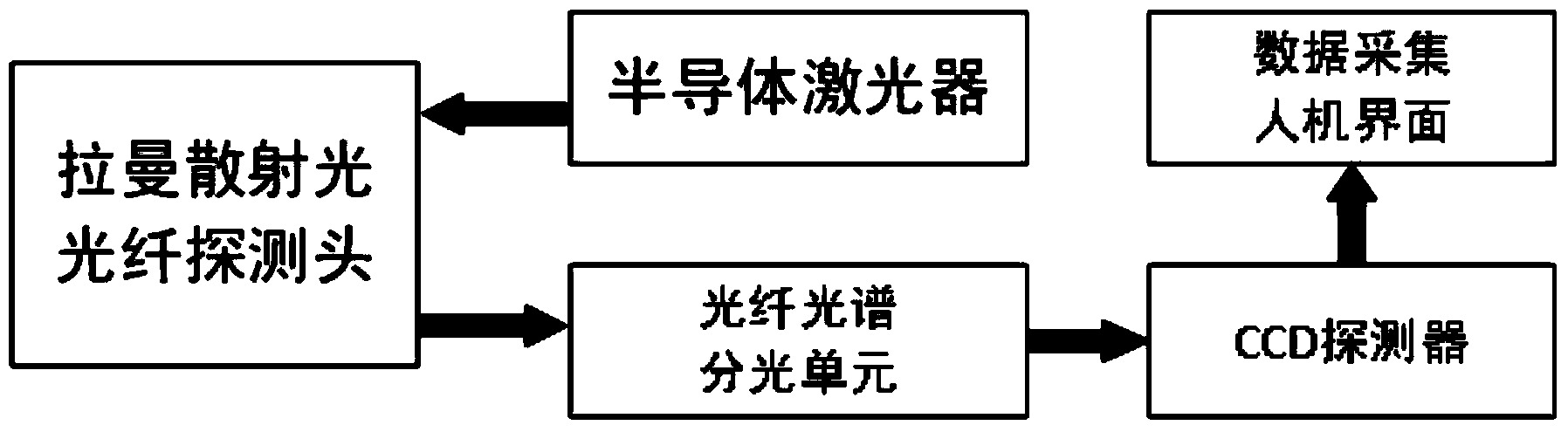
Linear focus Raman scattering probe
A Raman scattering and linear focusing technology, used in Raman scattering, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of sample Raman signal distortion, damage to the sample, and increase in the surface temperature of the sample, so as to improve the light transmission efficiency and prevent damage. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
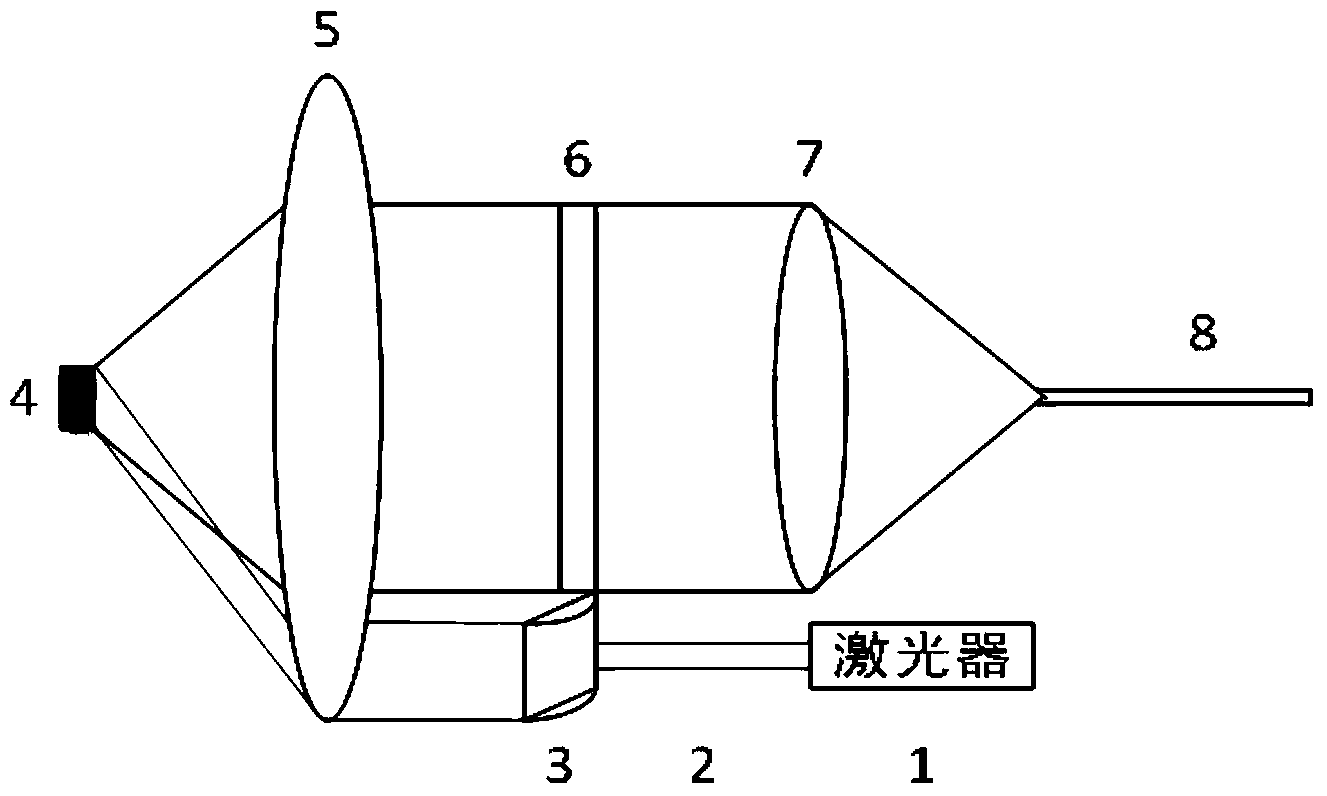
[0022] Such as figure 2 As shown, the linear focusing Raman scattering probe includes a laser light source 1, a laser transmission fiber 2, a linear cylindrical mirror lens group 3, a scattered light collection lens group 5, a narrow band-stop high-pass filter 6, and a parallel light converging lens group 7 And scattered light guide fiber 8.
