Bacillus subtilis strain capable of efficiently expressing exogenous secretory proteinase
A Bacillus subtilis and exogenous protein technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of high exocrine protease concentration and limited application, and achieve the effect of broad development prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1. Construction of pYF‐tsDE plasmid
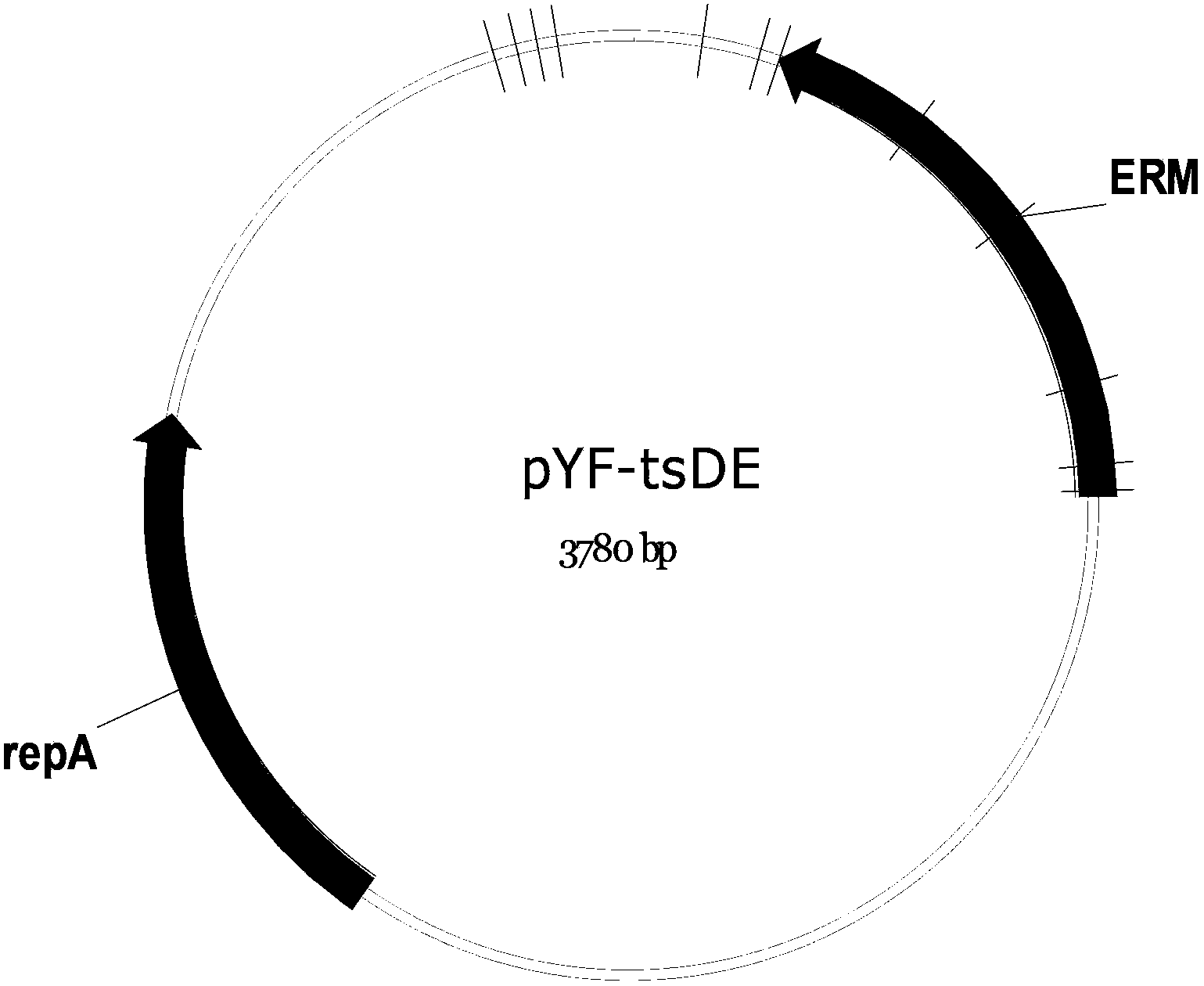
[0040] pYF‐tsDE ( figure 1) is an Escherichia coli / Bacillus shuttle plasmid designed by the inventor. Its composition mainly includes a heat-sensitive replication origin with replication activity at 30°C and an erythromycin resistance gene. The concentration of erythromycin resistance in Escherichia coli is 300ug / ml; the concentration in Bacillus subtilis is 5ug / ml. At 37°C, the origin of replication of the plasmid cannot replicate so that the plasmid is integrated into the host genome through the designed site and screened by the erythromycin resistance gene. The construction of the pYF-tsDE plasmid is described as follows:
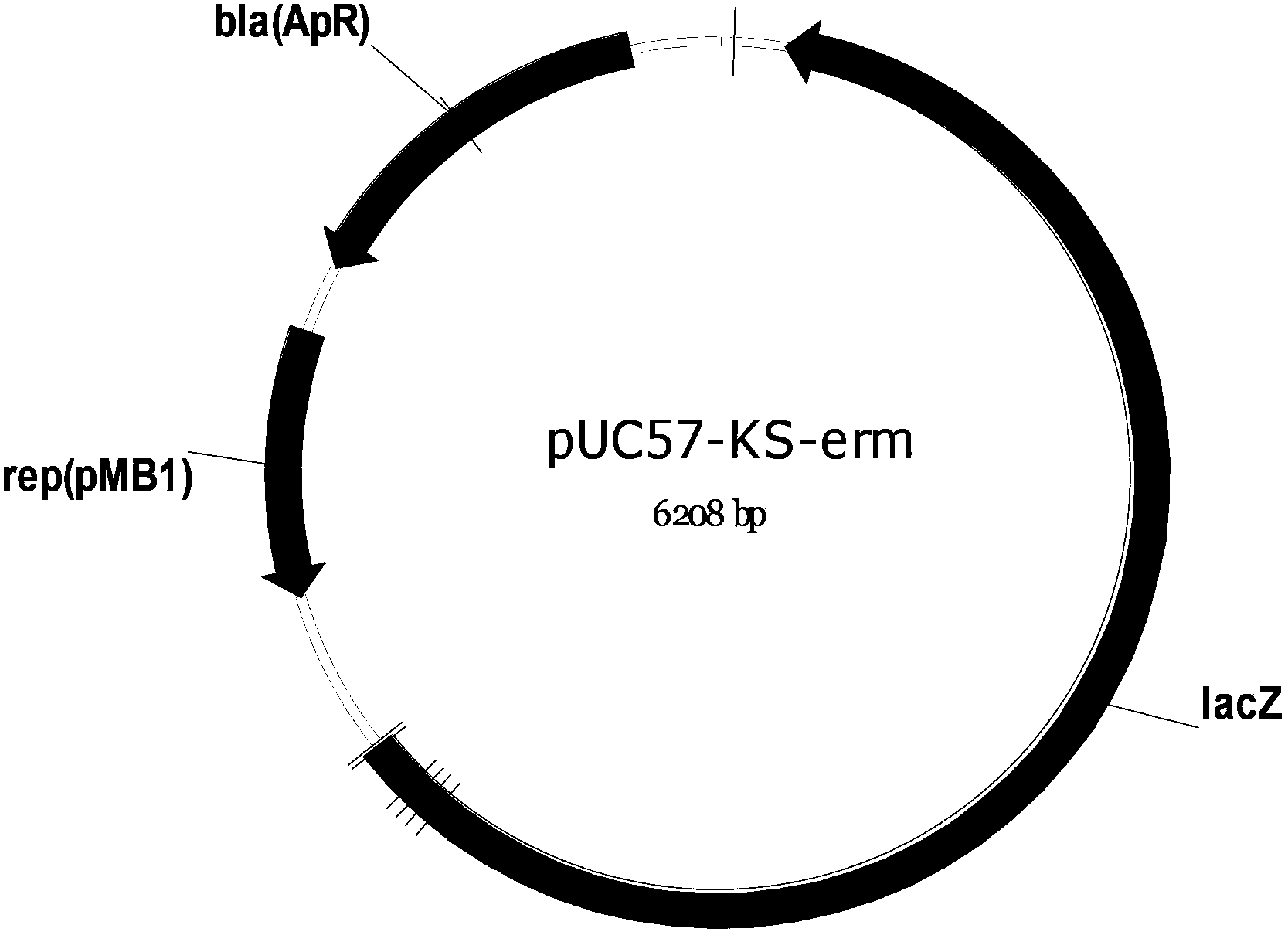
[0041] pUC57‐KS‐erm (plasmid constructed by Genscript) ( figure 2 , see SEQ ID NO.9 for the sequence) after digestion with BglII, the 3.8 kbp fragment was recovered and then self-ligated with T4 ligase (provided by NEB). The resulting 3.8kbp plasmid was named pYF-tsDE. This plasmid was trans...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2. Construction of a Bacillus subtilis strain lacking exogenous secretory protease and sporulation
