Biosynthesis method of alpha-lipoic acid, engineered strain and preparation method thereof
A technology for biosynthesis and engineering strains, applied in the field of biosynthesis of alpha-lipoic acid, which can solve problems such as complex process, cumbersome steps, and doubts about product safety.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0145] A preparation method of an engineering strain for biosynthesizing α-lipoic acid, comprising the steps of:
[0146] (1) Construction of prokaryotic expression vector pET28-lipD
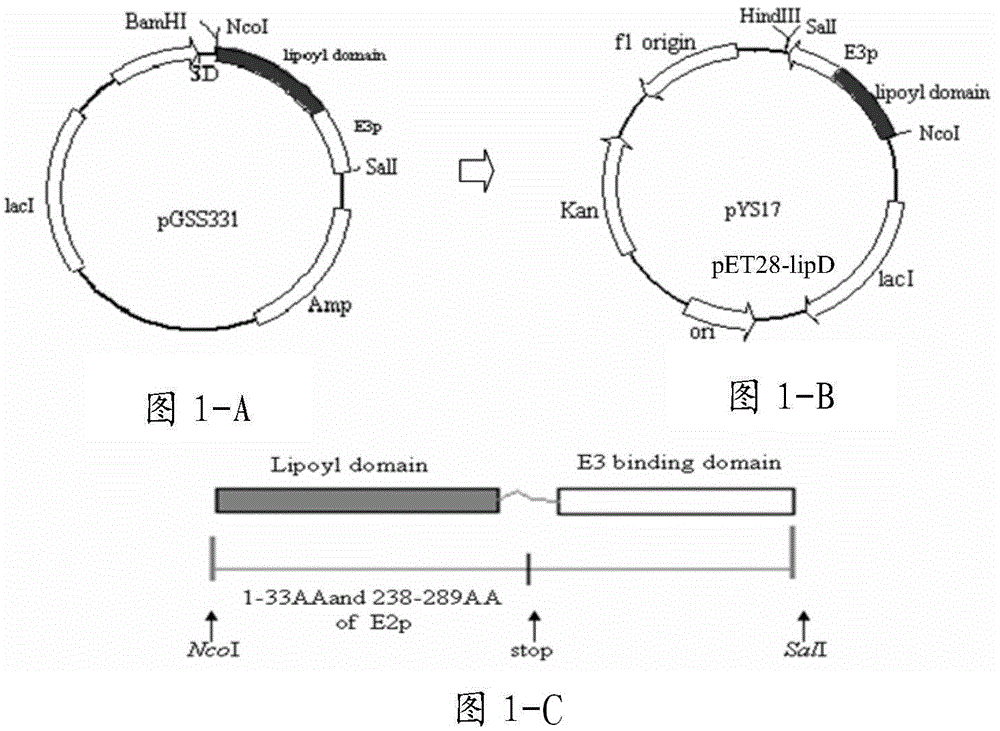
[0147] The plasmid pGSS331 containing lipD and the expression vector pET28 were double digested with Nco I and Sal I, purified and recovered, and ligated with ligase to obtain the recombinant vector pET28-lipD, see Figure 1-A with Figure 1-B ;
[0148] The recombinant vector pET28-lipD was detected by double enzyme digestion with Nco I and Sal I, which showed that the lipD gene fragment carried by pET28-lipD was consistent with that on pGSS331. DNA sequencing and DNAstar software analysis showed that the protein encoded by lipD included the N-terminal 33 amino acid residues (1-33) and the middle 52 amino acid residues (238-289) of the pyruvate dehydrogenase E2 subunit, a total of 85 amino acids The residue composition is a hybrid lipoic acid domain (Miles and Guest1987); at the 3' end of th...
Embodiment 2
[0170] A preparation method of an engineering strain for biosynthesizing α-lipoic acid, comprising the steps of:
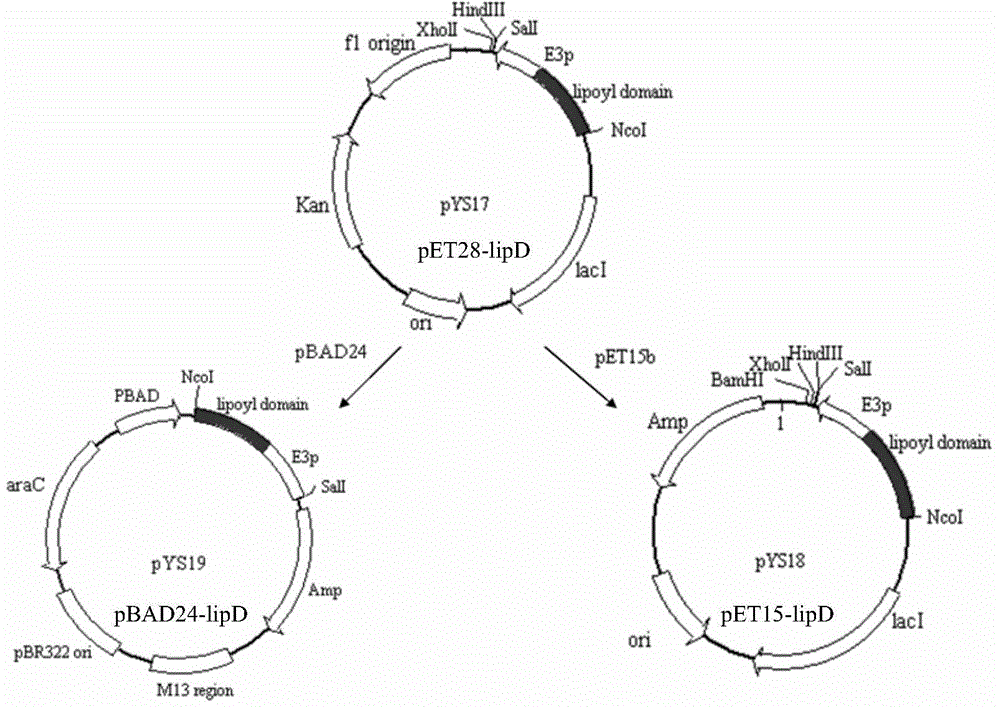
[0171] (1) Construction of the prokaryotic expression vector pET28-lipD: see step (1) of Example 1;
[0172] (2) Construction of the expression vector pSU18-lplA: see step (2) of Example 1;
