Compositions comprising injectable biomaterial cement and radiopacity-improving agent
A radiopaque, biomaterial technology applied in the field of strontium bromide and/or strontium iodide, which can solve the problems of reduced mechanical properties, low solubility, etc. of the hardened end product
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
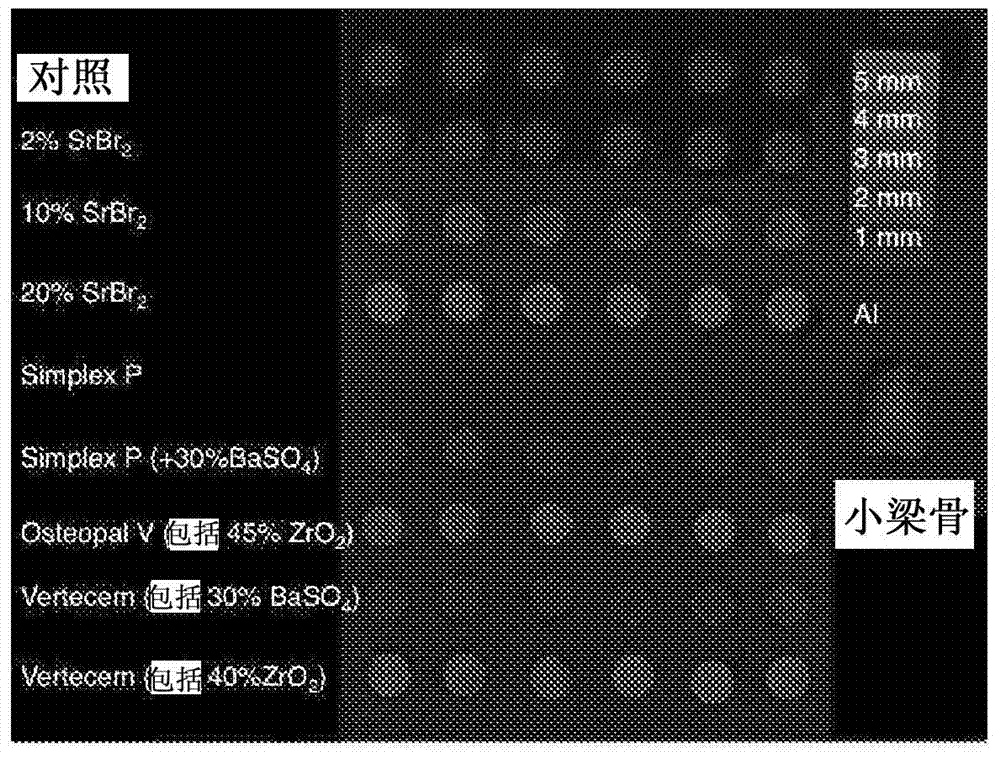
[0059] Brushite cement having the composition as in Table 1 was prepared by first dissolving monocalcium phosphate monohydrate (MCPM) and disodium dihydrogen pyrophosphate (1 wt %) in distilled water. Upon dissolution, a mixture of β-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) and strontium bromide (2, 10, and 20 wt%, respectively) was introduced. The total powder to liquid ratio was 3.3 g / mL and the molar ratio of MCPM:β-TCP was 1:1.
[0060] Table 1: Containing SrBr 2 Radiopaque brushite preparations
[0061]
Embodiment 2
[0063] Brushite cement having the composition as in Table 2 was prepared by first dissolving monocalcium phosphate monohydrate (MCPM) and disodium dihydrogen pyrophosphate (1 wt %) in distilled water. Upon dissolution, a mixture of β-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) and strontium iodide (2, 5, 10, 15, and 20 wt%, respectively) was introduced. The total powder to liquid ratio was 3.3 g / mL and the molar ratio of MCPM:β-TCP was 1:1.
[0064] Table 2: Containing SrI 2 Radiopaque brushite preparations
[0065]
[0066] The preparation and testing methods are the same for Examples 1 and 2, which will be explained next. When the liquid and powder components were mixed for 30 seconds, samples were molded for radiopacity studies, compression tests, and in vitro direct contact viability assays.