[0043] The extracellular protease activity of Bacillus subtilis itself is unfavorable to the secretion of heterologous enzymes. Two extracellular proteases that have been identified: Bacillus subtilis alkaline protease aprE and Bacillus subtilis neutral metalloprotease nprE constitute 85% of the extracellular protease activity of Bacillus subtilis. In addition, spores can form dormant cells during fermentation which will result in a double reduction in production efficiency. The sigF gene encodes the sigma-F factor that controls sporulation, which plays a key role in directing the transcription of RNA polymerase and the specificity of the expression product in sporulation.
[0044] In the present invention, the deletions of the above three genes are inserted into the target gene through homologous insertion by a single cross-over Campbell-type mechanism in a...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Embodiment 3. Construction of pullulanase-producing strains
[0098] 3.1 Construction of pullulanase expression framework
[0099] A typical pullulanase expression cassette consists of the following parts:
[0100] (1) Two to three tandem natural promoters (natural promoters from B. subtilis, B. licheniformis and B. amyloliquefaciens can be selected); the sequence is SEQ ID NO.5;
[0101] (2) Synthetic ribosome binding site sequence, see SEQ ID NO.6;
[0102] (3) The expression framework inserts a strong natural signal peptide sequence upstream of the start codon of the pullulanase coding gene, see SEQ ID NO.8;
[0103] (4) The expression framework pullulanase gene is derived from B.acidopulluticus, see SEQ ID NO.1;
[0104] (5) The expression framework contains a synthetic termination sequence, see SEQ ID NO.7;
[0105] The synthesis of the above sequences was completed by Genscript Company, and the above sequences were sequentially and seamlessly concatenated to ob...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com