Welding process for mold tungsten steel core rod
A welding process, tungsten steel technology, applied in the direction of welding medium, welding equipment, welding equipment, etc., can solve the problems of easy to burst, difficult to process, high price of tungsten steel, etc., to achieve simple welding process operation, reduced processing costs, and reduced processing procedures Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
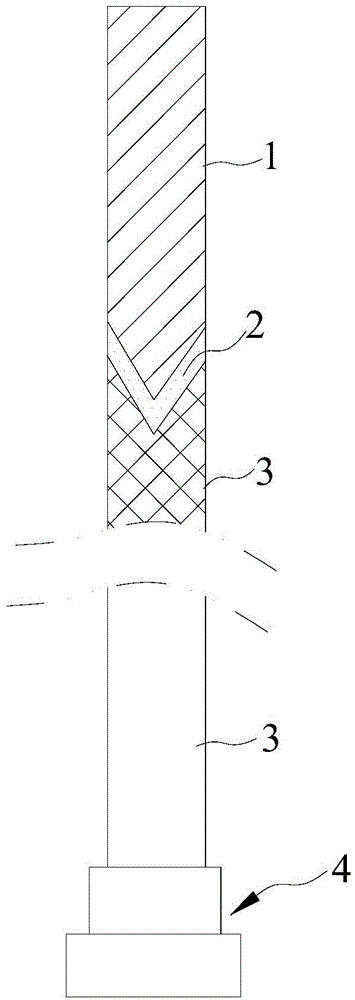
[0020] The welding process of the mold tungsten steel mandrel of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0021] (1) Pretreatment, process a V-shaped groove on the welding end of the carbon steel part 3, and process a V-shaped groove on the welding end of the tungsten steel mandrel 1, that is, it can be inserted into the V-shaped groove V-shaped convex part. In order to obtain a stronger welding effect, the included angle of the V-shaped groove is 70°-100°, specifically 85° in this embodiment, and the V-shaped groove and the V-shaped convex portion respectively have left-right symmetrical structures.
[0022] (2) Welding, pre-fill the welding material 2 at the interface between the carbon steel part 3 and the tungsten steel core rod 1, heat with an oxygen gun, first heat the welding end of the carbon steel part 3 to orange, and then heat the tungsten steel core Solder end of rod 1. Heat the welding material 2 with the waste heat of heating the carbon steel par...
Embodiment 2
[0027] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the structure of the welding material used during welding—the welding wire is: the welding wire includes a welding core and an outer skin wrapped around the welding core, and the welding core accounts for 18% of the total weight of the welding wire. The proportion of each component in the total weight of the welding wire is 2.5% of sodium fluoride, 0.4% of ferrosilicon, 0.02% of ferromolybdenum, 0.5% of high carbon ferrochrome, 0.8% of nickel powder, 0.3% of cryolite, and 12% of iron powder. Diboron trioxide is 0.3%, and the rest is titanium dioxide.
[0028] In this embodiment, the welding process of the mold tungsten steel mandrel is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0030] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the structure of the welding material used during welding—the welding wire is: the welding wire includes a welding core and an outer skin wrapped around the welding core, and the welding core accounts for 20% of the total weight of the welding wire. The proportion of each component in the total weight of the welding wire is 3.0% of sodium fluoride, 0.45% of ferrosilicon, 0.03% of ferromolybdenum, 1.0% of high carbon ferrochrome, 1.2% of nickel powder, 0.6% of cryolite, and 15% of iron powder. Diboron trioxide is 0.35%, and the rest is titanium dioxide.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com