[0067] radiopacity
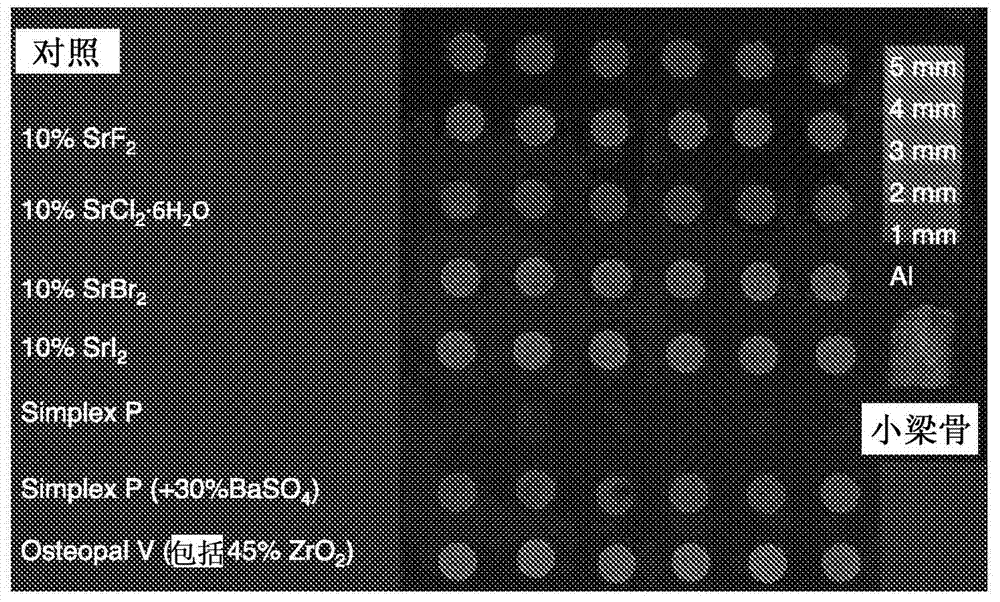
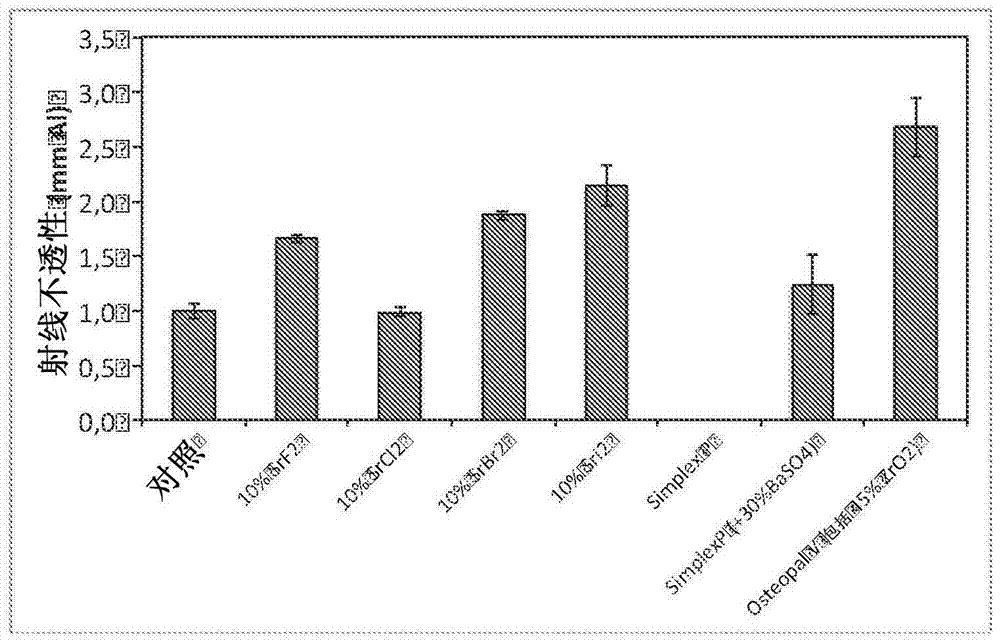
[0068] For radiopacity testing, discs of 1 mm height and 10 mm diameter were molded. at 72kV p Samples were down-illuminated and radiopacity was calculated relative ...
Embodiment 3
[0082] In this example, cements prepared from compositions according to the invention were compared with various comparative and commercial products containing conventional additives. All reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), unless otherwise specified. The composition according to the invention was prepared with a powder to liquid ratio of 3.3 g / ml and a molar ratio of MCPM:P-TCP of 1:1. First, appropriate amounts of MCPM (purum p.a., ≥85, KT) and disodium dihydrogen pyrophosphate (1 wt% of the total amount of powder) were mixed with distilled water to form a slurry. Second, an appropriate amount of β-TCP (purum p.a., ≥96, calculated as Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 , KT) and SrX (10 wt% of the total mass), were added to the slurry and mixed with a metal spatula for 30 seconds. The following SrXs were tested: strontium fluoride, strontium chloride hexahydrate (SrCl 2 ? 6H2 O), strontium bromide, and strontium iodide. For simplicity, the mater...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com