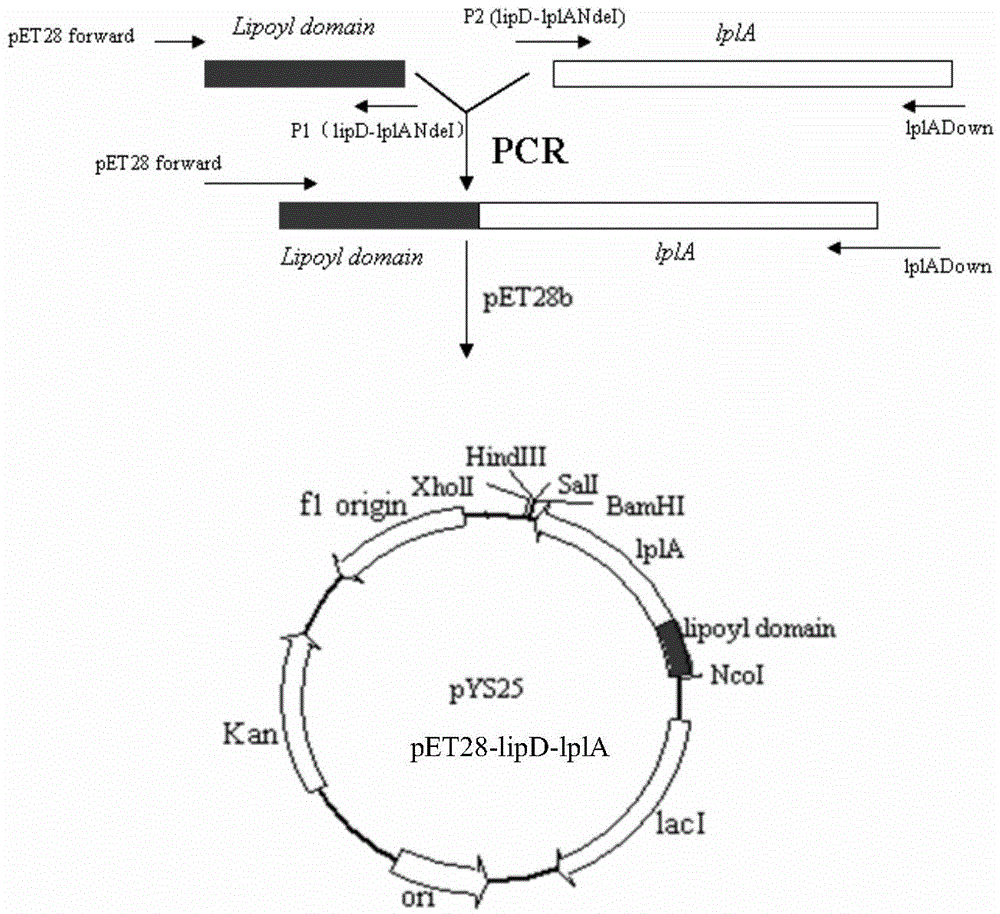
[0173] (3) Preparation of recombinant vector pET28-lipD-lplA
[0174] A. Amplify the lipD gene fragment: see A in step (3) of Example 1;
[0175] B. Amplify the lplA gene fragment: refer to B in step (3) of Example 1;
[0176] C. Refer to C in step (3) of Example 1;
[0177] (4) Construction of the recombinant vector pBAD34-lipA-SD-metK (see Figure 4 )
[0178] A. Construction of cloning vectors pMD19-T-lipA and pMD19-T-metK
[0179] Using the total DNA of wild-type Escherichia coli MG1655 as a template, the lipA gene and the metK gene were amplified by PCR, and respectively TA cloned and connected to the expression vector pMD19-T to obtain pMD19-T-lipA and pMD19-T-met...
Embodiment 3
[0192] A preparation method of an engineering strain for biosynthesizing α-lipoic acid, comprising the steps of:
[0193] (1) Construction of the prokaryotic expression vector pET28-lipD: see step (1) of Example 1;
[0194] (2) Construction of the expression vector pSU18-lplA: see step (2) of Example 1;
[0195] (3) Construction of recombinant vector pET28-lipD-tac-lplA
[0196] In order to achieve an optimal balance between the expression levels of lplA and lipD, a tac promoter was added before lplA in this embodiment.
[0197] A. Amplify the tac promoter gene: use pfuDNA as a polymerase, plasmid pGSS331 as a template, Ptacpromoter down and Ptacpromoter up as primers, and PCR amplify to obtain a 105bp tac promoter gene;
[0198] Ptacpromoter up (upstream primer):
[0199] GTCTATGAATTCACTCCCCATCCCCCTGT (SEQ ID NO. 7);
[0200] Ptacpromoter down (downstream primer):
[0201] GAGCAGGCGTAATGTGGACATGGATCCTGTTTCCTG (SEQ ID NO. 8);
[0202] B. Amplify the lplA gene fragment: u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com