Method for evaluating destroy degree on nucleotide of determination method and production technology of free nucleic acid hydrolysate in protein product
A technology of free nucleic acid and determination method, which can be used in measurement devices, material separation, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as animal toxicity, yeast product quality decline, and nucleotide content reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
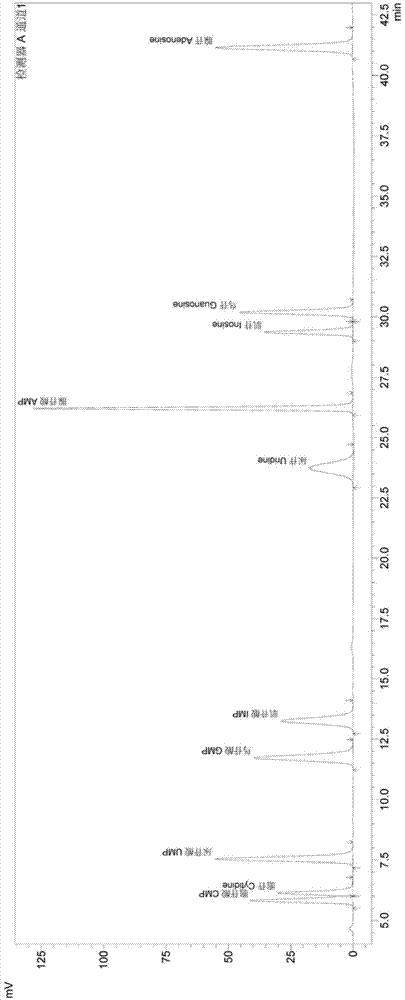
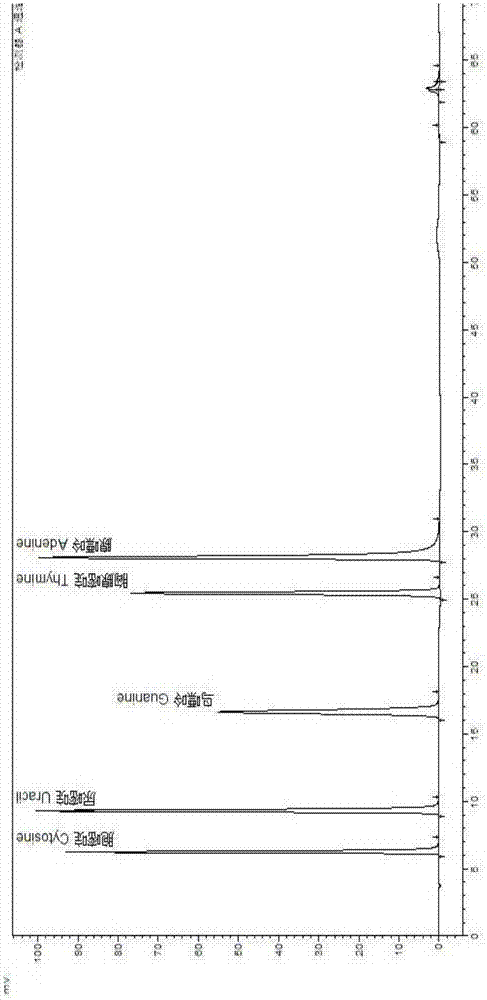
[0030] The following are the implementation steps of the present invention:
[0031] 1 Reagents and solutions
[0032] 1.1 Unless otherwise specified, the reagents used in this method are all analytically pure, and the water is deionized water, which meets the requirements of GB / T 6682 secondary water.
[0033] 1.2 Potassium dihydrogen phosphate: analytically pure.
[0034] 1.3 Potassium hydroxide: analytically pure.
[0035] 1.4 Methanol: chromatographically pure.
[0036] 1.5 Acetonitrile: chromatographically pure.
[0037] 1.6 20% w / v potassium hydroxide solution: Weigh 100 grams of potassium hydroxide, dissolve it in 500ml of water, and store it in a volumetric flask.
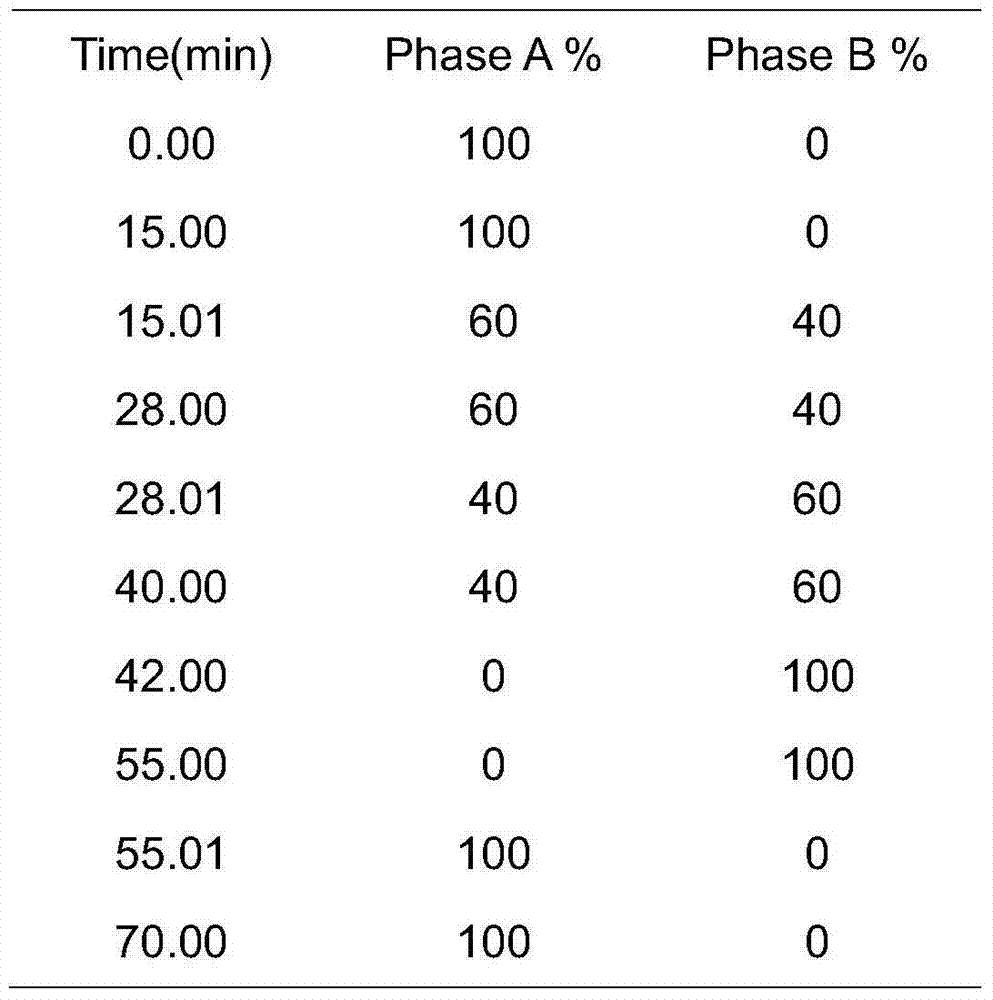
[0038] 1.7 Mobile phase A: 0.1M potassium dihydrogen phosphate solution, weigh 27.2 grams of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, dissolve in 1000ml of water, add 1.0ml of 20% potassium hydroxide solution, add water to make the volume to 2 liters. The 0.45um water system filter membrane is used for use after filtration.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com