Recovery method for valuable metals in tailings
A valuable metal, recovery method technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of consuming sulfuric acid, wasting secondary resources, large amount of waste liquid, etc., and achieving a short process flow, strong adaptability, and high recovery rate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
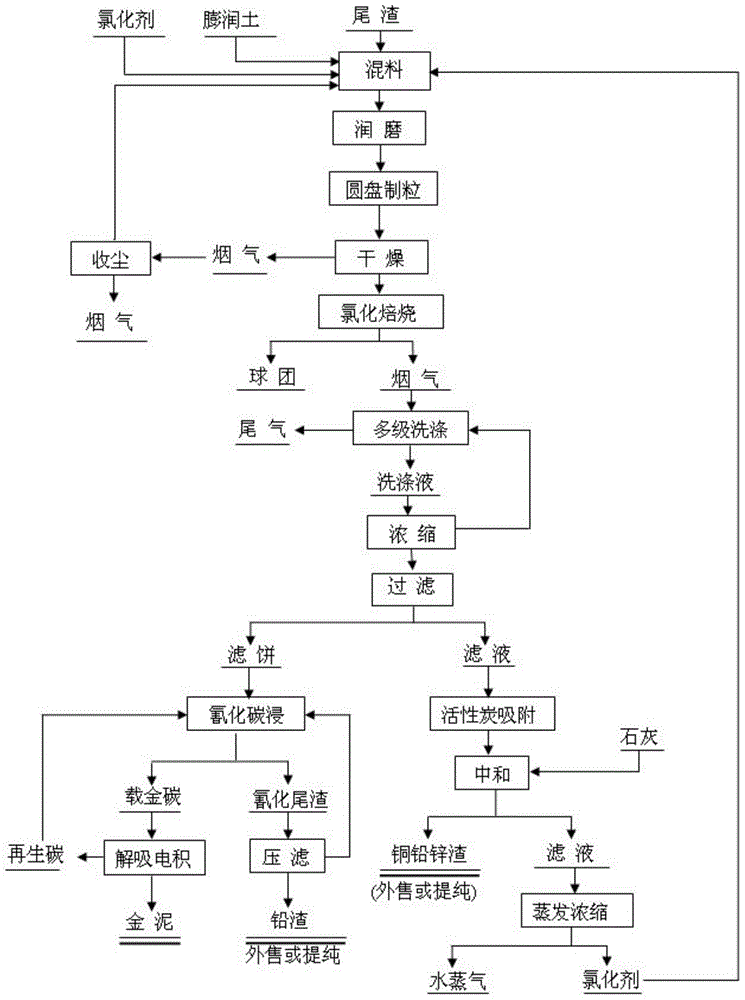
[0034] This embodiment provides a method for recovering valuable metals such as gold and silver in tailings. The tailings are high-sulfur concentrate cinders, and the main components (weight unit: g / t): Au 2.26, Ag 39.61, Fe 62.13, S 0.54, Cu 0.28, Pb 0.32, Zn 0.35, SiO 2 5.15, As 0.07, the tailings particle size is -200 mesh, accounting for 90% (referring to 90% of tailings below 200 mesh); use the mixer to mix tailings, bentonite, calcium chloride (chlorinating agent) by 100: Mixing at a weight ratio of 1:5, after mixing, the raw materials are hoisted into the mine bin, fed continuously to the disc granulator, and at the same time, spray production water into the granulator to control the water content of the wet pellets to 10-15%. The particle size is 8-10mm; the wet pellets are sent to the grate silo through the belt, and the drying capacity of the grate is adjusted by adjusting the height of the ram (ie, the height of the material layer), and the drying temperature is con...
Embodiment 2
[0037] This embodiment provides a method for recovering valuable metals such as gold and silver in tailings. The tailings are cyanide tailings. The main components (weight unit: g / t): Au 13.2, Ag 13, Fe 43.65, S 2.65, Cu 0.35, Pb 0.21, Zn 0.10, SiO 217.66, As 1.45, tailings particle size-300 order 85%; Adopt the same step of embodiment 1; In chlorination roasting process, gold volatilization rate 92%, silver volatilization rate 73%, copper volatilization rate 85%, lead volatilization rate 90%, zinc volatilization rate 73.2%; in this technological process, the recovery rate of gold is 91.2%, the recovery rate of silver is 70%, the recovery rate of copper is 82.5%, the recovery rate of lead is 88%, and the recovery rate of zinc is 71.5%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com