[0023] The linear cylindrical mirror lens group 3 includes a collimator, a cylindrical mirror whose axes are perpendicular to each other and a converging lens,
[0024] The laser light emitted by the laser light source 1 is coupled to the laser transmission fiber 2, and then coupled to the linear cylindrical mirror lens group 3 through the laser transmission fiber 2 to form a parallel linear laser. The specific process of forming a parallel linear laser by the linear cylindrical mirror lens group is as follows:
[0025] The collimator transforms the Gaussian-distributed circular spot laser emitted by the laser into a square spot of par...
Embodiment 2
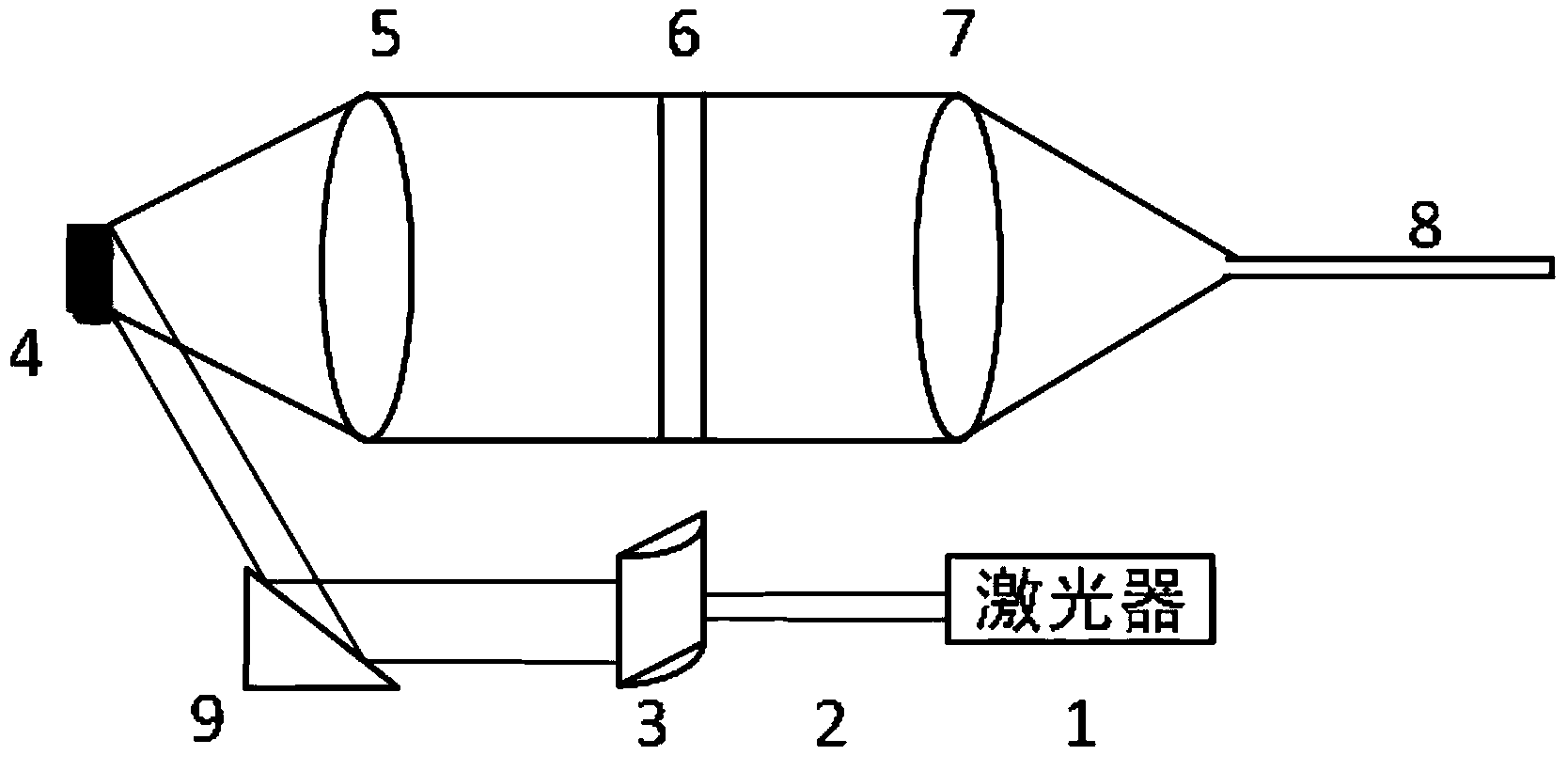
[0029] Such as image 3 As shown, in Embodiment 1, the parallel linear laser transmission device is a part of the scattered light collection lens group, the parallel linear laser transmission device in the present invention can also be a total reflection lens group 9, and the parallel linear laser light passes through the total reflection lens group and meets again Concentration on sample 4 also presents a linear spot.
[0030]Compared with the use of a part of the collection lens group as the parallel linear laser transmission device, the use of the total reflection lens group in this embodiment has the following advantages. Due to the side incident method, the line laser no longer passes through the scattered light collection lens, avoiding the The reflected laser light on the surface directly enters the collection lens, which greatly reduces the elastic scattering signal entering the scattered light collection lens, which not only reduces the optical density (OD) usage inde...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com