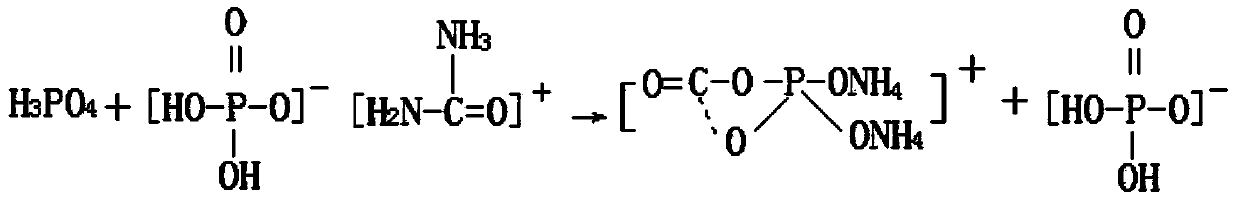Method for preparing sodium dihydrogen phosphate and preparing special fertilizer for Rosa roxbunghii as byproduct
A technology of sodium dihydrogen phosphate and special fertilizer, which is applied in the direction of ammonium orthophosphate fertilizer, alkaline orthophosphate fertilizer, phosphate fertilizer, etc., and can solve the problems of large sodium dihydrogen phosphate products, waste of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, and waste of dihydrogen phosphate Solve the problems of low purity of sodium products, achieve significant environmental protection value and economic benefits, avoid the discharge of waste liquid, and achieve significant economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
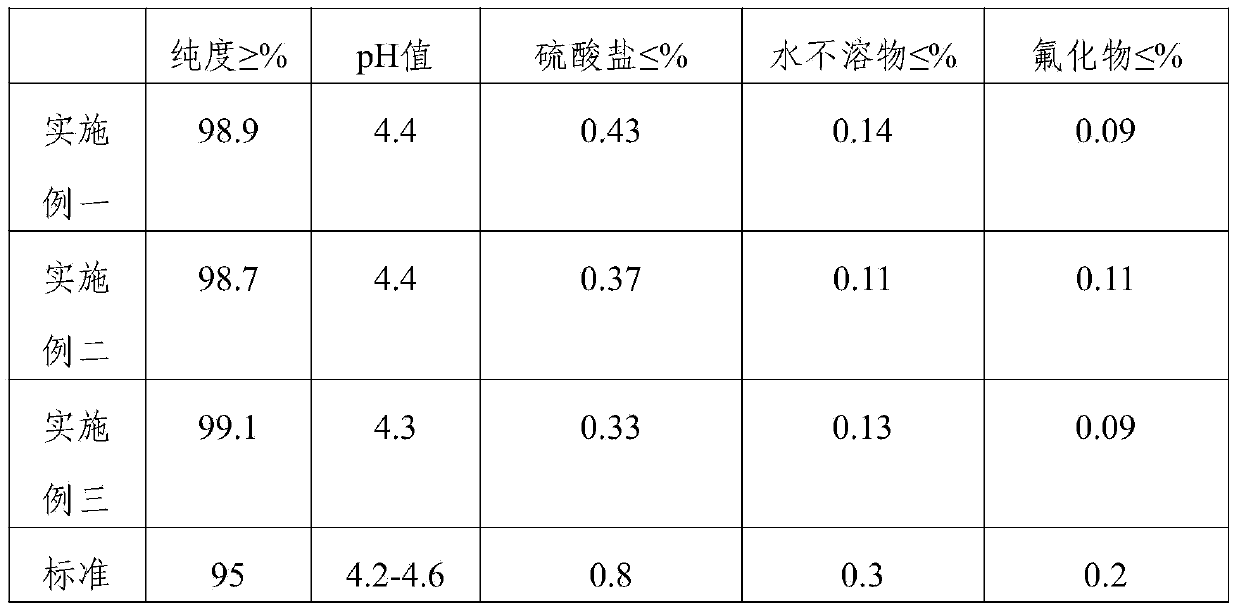
Embodiment 1
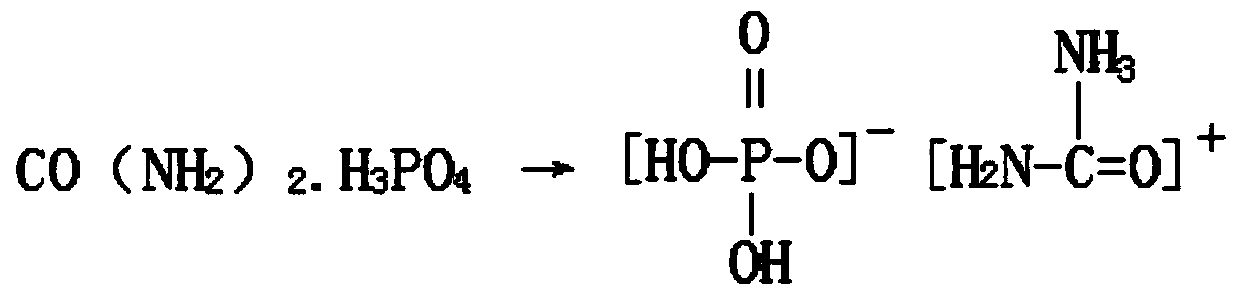
[0040] A method for preparing sodium dihydrogen phosphate and by-product special fertilizer for Rosa roxburghii. Phosphoric acid and carbonamide are added into the reactor at a molar ratio of 1.1:1 and mixed, and then the temperature of the two mixtures is raised at a heating rate of 5°C / min. High to 90°C, stirred and reacted for 120min, then cooled to 35°C at a speed of 3°C / min, and then centrifuged to obtain the intermediate of urea phosphate; the intermediate and sodium hydroxide were added in the molar ratio of 1:1.1 Mix the reaction in the reaction kettle, adjust the pH value of the reaction to 8.5, and stir the reaction at a stirring speed of 200r / min for 60min. After the reaction is completed, obtain a slurry containing nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, and place the slurry in a cooling crystallizer for circulation and crystallization process, and detect and analyze the filtrate at the same time, when the molar ratio of nitrogen and phosphorus in the filtrate is 6:1, s...
Embodiment 2
