A phage capable of lysing multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its application in treating infection
A Pseudomonas aeruginosa, multi-drug resistance technology, applied in the direction of medical raw materials derived from viruses/phages, viruses/phages, antibacterial drugs, etc., can solve problems such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0058] Collection and processing of specimens:
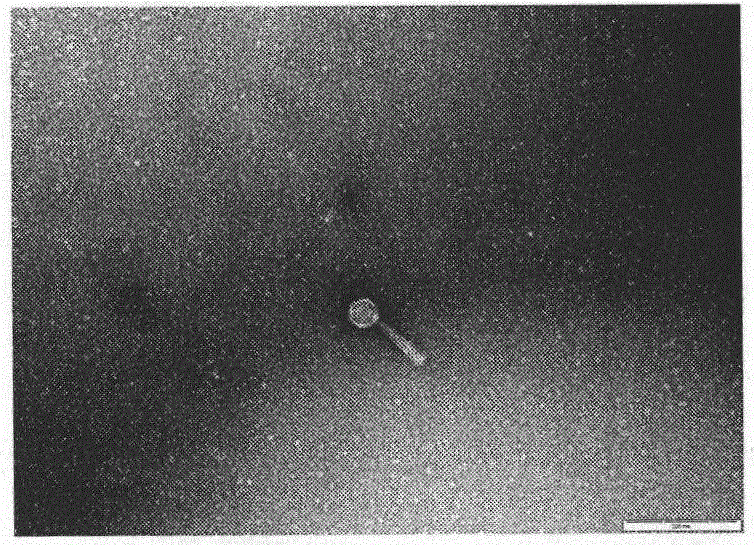
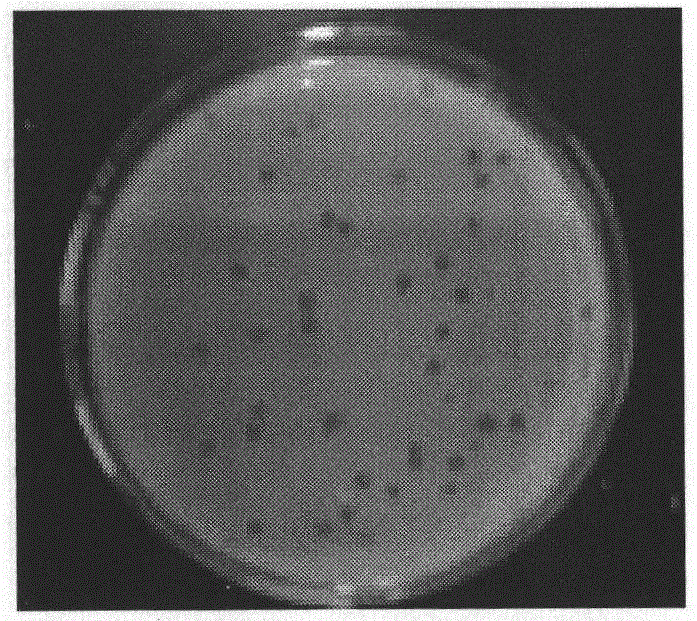
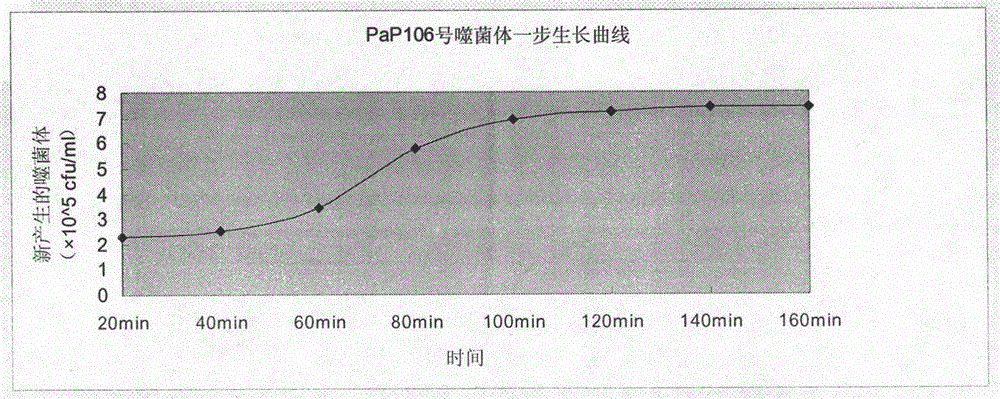
[0059] Take the sewage from Ruide Avenue, Lanzhou City, Gansu Province, 3000ml each time, add 0.333gCaCl 2 . Another 3ml of Pseudomonas aeruginosa standard strain bacterial solution was added, and the next day, it was sterilized by filtration with a 0.22 μm filter membrane. Take 200ml of treated sewage, add 50ml of liquid LB medium, 1.2ml of host bacteria suspension, mix well and place in a 37°C incubator for overnight cultivation. On the next day, 10ml of the amplification solution was taken and centrifuged at 2000r / min for 15mim, and the supernatant was the stock solution containing Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage. Take 0.3ml of the stock solution and 0.6ml of the standard host bacterial solution, mix well and incubate at room temperature for 15 minutes, then add 2ml of semi-solid at 47°C, mix well and pour on solid agar plates to make double plates, incubate at 37°C for 4-6 hours Then observe plaques. If there are plaques, it ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com