Differential drive mechanism of internal combustion engine
A technology of differential transmission and internal combustion engine, which is applied in the direction of machines/engines, mechanical equipment, etc. It can solve the problems of cylinder seal design and manufacture difficulty in cylinder processing and manufacturing, insufficient gas pressure, and reduced service life of crankshaft bearings, etc., so as to improve running stability , Improve fuel economy, reduce vibration and noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
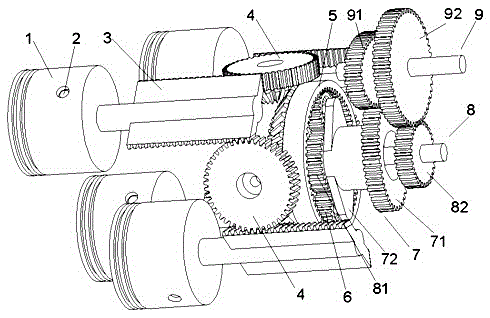
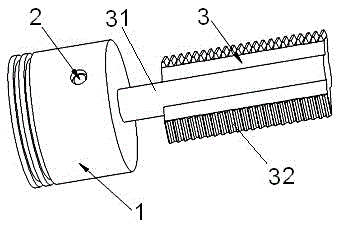
[0075] Example 1: For the first technical solution of the present invention, see Figure 1 to Figure 11 . The differential transmission mechanism of an internal combustion engine includes a piston 1, a piston pin 2, a first rack 3, a first transfer gear shaft 4, a first incomplete gear 5, a first planetary gear 6, a first planetary carrier gear 7, a first A central gear shaft 8 and an output gear shaft 9.
[0076] The internal combustion engine adopts a four-stroke working mode, and has four cylinders of cylinder A, cylinder B, cylinder C and cylinder D in total. The axes of the cylinders are parallel to each other, and the axes of the cylinders are equidistantly distributed in the circumferential direction. During the operation of the internal combustion engine, each cylinder performs the suction, compression, work, and exhaust strokes in a clockwise direction. In each cylinder, the piston pin 2 connects and fixes the first rack 3 to the piston 1, and reciprocates as a wh...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2: For the second technical solution of the present invention, see Figure 12 to Figure 16 , the present embodiment is a differential transmission mechanism that can be applied to an internal combustion engine, and its differential transmission system consists of a piston 1, a piston pin 2, a second rack 3a, a second transfer gear shaft 4a, and a second incomplete gear 5a , the first planetary gear 6, the first planetary carrier gear 7, the first sun gear shaft 8 and the output gear shaft 9.
[0082] The internal combustion engine adopts a four-stroke working mode, and there are four cylinders of cylinder A', cylinder B', cylinder C' and cylinder D'. The axes of the cylinders are parallel to each other, and the axes of the cylinders are distributed in a rectangular array. During the operation of the internal combustion engine, each cylinder is Figure 24 The numbers of cylinder A', cylinder B', cylinder C' and cylinder D' shown in the sequence carry out sucti...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Example 3: The third technical scheme of the present invention, see Figure 17 to Figure 22 . This embodiment is a differential transmission mechanism that can be applied to an internal combustion engine, and its differential transmission system consists of a piston 1, a piston pin 2, a second rack 3a, a second transfer gear shaft 4a, a third incomplete gear 5b, The second planetary gear 6a, the second planetary carrier gear 7a, the second sun gear shaft 8a, and the output gear shaft 9 are composed.
[0088] The internal combustion engine adopts a four-stroke working method and has four cylinders in total, such as Figure 24 As shown, the spatial arrangement of the cylinders, the stroke sequence of the cylinders, the force transmission and motion coordination between the second racks 3a in each cylinder, and the output of the piston work to the third incomplete gear 5b, etc., are related to The same as that of embodiment 2.
[0089] The complete teeth on the third ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com