main mirror 1, a beam splitter 2, a wavefront detector 3, a first lens 4, a shutter array 5, The second lens 6 and scientific imaging camera 7 are composed; the optical wavefront error improvement system is also provided with a computer (not shown in the figure), the wavefront detector 3 and the shutter array 5 are all connected to the computer, and the computer is used to detect The wavefront distortion information of the device 3 is used to control the shutter array 5 to gate the discrete wavefront of the pupil. The beam splitter 2 is installed between the main mirror 1 and the focal plane of the main mirror, and the shutter array 5 is installed at the exit pupil of the optical imaging system, between the first lens 4 and the second lens 6 . The first lens 4 , the shutter array 5 and the second lens 6 constitute a discrete gating sy...
Embodiment 2
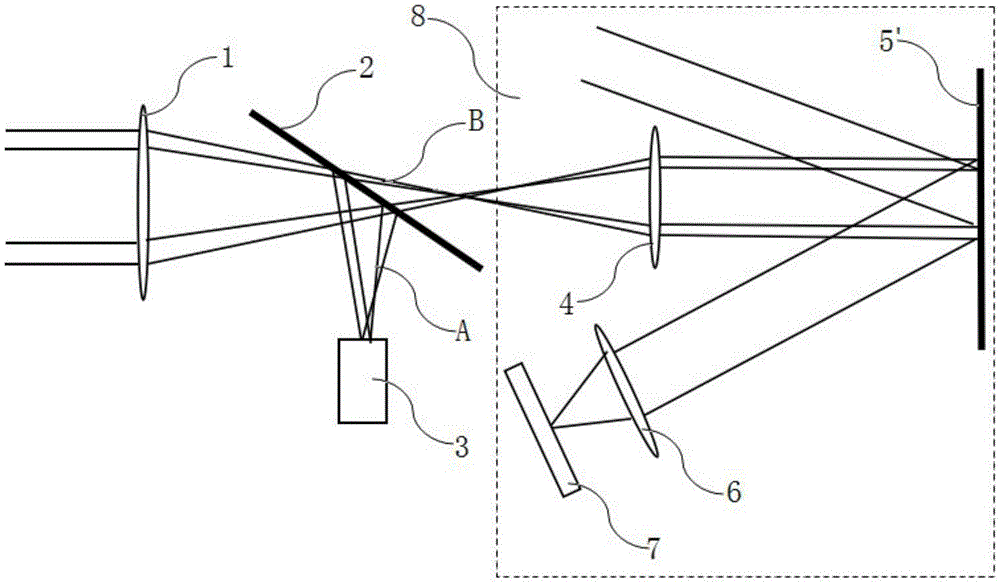
[0025] The composition of this embodiment is similar to that of Embodiment 1, except that the shutter array 5 in Embodiment 1 is replaced by a DMD system 5′. The first lens 4 , the DMD system 5′ and the second lens 6 constitute a discrete gating system 8 .
[0026] The conventional DMD system is developed by the Texas company of the United States, adopts the principle of microelectromechanical, and is a digital light modulator controlled by a binary digital signal. Its surface is distributed with closely arranged square microreflectors, and each microreflector can be flipped along its diagonal axis by ±12°, and the flipping frequency can reach several thousand hertz. When the deflection is +12°, the micro-mirror is in the on state, reflecting the light to the target optical system; when the deflection is -12°, the micro-mirror is in the off state, reflecting the light out of the optical system.
[0027] The system consists of an optical system main mirror 1, a beam splitter 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com