[0043] A method for preparing sodium dihydrogen phosphate and by-product special fertilizer for Rosa roxburghii. Phosphoric acid and carbonamide are added into the reactor at a molar ratio of 1.3:1 and mixed, and then the temperature of the two mixtures is raised at a heating rate of 5°C / min. High to 120°C, stirred and reacted for 90min, then cooled to 45°C at a speed of 3°C / min, and then centrifuged to obtain the intermediate of urea phosphate; the intermediate and sodium hydroxide were added in a molar ratio of 1:1.3 Mix the reaction in the reaction kettle, adjust the pH value of the reaction to 9.5, and stir the reaction for 40 minutes at a stirring speed of 250r / min. After the reaction is completed, obtain a slurry containing nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, and place the slurry in a cooling crystallizer for circulation crystallization treatment , while detecting and analyzing the filtrate, when the mol ratio of nitrogen and phosphorus in the filtrate is 8:3, stop crysta...
Embodiment 3
[0046] A method for preparing sodium dihydrogen phosphate and by-product special fertilizer for Rosa roxburghii. Phosphoric acid and carbonamide are mixed in a reaction kettle at a molar ratio of 1.2:1, and then the temperature of the two mixtures is raised at a heating rate of 5°C / min. High to 110°C, stirred and reacted for 110min, then cooled to 40°C at a speed of 3°C / min, and then centrifuged to obtain the intermediate of urea phosphate; the intermediate and sodium hydroxide were added in a molar ratio of 1:1.2 Mixed reaction in the reaction kettle, adjust the pH value of the reaction to be 9, and the stirring speed is 220r / min stirring reaction for 50min. After the reaction is completed, obtain a slurry containing nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, and place the slurry in a cooling crystallizer for circulation crystallization treatment. Simultaneously detect and analyze the filtrate, when the molar ratio of nitrogen and phosphorus in the filtrate is 7:2, stop crystallizati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com